Avoidant Attachment is characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance, while Disorganized Attachment presents a mix of avoidance and anxiety, often stemming from trauma or inconsistent caregiving. Discover the key differences and how they impact relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
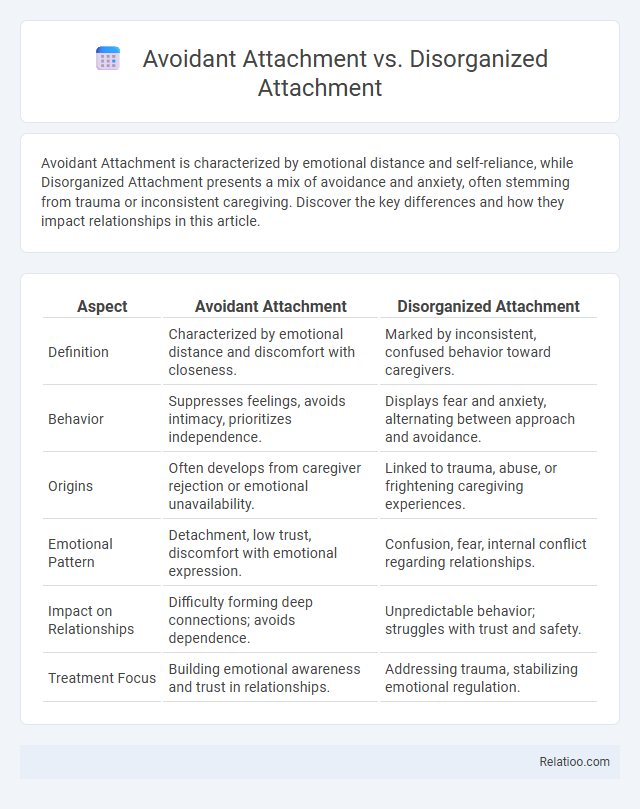
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Disorganized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Characterized by emotional distance and discomfort with closeness. | Marked by inconsistent, confused behavior toward caregivers. |
| Behavior | Suppresses feelings, avoids intimacy, prioritizes independence. | Displays fear and anxiety, alternating between approach and avoidance. |
| Origins | Often develops from caregiver rejection or emotional unavailability. | Linked to trauma, abuse, or frightening caregiving experiences. |
| Emotional Pattern | Detachment, low trust, discomfort with emotional expression. | Confusion, fear, internal conflict regarding relationships. |
| Impact on Relationships | Difficulty forming deep connections; avoids dependence. | Unpredictable behavior; struggles with trust and safety. |
| Treatment Focus | Building emotional awareness and trust in relationships. | Addressing trauma, stabilizing emotional regulation. |
Introduction to Attachment Styles
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and discomfort with closeness, often stemming from early caregiving that was consistently unresponsive or rejecting. Disorganized attachment involves a mix of fear and confusion, arising from caregivers who were unpredictable or frightening, leading to difficulty in forming a coherent strategy for seeking comfort. Bonding refers to the initial emotional connection between an infant and caregiver that is crucial for healthy attachment development and influences the formation of secure or insecure attachment styles.
Defining Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and discomfort with closeness, often developed from caregivers who are emotionally unresponsive, leading individuals to suppress attachment needs and maintain self-reliance. Disorganized attachment involves inconsistent and confused behaviors toward caregivers, combining avoidance and anxiety due to trauma or neglect. Bonding refers to the emotional connection formed between caregiver and child, essential for secure attachment and healthy social development.
What is Disorganized Attachment?
Disorganized attachment is characterized by a lack of clear attachment behavior, often resulting from inconsistent, frightening, or abusive caregiving, leading to confusion and fear in the child. Unlike avoidant attachment, where children minimize emotional expression to cope, disorganized attachment involves contradictory behaviors such as approaching and then avoiding caregivers. This attachment style can significantly impact emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships, highlighting the importance of secure bonding and consistent caregiving in early development.
Key Differences Between Avoidant and Disorganized Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance, often developing from caregivers who are consistently unresponsive or rejecting. Disorganized attachment arises from inconsistent or frightening caregiving, leading to confusion and fear in relationships without a clear strategy for seeking comfort. Unlike avoidant attachment's emotional detachment, disorganized attachment includes contradictory behaviors, such as seeking closeness while simultaneously exhibiting fear or resistance toward caregivers.
Signs and Behaviors of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance, discomfort with closeness, and a tendency to suppress feelings to maintain independence, often leading to difficulty trusting others and reluctance to seek support. Signs of avoidant attachment include a preference for self-reliance, avoidance of intimate conversations, and minimizing the importance of relationships. Understanding these behaviors can help you recognize patterns that may hinder forming secure bonds and foster healthier emotional connections.
Identifying Disorganized Attachment Patterns
Disorganized attachment patterns are characterized by inconsistent, erratic behaviors and confusion in response to caregivers, often stemming from trauma or unresolved fear. Unlike avoidant attachment, which shows emotional distance and suppression of feelings, disorganized attachment reflects a lack of coherent strategy for managing stress or seeking comfort. Identifying disorganized attachment involves observing contradictory actions such as approach-avoidance behaviors and signs of dissociation during relational stress.
Childhood Origins of Avoidant vs Disorganized Attachment
Avoidant attachment originates in childhood through caregivers who consistently reject or dismiss a child's emotional needs, leading the child to suppress feelings and avoid closeness as a defense mechanism. Disorganized attachment develops from unpredictable or frightening caregiving, where the child experiences fear without resolution, resulting in confusion and contradictory behaviors. Understanding these childhood origins helps you recognize patterns that influence your current relationships and emotional responses.
Impact on Adult Relationships
Avoidant attachment in adults often leads to emotional distance and difficulty trusting partners, causing challenges in forming close relationships. Disorganized attachment is associated with conflicting behaviors and fear of intimacy, frequently resulting in unstable and tumultuous adult relationships. Bonding, by contrast, fosters secure attachments that promote healthy communication, emotional closeness, and resilience in adult partnerships.
Healing and Overcoming Maladaptive Attachment
Healing from avoidant attachment, disorganized attachment, and challenges in bonding involves understanding the unique patterns of emotional withdrawal, fear of intimacy, and unpredictable behaviors these attachment styles manifest. Your journey to overcoming maladaptive attachment requires consistent therapeutic support, such as trauma-informed therapy or attachment-based interventions, to build secure relational foundations and emotional regulation skills. Cultivating self-awareness and safe relational experiences plays a critical role in transforming attachment wounds into resilient, healthy connections.
Choosing the Right Support and Therapy
Avoidant attachment involves emotional distancing and difficulty trusting others, while disorganized attachment manifests as a mix of fear and confusion in relationships, often stemming from traumatic experiences. Bonding, distinct from attachment styles, refers to the initial emotional connection formed, impacting future relational patterns. Your choice of support and therapy should be tailored to address specific attachment challenges, with cognitive-behavioral therapy effective for avoidant traits and trauma-informed therapy beneficial for disorganized attachment to foster secure bonds.
Infographic: Avoidant Attachment vs Disorganized Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com