Dismissive attachment style avoids intimacy and prioritizes independence, while anxious attachment craves closeness and fears abandonment. Explore deeper insights and strategies for managing these dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
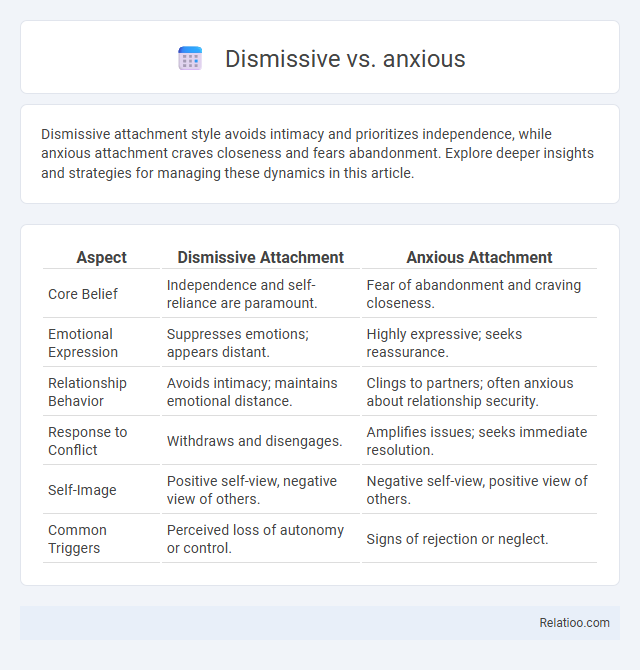
| Aspect | Dismissive Attachment | Anxious Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Independence and self-reliance are paramount. | Fear of abandonment and craving closeness. |
| Emotional Expression | Suppresses emotions; appears distant. | Highly expressive; seeks reassurance. |
| Relationship Behavior | Avoids intimacy; maintains emotional distance. | Clings to partners; often anxious about relationship security. |
| Response to Conflict | Withdraws and disengages. | Amplifies issues; seeks immediate resolution. |
| Self-Image | Positive self-view, negative view of others. | Negative self-view, positive view of others. |
| Common Triggers | Perceived loss of autonomy or control. | Signs of rejection or neglect. |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Dismissive vs Anxious
Understanding attachment styles, specifically dismissive and anxious, reveals how individuals manage intimacy and emotional expression differently. You may notice that dismissive attachment often involves distancing oneself to maintain independence, while anxious attachment manifests through a heightened need for closeness and fear of abandonment. Recognizing these contrasting behaviors is crucial for improving communication and building healthier relationships.
Key Traits of Dismissive Attachment
Dismissive attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and emotional distance, often leading to avoidance of intimacy and reluctance to rely on others. Key traits include a high level of self-sufficiency, suppression of emotions, and discomfort with closeness, which can make forming deep connections challenging. Understanding your dismissive attachment style helps in recognizing patterns that impact relationships and guides you toward healthier emotional expression and connection.
Key Traits of Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a strong desire for closeness, fear of abandonment, and heightened sensitivity to relationship cues, often leading to clinginess and emotional insecurity. Individuals with anxious attachment frequently seek reassurance and struggle with trust, causing fluctuating self-esteem and dependence on their partner's responsiveness. Your awareness of these key traits can improve emotional regulation and foster healthier relationship dynamics.
Childhood Origins of Dismissive and Anxious Styles
Childhood experiences significantly shape dismissive and anxious attachment styles, with dismissive individuals often developing emotional independence due to caregivers' unresponsiveness or rejection, leading to a self-reliant yet distant approach to relationships. Anxious attachment commonly arises from inconsistent caregiving where children receive unpredictable attention, fostering heightened sensitivity to abandonment and a persistent need for reassurance. Understanding your attachment style's childhood roots can enhance self-awareness and improve relational dynamics by addressing unmet emotional needs.
Communication Patterns in Dismissive and Anxious Individuals
Dismissive individuals often communicate by distancing themselves emotionally and minimizing the importance of relationships, creating a pattern of avoiding vulnerability and intimacy. Anxious individuals, in contrast, frequently express their fears and need for reassurance through heightened emotional responses and persistent seeking of validation from others. Your awareness of these distinct communication patterns can help navigate interactions more effectively, fostering understanding and reducing conflict.
Impact on Romantic Relationships
Dismissive attachment often leads to emotional distance in romantic relationships, making it difficult for partners to establish deep intimacy and trust. Anxious attachment triggers constant worry about abandonment, resulting in clinginess and heightened sensitivity to relationship dynamics. Your awareness of these attachment styles can help navigate and improve communication, fostering healthier emotional connections.
Challenges in Friendships and Family Dynamics
Dismissive attachment can create challenges in friendships and family dynamics due to emotional distance and reluctance to share feelings, leading to misunderstandings and feelings of neglect. Anxious attachment often causes you to experience insecurity and fear of abandonment, resulting in clinginess or over-dependence that strains relationships. When dismissive and anxious attachment styles interact, conflicts arise from mismatched emotional needs and communication styles, complicating efforts to maintain trust and closeness.
Common Misunderstandings and Conflicts
Dismissive attachment often leads to misunderstandings with anxious partners due to their contrasting needs for intimacy and independence, causing frequent conflicts rooted in unmet expectations. Anxious individuals may misinterpret dismissive behavior as rejection, escalating tension and communication breakdowns. These dynamics generate a cycle of mistrust and frustration, complicating relationship stability and emotional connection.
How to Cope with a Dismissive or Anxious Partner
Coping with a dismissive or anxious partner requires understanding their attachment styles and communicating effectively to address emotional needs. You can foster trust by practicing patience, validating feelings, and setting clear boundaries that promote security without triggering avoidance or clinginess. Consistent reassurance and mindful listening help bridge gaps between dismissive detachment and anxious clinginess, creating a balanced relationship dynamic.
Steps Toward Healing and Secure Attachment
Steps toward healing dismissive, anxious, and dismissive-anxious attachment styles involve developing self-awareness, practicing emotional regulation, and fostering trust through consistent, empathetic communication. Therapeutic interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and attachment-based therapy can help individuals reframe negative beliefs and increase relational security. Building secure attachment requires gradual vulnerability, validating emotions, and establishing healthy boundaries to promote emotional safety in relationships.
Infographic: Dismissive vs Anxious
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com