Avoidant attachment often leads to emotional distance and difficulty managing distress, whereas secure attachment promotes healthy communication and higher distress tolerance in relationships. Discover effective strategies to improve attachment styles and strengthen bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
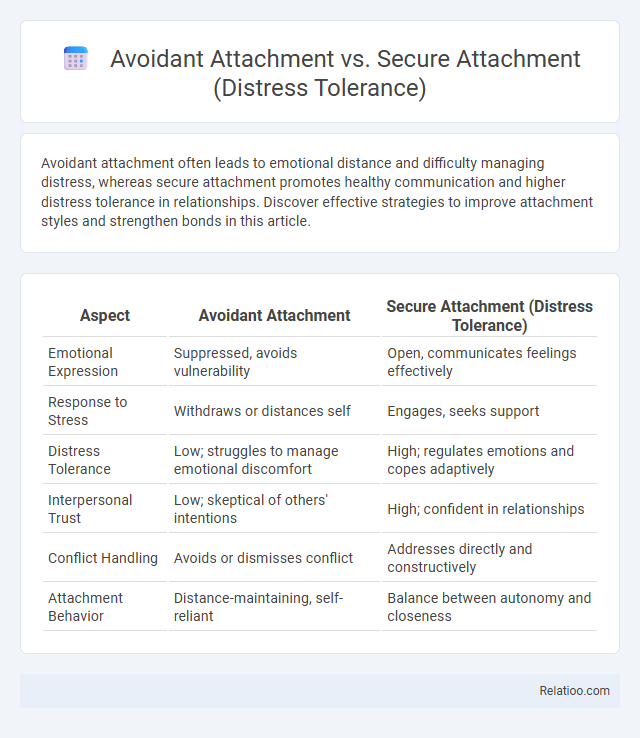
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Secure Attachment (Distress Tolerance) |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Expression | Suppressed, avoids vulnerability | Open, communicates feelings effectively |
| Response to Stress | Withdraws or distances self | Engages, seeks support |
| Distress Tolerance | Low; struggles to manage emotional discomfort | High; regulates emotions and copes adaptively |
| Interpersonal Trust | Low; skeptical of others' intentions | High; confident in relationships |
| Conflict Handling | Avoids or dismisses conflict | Addresses directly and constructively |
| Attachment Behavior | Distance-maintaining, self-reliant | Balance between autonomy and closeness |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Avoidant vs Secure
Avoidant attachment is characterized by discomfort with closeness and a tendency to suppress emotional expression, leading to challenges in distress tolerance due to avoidance of vulnerability. Secure attachment demonstrates effective distress tolerance through openness to emotional experiences and reliance on supportive relationships for regulation. Understanding these attachment styles clarifies how individuals manage stress and emotional challenges, with secure attachment fostering resilience and avoidant attachment often resulting in emotional withdrawal.
Core Traits of Avoidant and Secure Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance, discomfort with closeness, and a tendency to suppress distress to maintain independence, whereas secure attachment involves comfort with intimacy, effective emotional regulation, and confidence in support-seeking during stress. Core traits of avoidant attachment include distrust in others' availability, minimizing emotional expression, and hesitance to rely on social support. Secure attachment features include resilience in distress tolerance, openness to vulnerability, and balanced self-reliance combined with trust in relationships.
Distress Tolerance Defined in Attachment Theory
Distress tolerance in attachment theory refers to your ability to manage and endure emotional discomfort without becoming overwhelmed or disconnected. Avoidant attachment typically results in low distress tolerance, causing individuals to suppress or avoid emotional pain, whereas secure attachment is characterized by healthy distress tolerance, allowing you to confront and process distress effectively. Developing secure attachment promotes resilience and emotional regulation, essential for sustaining relationships and personal well-being.
Emotional Regulation: Avoidant vs Secure Individuals
Securely attached individuals demonstrate higher distress tolerance through effective emotional regulation, openly acknowledging and processing their feelings. In contrast, avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional suppression and discomfort with intimacy, leading to poor distress tolerance and difficulty managing negative emotions. These differences in emotional regulation impact interpersonal relationships and coping strategies during stress.
Coping Mechanisms Under Stress
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distancing and suppressed distress expression, leading individuals to rely on self-soothing and avoidance as primary coping mechanisms under stress. In contrast, secure attachment fosters effective distress tolerance through open emotional communication and seeking support from trusted relationships, enhancing resilience during challenging situations. Distress tolerance skills, such as mindfulness and emotional regulation, complement secure attachment by providing practical tools to manage negative affect and reduce maladaptive avoidance behaviors.
Communication Patterns in Difficult Situations
Avoidant attachment often leads to withdrawal and suppression of emotions during difficult situations, causing communication barriers and unmet emotional needs. Secure attachment promotes open and honest dialogue, enabling you to express distress while fostering mutual understanding and effective problem-solving. Distress tolerance skills support maintaining calm and clarity, allowing clearer communication without escalating conflict or emotional shutdown.
Impact of Attachment Styles on Relationships
Avoidant attachment often leads to difficulties in expressing emotions and maintaining close connections, causing challenges in trust and intimacy within relationships. Secure attachment enhances distress tolerance by promoting effective emotional regulation and openness, fostering healthier communication and deeper bonds. Your ability to manage distress is significantly influenced by your attachment style, impacting relationship satisfaction and resilience.
Long-Term Effects of Distress Tolerance Levels
Avoidant attachment often leads to poor distress tolerance, causing individuals to suppress emotions and struggle with intimacy, which can result in long-term difficulties in forming stable relationships. Secure attachment fosters healthy distress tolerance, enabling you to manage emotional challenges effectively and build resilience over time. High distress tolerance contributes to emotional regulation and psychological well-being, while low distress tolerance increases vulnerability to anxiety, depression, and interpersonal conflicts throughout life.
Enhancing Distress Tolerance for Healthier Attachments
Enhancing distress tolerance plays a crucial role in transforming avoidant attachment patterns into secure attachments by enabling you to manage emotional discomfort without withdrawal or suppression. Secure attachment fosters healthier relationships through effective distress regulation, promoting emotional openness and resilience in the face of stress. Building distress tolerance skills strengthens your capacity to face relational challenges, ultimately supporting deeper emotional connections and psychological well-being.
Steps Toward Secure Attachment Development
Developing secure attachment involves recognizing avoidant patterns and gradually increasing your tolerance for emotional distress without disengaging. Practice mindful awareness of your feelings and improve communication skills to express needs openly, fostering connection rather than withdrawal. Consistent experiences of safety and responsiveness from others strengthen distress tolerance and promote secure attachment growth.
Infographic: Avoidant Attachment vs Secure Attachment (Distress Tolerance)
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com