Avoidant individuals often seek emotional distance and fear intimacy, while narcissists crave admiration and control, creating a volatile dynamic in relationships. Explore this article to understand the complexities of Avoidant versus Narcissist interactions and how to navigate them.
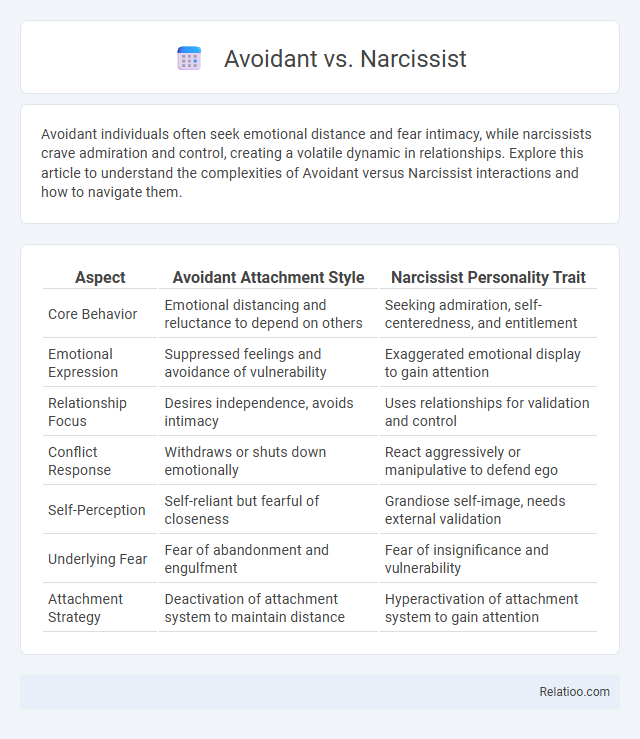
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment Style | Narcissist Personality Trait |
|---|---|---|
| Core Behavior | Emotional distancing and reluctance to depend on others | Seeking admiration, self-centeredness, and entitlement |
| Emotional Expression | Suppressed feelings and avoidance of vulnerability | Exaggerated emotional display to gain attention |
| Relationship Focus | Desires independence, avoids intimacy | Uses relationships for validation and control |
| Conflict Response | Withdraws or shuts down emotionally | React aggressively or manipulative to defend ego |
| Self-Perception | Self-reliant but fearful of closeness | Grandiose self-image, needs external validation |
| Underlying Fear | Fear of abandonment and engulfment | Fear of insignificance and vulnerability |
| Attachment Strategy | Deactivation of attachment system to maintain distance | Hyperactivation of attachment system to gain attention |
Understanding Avoidant and Narcissist Personalities
Avoidant personalities are characterized by intense fear of rejection and social anxiety, leading to withdrawal from interpersonal relationships, whereas narcissist personalities exhibit grandiosity, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy. Understanding the differences between avoidant and narcissist traits helps you recognize that avoidants seek safety and acceptance, while narcissists pursue validation and control. This clarity enables more effective communication and tailored strategies for managing interactions with each personality type.
Key Traits of Avoidant Individuals
Avoidant individuals exhibit key traits such as intense fear of rejection, chronic social anxiety, and a pervasive sense of inadequacy that leads them to avoid close relationships. Unlike narcissists who seek admiration and superiority, avoidant personalities prioritize emotional safety by maintaining distance and minimizing vulnerability. Their core characteristic is a deep-seated desire for connection hindered by extreme discomfort with intimacy and judgment.
Defining Characteristics of Narcissists
Narcissists exhibit defining characteristics such as an inflated sense of self-importance, a deep need for excessive admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. Unlike avoidant individuals who tend to withdraw due to fear of rejection, narcissists actively seek validation and control in relationships, often displaying manipulative or exploitative behaviors. Understanding these traits is crucial for distinguishing narcissistic personality disorder from avoidant personality disorder, where social inhibition and feelings of inadequacy dominate.
Core Differences Between Avoidant and Narcissist Behavior
Avoidant behavior is characterized by social withdrawal, fear of rejection, and a deep-seated need to avoid emotional intimacy, while narcissist behavior centers around grandiosity, a constant need for admiration, and a lack of empathy toward others. You can distinguish core differences by noting that avoidants seek safety through isolation and fear vulnerability, whereas narcissists seek validation through attention and often manipulate relationships to maintain their self-image. Understanding these distinctions helps in identifying relational patterns and tailoring effective communication or therapeutic approaches.
How Each Style Approaches Relationships
Avoidant individuals prioritize emotional distance and self-reliance, often withdrawing to protect themselves from intimacy or vulnerability in relationships. Narcissists seek validation and admiration, approaching relationships with a focus on control, superiority, and fulfilling their own needs rather than mutual connection. Avoidant Narcissists combine these traits by simultaneously craving attention while pushing partners away to maintain emotional distance and protect their fragile self-esteem.
Emotional Response Patterns: Avoidant vs. Narcissist
Avoidant individuals typically exhibit emotional responses characterized by withdrawal and suppression to protect themselves from perceived rejection or vulnerability, while narcissists often react with defensiveness, entitlement, and manipulation to maintain their self-image and control. Avoidants tend to internalize emotions and avoid confrontation, reflecting fear of intimacy, whereas narcissists externalize emotions, showing aggression or invalidation to assert dominance. These contrasting emotional response patterns highlight the avoidant's need for emotional distance versus the narcissist's need for validation and superiority.
Communication Styles: What Sets Them Apart
Avoidant individuals often exhibit reserved communication, characterized by withdrawal and minimal self-disclosure to protect their inner vulnerability. Narcissists dominate conversations with self-centered narratives, seeking admiration and control, often disregarding others' feelings. Avoidant Narcissists blend emotional detachment with manipulation, balancing avoidance of intimacy and a need for validation, resulting in unpredictable and conflicting communication patterns.
Impact on Loved Ones and Partners
Avoidant, Narcissist, and Avoidant-Narcissist personality types each impact loved ones and partners differently. Avoidant individuals often create distance due to fear of intimacy, causing partners to feel neglected or unvalued. Narcissists tend to manipulate and exploit loved ones for validation, resulting in emotional exhaustion and diminished self-esteem, while those with Avoidant-Narcissist traits combine withdrawal with self-centeredness, amplifying relationship instability and confusion.
Typical Triggers for Avoidant and Narcissist Reactions
Avoidant individuals typically react to triggers involving emotional vulnerability, fear of rejection, or situations requiring intimacy, leading to withdrawal or avoidance behavior. Narcissists often respond defensively to perceived criticism, threats to their self-esteem, or challenges to their superiority, resulting in anger, manipulation, or grandiosity. Understanding these distinct triggers helps differentiate the avoidant's need for emotional safety from the narcissist's need for validation and control.
Strategies for Coping and Healing in Relationships
Effective strategies for coping with avoidant and narcissistic behaviors in relationships involve setting clear boundaries and fostering open communication to address emotional needs. Developing self-awareness through therapy or mindfulness techniques helps individuals recognize patterns of avoidance or entitlement, promoting healthier interactions. Building trust gradually while maintaining personal well-being supports healing and resilience when navigating complex attachment dynamics.
Infographic: Avoidant vs Narcissist
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com