Secure relationships are characterized by trust, open communication, and emotional safety, fostering deeper connection and stability. Insecure relationships often involve anxiety, mistrust, and poor communication, which can lead to conflict and detachment; discover how to build secure bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
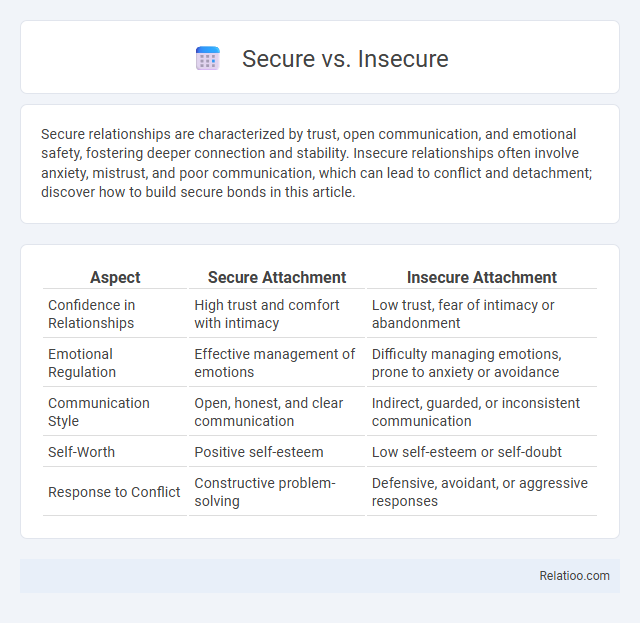
| Aspect | Secure Attachment | Insecure Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Confidence in Relationships | High trust and comfort with intimacy | Low trust, fear of intimacy or abandonment |
| Emotional Regulation | Effective management of emotions | Difficulty managing emotions, prone to anxiety or avoidance |
| Communication Style | Open, honest, and clear communication | Indirect, guarded, or inconsistent communication |
| Self-Worth | Positive self-esteem | Low self-esteem or self-doubt |
| Response to Conflict | Constructive problem-solving | Defensive, avoidant, or aggressive responses |
Understanding Secure vs Insecure: Core Definitions
Secure systems protect data through encryption, authentication, and access controls to prevent unauthorized access and breaches. Insecure systems lack these protective measures, making them vulnerable to attacks, data leaks, and manipulation. Understanding secure versus insecure environments hinges on the presence of robust security protocols that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Key Characteristics of Secure Systems
Secure systems feature strong encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and robust access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. They implement continuous monitoring, automated threat detection, and timely patch management to minimize vulnerabilities and potential breaches. In contrast, insecure systems lack these defenses, leaving critical data exposed to cyberattacks and data theft.
Warning Signs of Insecurity
Warning signs of insecurity often include frequent self-doubt, excessive need for validation, and avoidance of challenges, which contrast sharply with secure individuals who demonstrate confidence, resilience, and balanced self-awareness. Insecure behaviors manifest as overreacting to criticism, difficulty trusting others, and persistent negative self-talk, hindering personal growth and relationship health. Your ability to recognize these warning signs can lead to targeted actions for building a more secure mindset and emotional stability.
Comparing Security Models: Best Practices
Secure security models emphasize robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to mitigate risks effectively. Insecure models often lack comprehensive access controls and fail to implement regular updates, leaving systems vulnerable to breaches. Best practices prioritize adopting secure frameworks that enforce least privilege, conduct frequent security audits, and integrate real-time threat detection for enhanced protection.
Common Risks Associated with Insecure Systems
Insecure systems commonly face risks such as data breaches, malware infections, and unauthorized access that can compromise sensitive information and disrupt operations. Your digital assets are vulnerable to exploitation through weak passwords, outdated software, and insufficient encryption, increasing the potential for financial loss and reputational damage. Implementing robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication and regular security audits, helps mitigate these risks by transforming insecure systems into secure environments.
Strategies to Enhance Security
Strategies to enhance security focus on implementing robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and regular software updates to protect your systems from cyber threats. Establishing comprehensive access controls and conducting frequent security audits help identify vulnerabilities and prevent unauthorized access. Educating employees on security best practices further strengthens your overall defense against potential breaches.
The Role of User Behavior in Security and Insecurity
User behavior significantly influences the distinction between secure and insecure systems by determining vulnerability exposure through actions such as password management, software updates, and cautious handling of suspicious links. Security protocols can be undermined by poor user practices, leading to increased risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. Promoting user education and awareness is essential to reinforce secure behavior patterns and mitigate security threats effectively.
Real-World Examples: Secure vs Insecure Scenarios
Secure systems utilize robust encryption protocols like AES-256 and multi-factor authentication to protect sensitive data, exemplified by financial institutions securing online banking platforms. Insecure scenarios include plaintext storage of passwords and absence of HTTPS, often seen in outdated websites vulnerable to data breaches. Real-world cases such as the Equifax data breach highlight insecure practices, while companies like Google exemplify secure measures through continuous security audits and advanced threat detection.
Impact of Insecurity on Organizations and Individuals
Insecurity in digital environments exposes organizations and individuals to significant risks such as data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. Cyberattacks exploiting insecure systems can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive information, and lead to regulatory penalties, directly impacting your business continuity and personal privacy. Prioritizing secure infrastructure and practices minimizes vulnerabilities, enhancing trust and safeguarding assets against evolving threats.
Future Trends in Security: Staying Ahead of Threats
Future trends in security emphasize proactive measures such as AI-driven threat detection, zero-trust architectures, and continuous monitoring to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Secure systems prioritize encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time analytics to safeguard sensitive data effectively. By adopting these advanced security strategies, your organization can transition from insecure vulnerabilities to a robust, secure environment that anticipates and mitigates emerging risks.
Infographic: Secure vs Insecure
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com