Avoidant Withdraw partners create distance to maintain independence, while Anxious Pursue partners seek closeness and reassurance, often leading to a push-pull dynamic in relationships. Explore this article to understand how these contrasting attachment styles impact intimacy and communication.
Table of Comparison
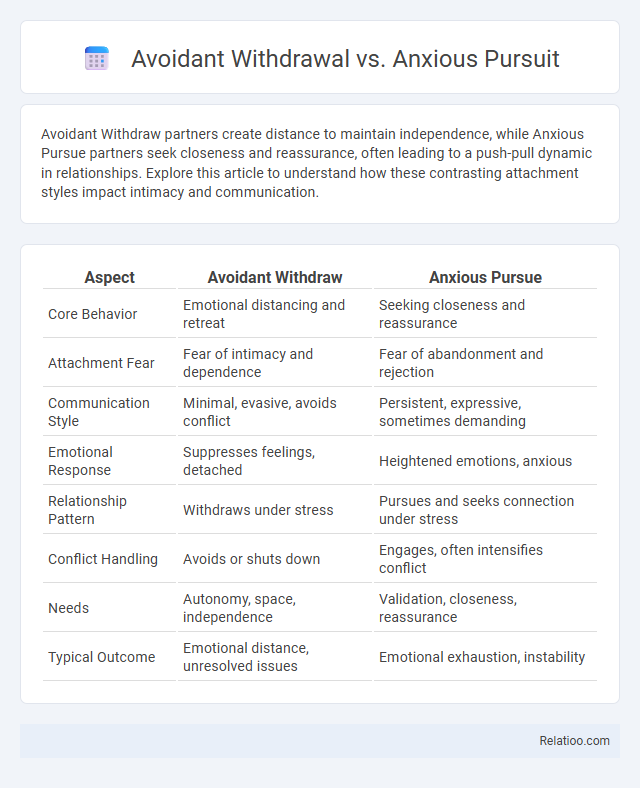
| Aspect | Avoidant Withdraw | Anxious Pursue |
|---|---|---|
| Core Behavior | Emotional distancing and retreat | Seeking closeness and reassurance |
| Attachment Fear | Fear of intimacy and dependence | Fear of abandonment and rejection |
| Communication Style | Minimal, evasive, avoids conflict | Persistent, expressive, sometimes demanding |
| Emotional Response | Suppresses feelings, detached | Heightened emotions, anxious |
| Relationship Pattern | Withdraws under stress | Pursues and seeks connection under stress |
| Conflict Handling | Avoids or shuts down | Engages, often intensifies conflict |
| Needs | Autonomy, space, independence | Validation, closeness, reassurance |
| Typical Outcome | Emotional distance, unresolved issues | Emotional exhaustion, instability |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Avoidant vs. Anxious
Understanding attachment styles reveals that avoidant individuals tend to withdraw emotionally to maintain independence, while anxious partners often pursue closeness to alleviate insecurity. Your relationship dynamics may reflect this push-pull pattern, where the avoidant partner distances themselves as the anxious partner seeks reassurance. Recognizing these tendencies helps improve communication and build healthier emotional connections tailored to each attachment style.
Defining the Withdraw-Pursue Dynamic
The Withdraw-Pursue dynamic characterizes interactions where one partner, often with an avoidant attachment style, retreats emotionally to create distance, while the other, frequently anxious, seeks closeness and reassurance through pursuing behaviors. This cyclical pattern intensifies relationship tension, as the avoidant partner's withdrawal triggers the anxious partner's pursuit, leading to misunderstandings and unmet emotional needs. Understanding Your role in this dynamic helps break the cycle by fostering communication that balances autonomy with intimacy.
Core Behaviors of Avoidant Withdrawers
Avoidant withdrawers core behaviors include emotional distancing, reluctance to communicate feelings, and a strong desire for independence, often leading them to pull away during conflicts. Your tendency to suppress vulnerability and avoid intimacy contrasts sharply with anxious pursuers, who seek constant reassurance and closeness. Understanding these patterns helps in navigating relationships with avoidant partners and fosters healthier emotional connections.
Key Traits of Anxious Pursuers
Anxious Pursuers often exhibit intense fear of abandonment, leading to clingy and demanding behavior in relationships. Your constant need for reassurance and heightened emotional sensitivity contrasts with Avoidant Withdrawers, who tend to distance themselves and suppress emotions. Understanding these key traits helps in managing relationship dynamics by recognizing the push-pull pattern between anxious pursuit and avoidant withdrawal.
The Emotional Cycle: Why Withdraw Meets Pursue
The emotional cycle between avoidant withdraw and anxious pursue creates a repetitive push-pull dynamic fueled by fear of intimacy and desire for connection. You experience periods where one partner seeks closeness while the other retreats to protect their emotional safety, intensifying misunderstandings and attachment insecurities. Understanding this cycle is crucial to breaking patterns of withdrawal and pursuit, fostering healthier communication and emotional regulation.
Communication Challenges Between Styles
Communication challenges between Avoidant Withdraw and Anxious Pursue attachment styles stem from contrasting needs: Avoidant Withdraw individuals seek distance and emotional self-reliance, while Anxious Pursue partners crave closeness and reassurance. This dynamic often results in misunderstandings, as the avoidant's retreat can trigger increased anxiety and pursuit behaviors from the anxious partner, creating a cycle of tension and unmet emotional needs. Effective communication requires recognizing these patterns and establishing boundaries that respect each style's emotional triggers and communication preferences.
Psychological Roots of Withdraw and Pursue Patterns
Avoidant withdraw and anxious pursue patterns stem from deep psychological roots involving attachment styles formed in early relationships, where avoidant individuals learn to suppress emotions to protect themselves from rejection, while anxious pursuers often develop heightened sensitivity to abandonment. Your interactions are influenced by these contrasting coping mechanisms: avoidants distance themselves to maintain control and reduce vulnerability, whereas anxious pursuers seek closeness to alleviate fears of being unloved or neglected. Understanding these patterns reveals how unmet emotional needs and fear responses drive the cycle of withdrawal and pursuit in relationships.
The Impact on Relationship Satisfaction
Avoidant withdraw, anxious pursue, and avoidant withdraw patterns critically influence relationship satisfaction by shaping emotional connection and communication dynamics. You may experience heightened frustration and misunderstandings when anxious partners seek closeness while avoidant partners distance themselves, creating a cycle of unmet needs. Recognizing these attachment behaviors helps improve emotional intimacy and fosters healthier, more satisfying relationships.
Breaking the Cycle: Steps Toward Secure Connection
Breaking the cycle between Avoidant Withdraw and Anxious Pursue attachment styles requires intentional communication and establishing clear boundaries to foster emotional safety. Practicing vulnerability and consistent responsiveness helps both partners move toward secure attachment by reducing fear of abandonment and need for excessive control. Engaging in therapeutic interventions such as Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) strengthens trust and encourages secure connection through understanding underlying attachment needs.
Healing and Growth for Avoidant and Anxious Partners
Avoidant withdraw patterns create distance in relationships, while anxious pursue behaviors seek closeness, often leading to a push-pull dynamic that challenges emotional connection. Healing for avoidant partners involves cultivating vulnerability and consistent communication, whereas anxious partners benefit from developing self-soothing techniques and secure attachment styles. Your growth relies on mutual understanding, patience, and implementing strategies that foster trust and emotional safety to break the cycle and nurture a balanced relationship.
Infographic: Avoidant Withdraw vs Anxious Pursue
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com