Fearful attachment is characterized by a desire for closeness coupled with a fear of rejection, while avoidant attachment involves maintaining emotional distance to prevent vulnerability. Discover more about these attachment styles and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
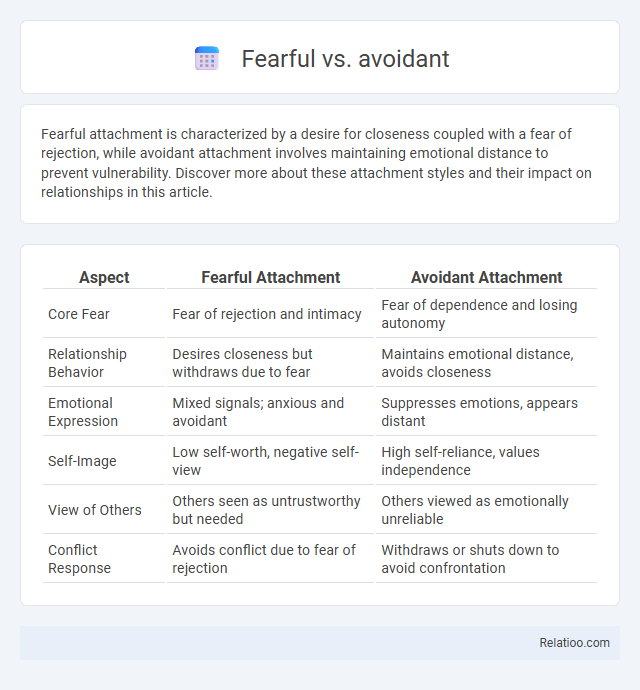
| Aspect | Fearful Attachment | Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Fear | Fear of rejection and intimacy | Fear of dependence and losing autonomy |
| Relationship Behavior | Desires closeness but withdraws due to fear | Maintains emotional distance, avoids closeness |
| Emotional Expression | Mixed signals; anxious and avoidant | Suppresses emotions, appears distant |
| Self-Image | Low self-worth, negative self-view | High self-reliance, values independence |
| View of Others | Others seen as untrustworthy but needed | Others viewed as emotionally unreliable |
| Conflict Response | Avoids conflict due to fear of rejection | Withdraws or shuts down to avoid confrontation |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Fearful vs Avoidant
Understanding attachment styles is crucial for navigating emotional connections, especially when distinguishing between fearful and avoidant types. Fearful attachment combines a desire for closeness with a fear of rejection, causing ambivalence in Your relationships, whereas avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance, leading to difficulty in intimacy. Recognizing these patterns helps You foster healthier interactions and develop more secure attachments.
Defining Fearful Attachment
Fearful attachment is defined by a deep-seated fear of rejection combined with a strong desire for close relationships, causing internal conflict and emotional distress. Unlike avoidant attachment, which emphasizes emotional distance and self-reliance, fearful attachment involves anxious anticipation of abandonment and difficulty trusting others. This style often results from trauma or inconsistent caregiving, leading to a complex blend of approach-avoidance behaviors in intimate relationships.
Defining Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by discomfort with closeness and a strong preference for emotional distance in relationships, often stemming from early experiences of rejection or neglect. Individuals with avoidant attachment typically suppress feelings and avoid dependence on others, prioritizing self-reliance and independence. This contrasts with fearful attachment, where there is a desire for intimacy coupled with a fear of rejection, and secure attachment, marked by comfort with closeness and trust.
Core Characteristics of Fearful Attachment
Fearful attachment is characterized by a deep fear of rejection combined with a strong desire for intimacy, leading to conflicting behaviors in relationships. You may struggle with trusting others while simultaneously craving closeness, resulting in emotional withdrawal and anxiety. This attachment style often stems from past trauma or inconsistent caregiving, causing heightened sensitivity to perceived abandonment.
Core Characteristics of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and self-reliance, often leading to emotional distance and difficulty trusting others. Individuals with avoidant attachment tend to suppress feelings and avoid intimacy to protect themselves from potential rejection or vulnerability. This core behavior contrasts with fearful attachment, which combines anxiety about relationships with avoidance, and fearful attachment, which involves fluctuating between fear of abandonment and desire for closeness.
Key Differences Between Fearful and Avoidant Attachment
Fearful attachment is characterized by a deep desire for closeness accompanied by a fear of rejection, leading to significant internal conflict and emotional turmoil. Avoidant attachment involves a consistent discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to maintain emotional distance to protect oneself from potential hurt. The key difference lies in fearful individuals craving connection yet being paralyzed by anxiety, whereas avoidant individuals suppress their need for closeness by prioritizing independence and emotional self-reliance.
How Fearful and Avoidant Styles Impact Relationships
Fearful attachment styles often lead to difficulty trusting partners and a persistent fear of rejection, causing emotional distance and instability in relationships. Avoidant attachment styles result in a tendency to suppress emotions and maintain independence, which can create barriers to intimacy and connection. Both styles hinder the development of secure bonds, increasing the risk of misunderstandings and emotional disconnection.
Triggers and Coping Mechanisms
Fearful attachment is often triggered by a fear of rejection and abandonment, causing intense emotional pain and difficulty trusting others, while avoidant attachment arises from discomfort with intimacy and a preference for emotional distance, triggered by feelings of vulnerability. Your coping mechanisms for fearful attachment include seeking reassurance and developing self-soothing techniques, whereas avoidant individuals tend to detach emotionally and prioritize independence to manage discomfort. Recognizing these triggers helps tailor coping strategies such as therapy, mindfulness, and communication skills to reduce anxiety and build healthier relationships.
Healing Strategies for Fearful and Avoidant Individuals
Healing strategies for Fearful individuals focus on building trust and emotional safety through consistent, supportive relationships and therapy that addresses fears of rejection and abandonment. Avoidant individuals benefit from gradual exposure to intimacy, enhancing emotional awareness and vulnerability while practicing communication skills to reduce avoidance behaviors. Both styles improve through mindfulness practices and self-compassion exercises that cultivate secure attachment and resilience.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
Fearful, avoidant, and fearful-avoidant attachment styles often struggle with intimacy and trust, making professional help crucial for healing. Therapy focused on attachment can guide you in recognizing patterns, building healthier relationships, and managing anxiety linked to fear of rejection or abandonment. Support groups and counseling provide safe environments to explore emotions, develop coping skills, and foster secure connections essential for personal growth.
Infographic: Fearful vs Avoidant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com