Attachment issues stem from early emotional bonds affecting relationship stability, while trust issues arise from fear of betrayal and insecurity. Explore how to identify and address these challenges for healthier connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
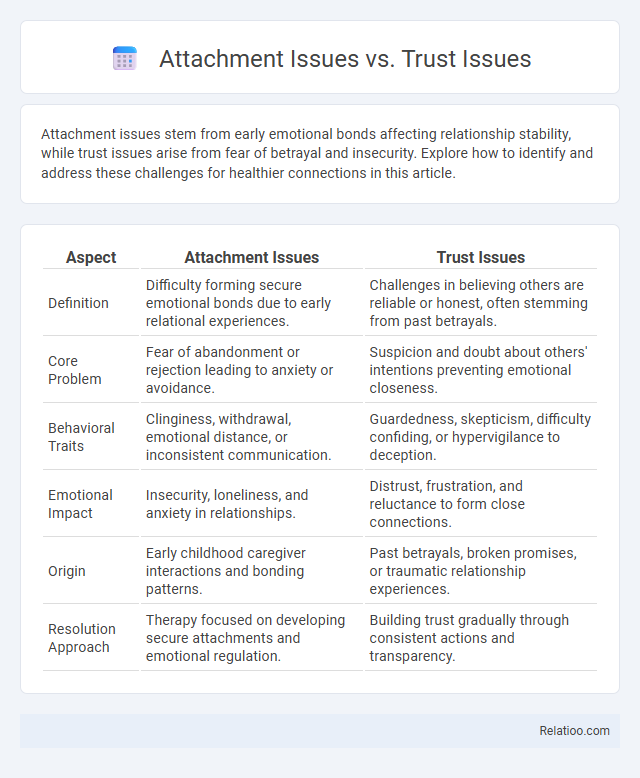
| Aspect | Attachment Issues | Trust Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difficulty forming secure emotional bonds due to early relational experiences. | Challenges in believing others are reliable or honest, often stemming from past betrayals. |
| Core Problem | Fear of abandonment or rejection leading to anxiety or avoidance. | Suspicion and doubt about others' intentions preventing emotional closeness. |
| Behavioral Traits | Clinginess, withdrawal, emotional distance, or inconsistent communication. | Guardedness, skepticism, difficulty confiding, or hypervigilance to deception. |
| Emotional Impact | Insecurity, loneliness, and anxiety in relationships. | Distrust, frustration, and reluctance to form close connections. |
| Origin | Early childhood caregiver interactions and bonding patterns. | Past betrayals, broken promises, or traumatic relationship experiences. |
| Resolution Approach | Therapy focused on developing secure attachments and emotional regulation. | Building trust gradually through consistent actions and transparency. |
Understanding Attachment Issues
Attachment issues stem from early childhood experiences where inconsistent or neglectful caregiving disrupts the ability to form secure emotional bonds, leading to challenges in relationships throughout life. Unlike trust issues, which often result from specific incidents of betrayal or broken promises, attachment issues are deeply rooted in developmental patterns affecting emotional regulation and intimacy. Understanding attachment theory helps identify patterns such as anxious, avoidant, or disorganized attachment styles, providing a framework for addressing relationship difficulties and trauma related to betrayal.
Defining Trust Issues
Trust issues stem from an individual's difficulty in believing others' reliability, truthfulness, or intentions, often rooted in past experiences of deception, neglect, or emotional harm. Unlike attachment issues, which primarily involve difficulties forming emotional bonds due to early relational patterns, trust issues specifically impact one's ability to feel secure and confident in interpersonal interactions. Betrayal trauma involves a profound psychological response to violation of trust by a close or significant other, often intensifying trust issues and complicating emotional recovery.
Attachment Styles and Their Impact
Attachment styles, formed in early childhood, profoundly influence how individuals navigate trust issues and betrayal trauma in relationships. Secure attachment fosters healthy trust and resilience, while anxious or avoidant attachment styles often exacerbate sensitivity to betrayal and create difficulties in forming stable bonds. Understanding these attachment styles is crucial for addressing attachment issues, mitigating trust challenges, and healing from betrayal trauma effectively.
Causes of Attachment Issues
Attachment issues often stem from inconsistent or neglectful caregiving during early childhood, leading to difficulties in forming secure emotional bonds later in life. These issues can result from traumatic experiences such as abandonment, abuse, or prolonged separation from primary caregivers. Trust issues frequently arise as a consequence of attachment disruptions, while betrayal trauma specifically involves the psychological impact of a close relationship's violation, intensifying the complexity of emotional healing.
Roots of Trust Issues
Trust issues often stem from insecure early attachments, where inconsistent caregiving disrupts the development of secure emotional bonds. Betrayal trauma specifically roots in significant breaches of trust, such as infidelity or abuse, challenging the ability to rely on others. While attachment issues relate to foundational relationship patterns, trust issues arise from both childhood experiences and traumatic breaches that undermine confidence in people's reliability.
Key Differences: Attachment vs Trust Issues
Attachment issues primarily stem from early relational experiences affecting emotional bonding and security, whereas trust issues arise from repeated breaches of confidence and reliability in relationships. Attachment problems influence the ability to form and maintain close connections, often rooted in childhood, while trust issues manifest as skepticism and fear of vulnerability in response to past betrayals. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify therapeutic approaches for addressing relational difficulties and emotional healing.
Signs and Symptoms to Recognize
Attachment issues often manifest as difficulty forming close relationships, fear of abandonment, or excessive dependency, indicating disruptions in early bonding experiences. Trust issues reveal themselves through persistent suspicion, reluctance to confide, and heightened anxiety about others' intentions, often rooted in past betrayals or inconsistent behavior. Betrayal trauma symptoms include emotional numbness, hypervigilance, and intrusive memories related to significant breaches of trust, helping you identify and differentiate these complex psychological patterns.
Effects on Relationships and Intimacy
Attachment issues affect your ability to form secure emotional bonds, often leading to anxiety or avoidance in close relationships. Trust issues create barriers to vulnerability, making intimacy difficult due to fear of being hurt or deceived. Betrayal trauma deeply erodes trust and safety, causing intense emotional pain and long-term challenges in maintaining healthy, intimate connections.
Strategies for Healing and Growth
Healing from attachment issues, trust issues, and betrayal trauma involves personalized strategies designed to rebuild emotional resilience and strengthen interpersonal connections. Your path to growth may include consistent therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or EMDR, to process past wounds and develop healthier attachment models. Building trust gradually through open communication, setting boundaries, and practicing self-compassion fosters long-term emotional recovery and empowerment.
When to Seek Professional Help
Attachment issues, trust issues, and betrayal trauma each impact emotional well-being differently and can become overwhelming when they interfere with daily functioning or relationships. You should seek professional help if feelings of insecurity, anxiety, or distrust persistently affect your ability to connect with others or recover from traumatic experiences. Early intervention from a therapist specializing in trauma and relational health can provide tailored strategies to restore emotional stability and improve interpersonal dynamics.
Infographic: Attachment Issues vs Trust Issues
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com