Preoccupied attachment is characterized by high anxiety and a strong desire for closeness, while anxious-avoidant attachment involves a mix of anxiety and discomfort with intimacy, often leading to emotional distancing. Explore the differences between these attachment styles and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
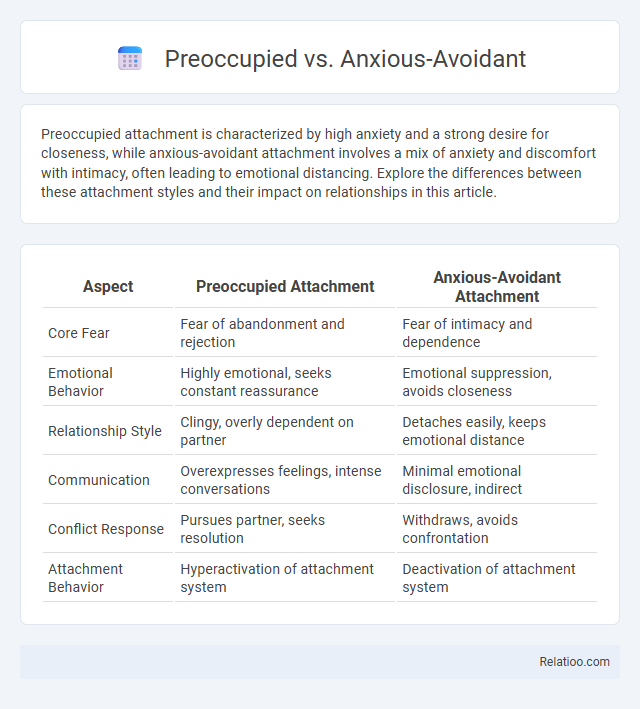
| Aspect | Preoccupied Attachment | Anxious-Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Fear | Fear of abandonment and rejection | Fear of intimacy and dependence |
| Emotional Behavior | Highly emotional, seeks constant reassurance | Emotional suppression, avoids closeness |
| Relationship Style | Clingy, overly dependent on partner | Detaches easily, keeps emotional distance |
| Communication | Overexpresses feelings, intense conversations | Minimal emotional disclosure, indirect |
| Conflict Response | Pursues partner, seeks resolution | Withdraws, avoids confrontation |
| Attachment Behavior | Hyperactivation of attachment system | Deactivation of attachment system |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Preoccupied vs Anxious-Avoidant
Understanding attachment styles reveals key differences between preoccupied and anxious-avoidant types. Preoccupied individuals often seek closeness and validation, feeling insecure when their emotional needs are unmet, while anxious-avoidant individuals suppress their desire for intimacy to maintain independence and avoid vulnerability. Recognizing your attachment style can improve relationship dynamics by fostering awareness of emotional patterns and responses.
Core Characteristics of Preoccupied Attachment
Preoccupied attachment is characterized by a strong desire for closeness combined with high anxiety about relationships, leading to dependency and fear of abandonment. Individuals with preoccupied attachment often have a negative self-view but a positive view of others, causing them to seek constant reassurance. This contrasts with anxious-avoidant attachment, which involves both anxiety and avoidance of intimacy, and dismissive-avoidant attachment, marked by emotional distance and a positive self-view paired with a negative view of others.
Key Traits of Anxious-Avoidant Attachment
Anxious-avoidant attachment is characterized by a conflicting desire for closeness and a fear of intimacy, often leading to emotional distance and difficulty trusting others. You might find it challenging to express your feelings or rely on others due to an intense need for independence combined with underlying anxiety about abandonment. Key traits include suppressing emotional needs, avoiding vulnerability, and fluctuating between seeking connection and pushing others away.
Emotional Patterns in Preoccupied vs Anxious-Avoidant Individuals
Preoccupied individuals exhibit heightened emotional sensitivity, often seeking constant reassurance due to fear of abandonment, which leads to intense emotional expression and dependency in relationships. Anxious-avoidant individuals display conflicting desires for closeness and independence, resulting in emotional suppression and withdrawal to avoid vulnerability despite underlying anxiety. These distinct emotional patterns reveal that preoccupied individuals amplify emotional engagement, while anxious-avoidant individuals minimize emotional exposure, impacting attachment dynamics and relational stability.
Relationship Dynamics and Challenges
Preoccupied attachment often leads to intense desire for closeness but fear of abandonment, creating dependency and insecurity in relationships. Anxious-avoidant attachment combines a craving for intimacy with a simultaneous discomfort with closeness, resulting in push-pull dynamics and emotional distance. These attachment styles challenge healthy communication and trust, as preoccupied individuals seek reassurance while anxious-avoidant partners withdraw, perpetuating cycles of misunderstanding and conflict.
Communication Styles in Both Attachment Types
Preoccupied attachment styles exhibit intense emotional expression and seek constant reassurance, often leading to overly dependent communication patterns. Anxious-avoidant individuals tend to suppress feelings and maintain emotional distance, resulting in minimal self-disclosure and avoidant communication cues. Understanding your communication tendencies within these attachment types can help enhance emotional clarity and relationship dynamics.
Impact on Romantic Relationships
Preoccupied attachment styles often lead to intense emotional dependency, causing instability and frequent conflicts in romantic relationships. Anxious-avoidant individuals tend to suppress their feelings and avoid intimacy, resulting in emotional distance and mistrust between partners. Understanding your attachment style helps improve communication and fosters healthier, more secure bonds in your romantic life.
Coping Mechanisms and Behavioral Differences
Preoccupied attachment involves hyperactivating coping mechanisms where You seek constant reassurance and validation, often exhibiting intense emotional expression and fear of abandonment. Anxious-avoidant attachment manifests through deactivating strategies, characterized by emotional suppression, self-reliance, and avoidance of closeness to reduce vulnerability. Behavioral differences include the preoccupied's tendency to amplify distress signals to engage others, while anxious-avoidant individuals minimize emotional expression and distance themselves to maintain control and independence.
Growth Strategies for Healthier Attachment
Preoccupied attachment is characterized by a heightened need for closeness and fear of abandonment, while anxious-avoidant attachment involves discomfort with intimacy and suppression of emotional needs. Growth strategies for healthier attachment include developing self-awareness, practicing emotional regulation, and engaging in secure communication patterns to build trust and intimacy. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based interventions also support shifting maladaptive attachment styles toward secure attachment.
Therapy and Healing: Moving Toward Secure Attachment
Therapy for preoccupied attachment focuses on developing self-worth and emotional regulation through techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy and emotion-focused therapy, promoting secure attachment patterns. Anxious-avoidant attachment benefits from creating safe relational experiences and increasing emotional openness via experiential and somatic therapies to heal attachment wounds. Moving toward secure attachment involves integrating therapist-guided reflective practices, vulnerability exercises, and consistent relational repair strategies to build trust, emotional safety, and balanced intimacy.
Infographic: Preoccupied vs Anxious-Avoidant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com