Fearful-Avoidant Attachment is characterized by a deep fear of intimacy paired with a strong desire for closeness, often leading to emotional confusion and instability, while Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment involves a preference for independence and emotional distance, suppressing attachment needs to avoid vulnerability. Explore this article to understand these attachment styles' impact on relationship dynamics and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
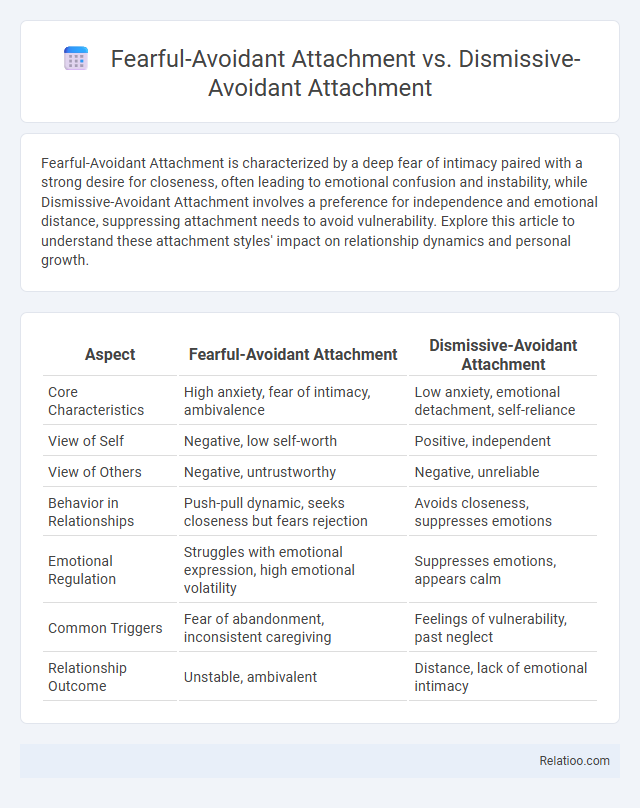
| Aspect | Fearful-Avoidant Attachment | Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Characteristics | High anxiety, fear of intimacy, ambivalence | Low anxiety, emotional detachment, self-reliance |
| View of Self | Negative, low self-worth | Positive, independent |
| View of Others | Negative, untrustworthy | Negative, unreliable |
| Behavior in Relationships | Push-pull dynamic, seeks closeness but fears rejection | Avoids closeness, suppresses emotions |
| Emotional Regulation | Struggles with emotional expression, high emotional volatility | Suppresses emotions, appears calm |
| Common Triggers | Fear of abandonment, inconsistent caregiving | Feelings of vulnerability, past neglect |
| Relationship Outcome | Unstable, ambivalent | Distance, lack of emotional intimacy |
Understanding Attachment Styles: An Overview
Fearful-avoidant attachment is characterized by a deep desire for closeness coupled with a fear of rejection, causing mixed signals in relationships. Dismissive-avoidant attachment involves a strong preference for emotional distance and self-reliance, leading to discomfort with intimacy and dependency. Understanding these attachment styles helps you recognize how fear of intimacy impacts relationship dynamics and fosters healthier interpersonal connections.
What is Fearful-Avoidant Attachment?
Fearful-avoidant attachment is characterized by a deep ambivalence about close relationships, driven by a fear of rejection and a simultaneous desire for intimacy. Individuals with this attachment style often struggle with trust and may exhibit erratic behavior, oscillating between seeking closeness and pushing others away. This contrasts with dismissive-avoidant attachment, where emotional detachment and a strong sense of independence minimize fears of intimacy, whereas fear of intimacy specifically refers to anxiety or discomfort about closeness without necessarily involving broader attachment patterns.
What is Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment?
Dismissive-avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and emotional distance, often leading individuals to suppress feelings and avoid close relationships. Unlike fearful-avoidant attachment, which combines anxiety and avoidance, dismissive-avoidant individuals prioritize self-reliance and view intimacy as a threat to their autonomy. Understanding your attachment style can help you navigate relationship challenges and address fears of intimacy effectively.
Core Differences Between Fearful-Avoidant and Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment
Fearful-avoidant attachment is characterized by a deep fear of rejection combined with a desire for closeness, leading to ambivalent and often conflicting behaviors in relationships. Dismissive-avoidant attachment, on the other hand, involves a strong preference for independence and emotional distance, with a tendency to downplay the importance of intimacy. Your understanding of these core differences helps address fear of intimacy by identifying whether you struggle primarily with anxiety around closeness or a need to maintain emotional detachment.
Childhood Origins of Fearful-Avoidant vs Dismissive-Avoidant Styles
Fearful-avoidant attachment often originates from inconsistent or traumatic childhood experiences, where caregivers were both a source of comfort and fear, leading to conflicting feelings about intimacy and trust. In contrast, dismissive-avoidant attachment typically develops from emotionally distant or unresponsive parenting, causing individuals to suppress their need for closeness and prioritize self-reliance. Understanding Your attachment style's childhood origins can help address deep-seated fears of intimacy and improve relationship dynamics.
Behavioral Patterns in Relationships
Fearful-avoidant attachment exhibits fluctuating behavior between seeking closeness and pushing partners away due to deep-seated fears of rejection, leading to inconsistent communication and emotional withdrawal. Dismissive-avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong preference for independence, emotional detachment, and minimizing intimacy, often resulting in reluctance to share feelings or commit fully. Fear of intimacy manifests through avoidance of vulnerability and difficulty forming deep emotional bonds, causing behaviors such as reluctance to discuss personal issues and maintaining emotional distance despite a desire for connection.
Emotional Responses and Coping Mechanisms
Fearful-Avoidant Attachment triggers intense emotional conflicts, blending desire for closeness with fear of rejection, leading to anxiety and emotional withdrawal as coping strategies. Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment prompts suppression of emotions in favor of self-reliance and detachment, often resulting in a stoic exterior to manage vulnerability. Your fear of intimacy may manifest through these patterns, where avoidance behaviors serve as defense mechanisms against perceived emotional threats.
Impact on Romantic Relationships
Fearful-avoidant attachment creates a cycle of longing and mistrust that disrupts emotional intimacy and stability in romantic relationships. Dismissive-avoidant attachment leads to emotional distancing and reluctance to depend on partners, often resulting in unresolved conflicts and a lack of deep connection. Your fear of intimacy can amplify these patterns, making it challenging to establish vulnerability and sustained closeness with your partner.
Healing and Growth: Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches for fearful-avoidant attachment emphasize building trust through consistent, empathetic relationships, often utilizing dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) and emotion-focused therapy to address deep-seated fears of abandonment and intimacy. Dismissive-avoidant attachment healing involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices aimed at increasing emotional awareness and vulnerability, helping individuals challenge avoidant beliefs about dependence and closeness. Fear of intimacy therapy integrates exposure therapy and interpersonal therapy, focusing on gradual emotional engagement and fostering secure attachments to promote relational growth and resilience.
Tips for Building Secure Attachment
Fearful-avoidant attachment involves a push-pull dynamic rooted in fear of rejection, while dismissive-avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance. Fear of intimacy can affect both attachment styles, leading to difficulties in forming close relationships. Tips for building secure attachment include practicing consistent emotional availability, fostering open communication, and developing self-awareness to challenge negative beliefs about closeness.
Infographic: Fearful-Avoidant Attachment vs Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com