Secure attachment fosters trust and healthy emotional bonds, while preoccupied attachment often results in anxiety and clinginess in relationships. Discover more insights on how these attachment styles impact your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
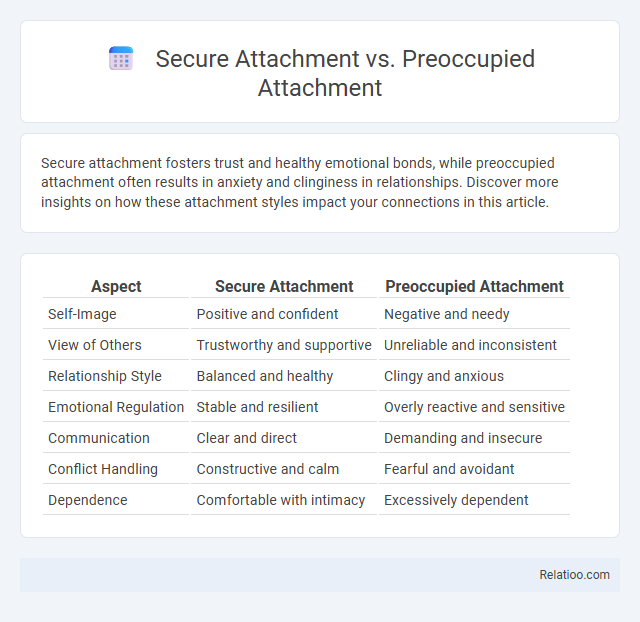
| Aspect | Secure Attachment | Preoccupied Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Image | Positive and confident | Negative and needy |
| View of Others | Trustworthy and supportive | Unreliable and inconsistent |
| Relationship Style | Balanced and healthy | Clingy and anxious |
| Emotional Regulation | Stable and resilient | Overly reactive and sensitive |
| Communication | Clear and direct | Demanding and insecure |
| Conflict Handling | Constructive and calm | Fearful and avoidant |
| Dependence | Comfortable with intimacy | Excessively dependent |
Understanding Attachment Theory
Understanding Attachment Theory reveals that secure attachment fosters healthy emotional bonds characterized by trust and autonomy, while preoccupied attachment involves anxiety and fear of abandonment, leading to clinginess. The dependency paradox highlights that although secure individuals comfortably rely on others, those with preoccupied attachment often feel overwhelmed by their own dependence, exacerbating insecurity. Recognizing these patterns enables you to identify and navigate your relational needs effectively, promoting emotional well-being.
What is Secure Attachment?
Secure attachment is characterized by a healthy balance of intimacy and autonomy, where individuals feel confident in their relationships and trust their partners while maintaining personal independence. This attachment style fosters emotional regulation, effective communication, and resilience in the face of relationship challenges. In contrast to preoccupied attachment and dependency paradox, secure attachment promotes stability and emotional security without excessive clinginess or fear of abandonment.
Characteristics of Secure Attachment
Secure attachment is characterized by a healthy balance of intimacy and independence, where individuals feel comfortable with closeness and are able to trust others without fear of abandonment. They exhibit emotional regulation, resilience in relationships, and effective communication, fostering stable and supportive connections. This contrasts sharply with preoccupied attachment's anxiety over relationships and dependency paradox, where reliance on others may undermine personal autonomy and emotional security.
What is Preoccupied Attachment?
Preoccupied attachment is characterized by an intense desire for closeness and approval, combined with anxiety about relationships and fear of abandonment. Individuals with preoccupied attachment often exhibit clinginess and a heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection, which can lead to emotional dependency. Understanding Your attachment style can help address the dependency paradox, where seeking security paradoxically results in increased insecurity.
Characteristics of Preoccupied Attachment
Preoccupied attachment is characterized by high anxiety and low avoidance, leading to an intense need for approval and fear of abandonment. Individuals with preoccupied attachment often exhibit clinginess, emotional hyper-reactivity, and difficulty trusting their partner's intentions. Your awareness of these traits can help manage dependency paradoxes and promote healthier relational patterns.
Key Differences: Secure vs Preoccupied Attachment
Secure attachment fosters trust, emotional stability, and healthy independence, enabling Your relationships to thrive with balanced closeness and autonomy. Preoccupied attachment often results in anxiety, clinginess, and fear of abandonment, causing emotional highs and lows that undermine relational security. The key difference lies in secure attachment's confidence in self-worth and partner reliability versus preoccupied attachment's dependency on external validation and heightened sensitivity to rejection.
Impacts on Adult Relationships
Secure attachment fosters healthy communication and trust, promoting stable and satisfying adult relationships marked by emotional intimacy. Preoccupied attachment often leads to anxiety and clinginess, causing difficulties in maintaining boundaries and resulting in relationship dissatisfaction. The dependency paradox reveals that excessive neediness can push partners away, whereas a balanced interdependence strengthens relational bonds and emotional resilience.
Factors Influencing Attachment Styles
Factors influencing attachment styles include early childhood experiences, caregiver responsiveness, and emotional availability, which shape how you form and maintain relationships. Secure attachment develops from consistent and nurturing care, fostering trust and autonomy, whereas preoccupied attachment arises from inconsistent caregiving, leading to anxiety and dependency in relationships. The dependency paradox highlights how a strong sense of security promotes healthy independence, while excessive dependency can undermine emotional stability despite a desire for closeness.
Healing and Shifting Attachment Patterns
Healing attachment patterns involves recognizing and shifting from preoccupied attachment, characterized by anxiety and a constant need for reassurance, toward secure attachment, which fosters emotional resilience and trust. Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness techniques help individuals address dependency paradoxes by developing self-soothing skills and healthy relational boundaries. Consistent practice in forming secure attachments promotes emotional regulation and reduces vulnerability to anxious dependency.
Building Secure Attachments in Adulthood
Building secure attachments in adulthood enhances emotional resilience and fosters healthy relationship dynamics by promoting trust and effective communication. Unlike preoccupied attachment, which involves anxiety and fear of rejection, secure attachment encourages autonomy alongside intimacy, reducing dependency paradoxes where individuals simultaneously crave closeness and fear loss of self. Developing secure attachment patterns involves consistent responsiveness, emotional regulation, and positive relational experiences that reshape attachment schemas formed in early life.
Infographic: Secure Attachment vs Preoccupied Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com