Attachment injury occurs when a significant breach of trust disrupts emotional bonds, while relational trauma involves repeated or overwhelming interpersonal stress impacting overall relationship health. Explore this article to understand how these distinct experiences affect connection and recovery.
Table of Comparison
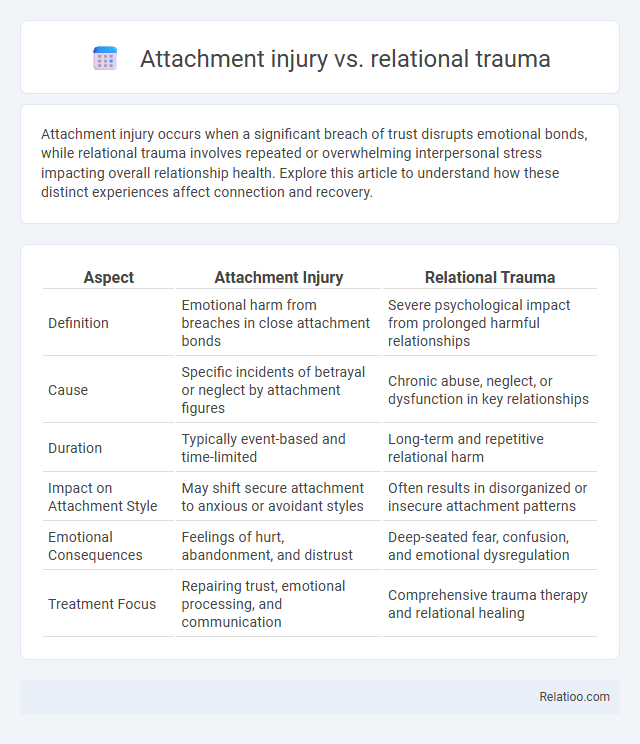
| Aspect | Attachment Injury | Relational Trauma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional harm from breaches in close attachment bonds | Severe psychological impact from prolonged harmful relationships |
| Cause | Specific incidents of betrayal or neglect by attachment figures | Chronic abuse, neglect, or dysfunction in key relationships |
| Duration | Typically event-based and time-limited | Long-term and repetitive relational harm |
| Impact on Attachment Style | May shift secure attachment to anxious or avoidant styles | Often results in disorganized or insecure attachment patterns |
| Emotional Consequences | Feelings of hurt, abandonment, and distrust | Deep-seated fear, confusion, and emotional dysregulation |
| Treatment Focus | Repairing trust, emotional processing, and communication | Comprehensive trauma therapy and relational healing |
Understanding Attachment Injury: Key Concepts
Attachment injury refers to significant breaches of trust and safety within close relationships, causing emotional wounds that disrupt secure bonding. Relational trauma encompasses broader patterns of repeated interpersonal harm affecting emotional regulation and attachment systems. Understanding attachment injury involves recognizing its impact on trust, emotional safety, and the potential for healing through repair and secure relational experiences.
Defining Relational Trauma: An Overview
Relational trauma refers to emotional and psychological harm caused by disrupted or unhealthy interpersonal relationships, often stemming from neglect, abuse, or inconsistent caregiving during critical developmental stages. Attachment injury is a specific type of relational trauma where trust and bonding are severely damaged due to breaches in attachment figures' reliability or responsiveness. Understanding these distinctions helps you address the root causes of emotional dysfunction related to attachment injury and broader relational trauma effectively.
Attachment Injury vs Relational Trauma: Core Differences
Attachment injury refers to a specific breach in trust and emotional connection between a caregiver and child, characterized by feelings of betrayal and rejection that disrupt secure attachment. Relational trauma encompasses a broader range of psychological harm caused by prolonged exposure to harmful interpersonal dynamics, including abuse, neglect, or chronic invalidation within relationships. The core difference lies in attachment injury being a precise rupture impacting attachment bonds, whereas relational trauma covers extensive damage affecting multiple relational domains and emotional development.
Causes and Origins of Attachment Injuries
Attachment injuries stem from breaches in trust or betrayal within close relationships, often triggered by caregivers' neglect, abandonment, or emotional unavailability during critical developmental periods. Relational trauma encompasses a broader range of chronic interpersonal stressors and abuse patterns that disrupt emotional bonding and security, frequently originating from ongoing caregiver maltreatment or inconsistent caregiving environments. Understanding the causes highlights how attachment injuries are specific breaches in attachment security, whereas relational trauma involves sustained, cumulative relational violations affecting emotional development.
Common Sources of Relational Trauma
Common sources of relational trauma include emotional neglect, inconsistent caregiving, and abuse within primary attachment relationships, which disrupt the development of secure bonds. Attachment injury occurs when a trusted caregiver violates this bond through betrayal or abandonment, leading to deep emotional wounds that affect your capacity for trust and intimacy. Recognizing these patterns helps differentiate attachment injury from broader relational trauma rooted in ongoing unhealthy dynamics.
Psychological Impact of Attachment Injury
Psychological impact of attachment injury includes deep emotional wounds such as feelings of betrayal, abandonment, and loss of trust, which can disrupt an individual's ability to form secure relationships. Unlike relational trauma, which often involves repeated abuse or neglect, attachment injury specifically refers to violations of the attachment bond, leading to insecurity and attachment disorders. This injury fundamentally alters attachment patterns, causing long-term effects like anxiety, depression, and difficulties with emotional regulation.
Relational Trauma: Effects on Emotional Well-being
Relational trauma involves sustained emotional harm resulting from dysfunctional or abusive relationships, profoundly impacting emotional well-being by fostering mistrust, anxiety, and difficulty regulating emotions. Unlike attachment injury, which specifically refers to breaches in early caregiver bonds, relational trauma extends across various interpersonal connections and can lead to long-term symptoms such as depression, PTSD, and impaired social functioning. Understanding relational trauma's effects on the brain and emotional health is crucial for effective therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring emotional resilience and healthy relationships.
Healing Approaches for Attachment Injury
Healing approaches for attachment injury emphasize rebuilding trust and safety in relationships through consistent emotional attunement and secure bonding experiences. Therapeutic modalities like Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) and trauma-informed care target the deep-seated relational wounds, differentiating attachment injury from broader relational trauma by focusing on ruptures in attachment bonds specifically. You can foster recovery by engaging in therapies that support emotional regulation, validate your experiences, and promote corrective emotional experiences within safe relational contexts.
Therapeutic Strategies for Relational Trauma
Therapeutic strategies for relational trauma emphasize rebuilding trust and safety within relationships through approaches like trauma-informed care, attachment-based therapy, and somatic experiencing. Your healing process often involves addressing attachment injuries by fostering secure emotional connections and processing past relational disruptions to enhance emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness. Tailored interventions such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and mindfulness techniques support the integration of traumatic memories to restore relational health.
Building Resilient Relationships After Injury and Trauma
Attachment injury, relational trauma, and attachment trauma each impact relational dynamics differently, with attachment injury arising from breaches of trust within close relationships, while relational trauma involves ongoing patterns of emotional harm. Building resilient relationships after injury and trauma requires recognizing emotional wounds, fostering open communication, and cultivating empathy to restore safety and connection. Your commitment to healing and understanding these distinctions enhances emotional resilience and deepens relational bonds.
Infographic: Attachment injury vs relational trauma
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com