Hyperactivation in relationships triggers intense emotional dependency and anxiety, contrasting sharply with secure attachment characterized by trust, emotional regulation, and stable intimacy. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles impact relationship dynamics and personal well-being.
Table of Comparison
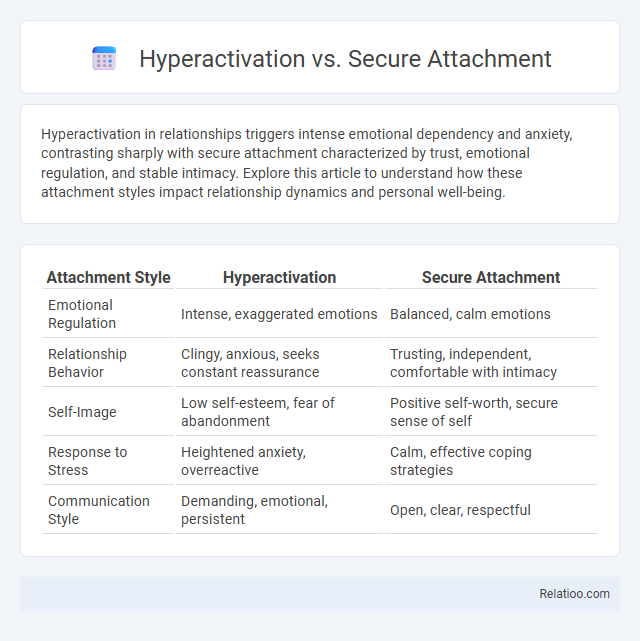
| Attachment Style | Hyperactivation | Secure Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Regulation | Intense, exaggerated emotions | Balanced, calm emotions |
| Relationship Behavior | Clingy, anxious, seeks constant reassurance | Trusting, independent, comfortable with intimacy |
| Self-Image | Low self-esteem, fear of abandonment | Positive self-worth, secure sense of self |
| Response to Stress | Heightened anxiety, overreactive | Calm, effective coping strategies |
| Communication Style | Demanding, emotional, persistent | Open, clear, respectful |
Understanding Hyperactivation and Secure Attachment
Hyperactivation involves intensified emotional responses aimed at gaining closeness and reassurance, often triggered by fears of abandonment or insecurity in relationships. Secure attachment reflects a balanced approach where emotional needs are expressed openly and met consistently, fostering trust and stable connections. Understanding how hyperactivation contrasts with secure attachment helps you manage emotional regulation and build healthier interpersonal bonds.
Key Features of Hyperactivation
Hyperactivation in attachment theory is characterized by intense emotional responses and heightened attachment behaviors such as clinginess, anxiety, and hypervigilance to relationship threats. Key features include persistent worry about abandonment, difficulty regulating emotions, and exaggeration of distress signals to elicit reassurance from attachment figures. Unlike secure attachment, which involves trusted connections and balanced emotional regulation, hyperactivation reflects an over-activation of attachment needs driven by inconsistent caregiving experiences.
Hallmarks of Secure Attachment
Secure attachment is characterized by trust, emotional regulation, and a balanced approach to intimacy and independence. You experience consistent support and safety, which fosters resilience and healthy relationship patterns. This contrasts with hyperactivation, where heightened anxiety and clinginess dominate, leading to emotional volatility and fear of abandonment.
Origins of Attachment Styles
Attachment styles originate from early caregiver interactions that shape emotional regulation and relationship expectations. Hyperactivation develops from inconsistent caregiving, leading to heightened anxiety and efforts to gain attention, while secure attachment emerges from sensitive and responsive caregiving, fostering trust and emotional stability. These foundational experiences influence lifelong relational patterns and emotional responses.
Emotional Regulation: Hyperactivation vs Secure Attachment
Hyperactivation in emotional regulation triggers intense and prolonged distress responses due to over-sensitivity to perceived threats, often leading to anxiety and difficulty calming down. Secure attachment promotes balanced emotional regulation by enabling individuals to recognize their feelings, seek support when needed, and recover from stress effectively. Unlike hyperactivation, secure attachment fosters resilience and adaptive coping, reducing emotional volatility and enhancing psychological well-being.
Impact on Adult Relationships
Hyperactivation in attachment leads to heightened anxiety and clinginess in adult relationships, often causing difficulties in managing intimacy and trust. Secure attachment fosters healthy communication, emotional regulation, and stable connections, enabling Your relationships to thrive with mutual support and understanding. In contrast, hyperactivation can cause emotional volatility and dependency, undermining relationship satisfaction and long-term stability.
Communication Patterns in Both Styles
Hyperactivation in attachment is characterized by intense emotional expressions and persistent seeking of reassurance, often resulting in anxious and confrontational communication patterns. Secure attachment fosters open, balanced dialogues where emotional needs are communicated clearly and met with empathy, promoting trust and understanding. Your ability to recognize these differing communication styles can improve relationship dynamics by tailoring responses to either soothe hyperactivated anxiety or reinforce secure connection.
Coping Strategies and Behaviors
Hyperactivation in attachment involves heightened emotional responses and clingy behaviors as coping strategies to manage fears of abandonment, whereas secure attachment features balanced emotional regulation and effective communication skills promoting healthy, resilient relationships. Individuals with hyperactivation often engage in persistent reassurance seeking and intense rumination, while secure attachment fosters adaptive coping through trust and constructive problem-solving. In contrast to hyperactivation, secure attachment leads to stable emotional well-being and consistent support-seeking without overwhelm or withdrawal.
Long-term Effects on Mental Health
Hyperactivation in attachment theory often leads to heightened emotional sensitivity and anxiety, increasing the risk of chronic stress, depression, and difficulties in emotional regulation over time. Secure attachment fosters resilience and emotional stability, promoting positive mental health outcomes such as reduced anxiety, stronger interpersonal relationships, and adaptive coping mechanisms. Conversely, hyperactivation may result in persistent fear of abandonment and vulnerability to mood disorders, whereas secure attachment supports long-term psychological well-being and secure relational patterns.
Moving Toward Secure Attachment
Moving toward secure attachment involves shifting from hyperactivation, characterized by heightened anxiety and clinginess, to a balanced emotional state where reliance on caregivers is confident and relaxed. Secure attachment fosters emotional regulation, trust, and healthy interpersonal boundaries, contrasting with hyperactivated patterns marked by fear of abandonment and intense dependency. Therapeutic interventions targeting attachment security emphasize developing self-soothing skills and reinforcing consistent, supportive relationships to stabilize attachment behaviors.
Infographic: Hyperactivation vs Secure Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com