Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and reluctance to seek closeness, while disorganized attachment involves inconsistent behaviors with erratic proximity seeking in relationships. Learn more about how these attachment styles impact relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
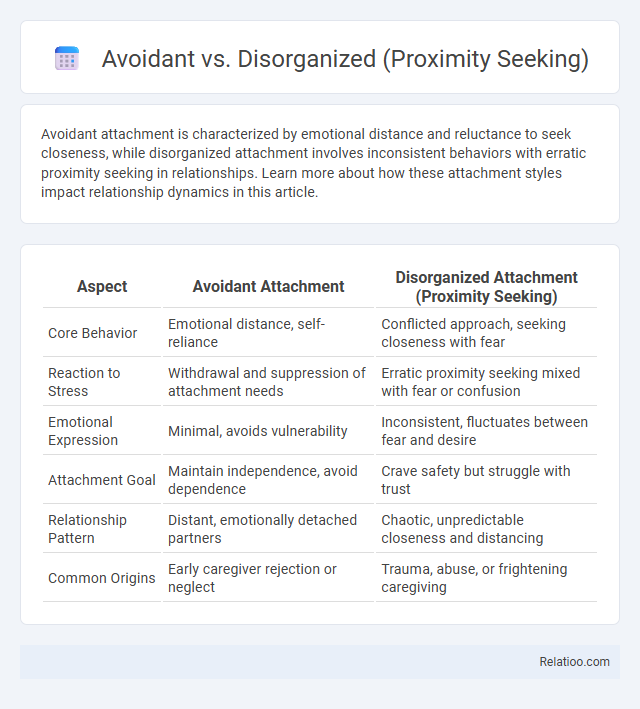
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Disorganized Attachment (Proximity Seeking) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Behavior | Emotional distance, self-reliance | Conflicted approach, seeking closeness with fear |
| Reaction to Stress | Withdrawal and suppression of attachment needs | Erratic proximity seeking mixed with fear or confusion |
| Emotional Expression | Minimal, avoids vulnerability | Inconsistent, fluctuates between fear and desire |
| Attachment Goal | Maintain independence, avoid dependence | Crave safety but struggle with trust |
| Relationship Pattern | Distant, emotionally detached partners | Chaotic, unpredictable closeness and distancing |
| Common Origins | Early caregiver rejection or neglect | Trauma, abuse, or frightening caregiving |
Understanding Attachment Styles: An Overview
Avoidant attachment style involves distancing behaviors and difficulty trusting others, while disorganized attachment features inconsistent proximity-seeking driven by confusion or fear. Proximity-seeking behaviors differ by attachment style, with securely attached individuals seeking comfort reliably, contrasted by avoidant types who resist closeness. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate relationships by recognizing how attachment influences emotional responses and connection needs.
Defining Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by discomfort with closeness and a tendency to maintain emotional distance in relationships, reflecting an underlying fear of dependence or rejection. In contrast, disorganized attachment, especially in proximity seeking behaviors, involves a confusing mix of approach and avoidance toward caregivers, often linked to unresolved trauma or fear. Understanding your attachment style helps clarify how you seek or avoid emotional closeness, impacting your relational patterns and emotional well-being.
Defining Disorganized (Proximity Seeking) Attachment
Disorganized (Proximity Seeking) attachment is characterized by inconsistent and contradictory behaviors toward caregivers, reflecting both a desire for closeness and fear of intimacy due to unresolved trauma or fear. Unlike Avoidant attachment, where proximity seeking is actively suppressed and the individual maintains emotional distance, disorganized attachment involves erratic attempts to seek comfort while simultaneously showing confusion or apprehension. This attachment style often emerges in contexts of abuse or neglect, leading to difficulty in forming secure emotional bonds despite the innate need for proximity.
Key Behavioral Differences: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a consistent suppression of proximity-seeking behaviors, leading individuals to maintain emotional distance and avoid closeness in relationships. In contrast, disorganized attachment displays contradictory proximity-seeking behaviors, where individuals simultaneously seek and fear closeness, resulting in unpredictable and confused responses to attachment figures. The key behavioral difference lies in avoidant individuals' active avoidance of intimacy, whereas disorganized individuals exhibit conflicted and erratic proximity-seeking driven by attachment anxiety and fear.
Emotional Regulation in Each Attachment Style
Avoidant attachment suppresses emotional expression and limits proximity seeking to maintain independence, leading to challenges in emotional regulation and discomfort with closeness. Disorganized attachment combines fear and desire for closeness, causing inconsistent proximity seeking and dysregulated emotions due to unresolved trauma or confusion about caregivers. Understanding your attachment style helps you identify emotional regulation patterns and develop healthier strategies for managing intimacy and stress.
Impact on Romantic and Platonic Relationships
Avoidant attachment often leads to emotional distance and difficulty trusting partners, negatively affecting intimacy in both romantic and platonic relationships. Disorganized attachment, characterized by conflicting desires for closeness and fear of rejection, can cause unpredictability and emotional volatility, creating challenges in maintaining stable connections. In contrast, healthy proximity seeking fosters secure bonds by promoting balanced closeness and emotional availability, enhancing mutual support and relationship satisfaction across all types of interpersonal interactions.
Childhood Roots and Developmental Influences
Avoidant attachment in childhood stems from caregivers' consistent unavailability, leading your child to minimize proximity seeking to manage emotional distance. Disorganized attachment arises from frightening or inconsistent caregiver behavior, causing your child to display confused proximity-seeking marked by approach-avoidance conflicts. Understanding these developmental influences helps you recognize how early relational experiences shape your child's attachment strategies and emotional regulation.
Coping Mechanisms: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment involves coping mechanisms centered on emotional suppression and distancing to minimize vulnerability, leading your relationships to emphasize independence and self-reliance. Disorganized attachment combines conflicting desires for proximity and avoidance, causing inconsistency in seeking closeness and heightened anxiety in attachment behaviors. Proximity seeking in this context reflects the active efforts to gain security and comfort, with coping strategies varying significantly between the avoidant's withdrawal and disorganized's unpredictable engagement.
Long-term Effects on Mental Health
Avoidant attachment often leads to emotional suppression and difficulties in forming close relationships, increasing the risk of anxiety and depression over time. Disorganized attachment, characterized by contradictory proximity-seeking behaviors, is strongly linked to higher incidences of trauma-related disorders and poor emotional regulation. Consistent healthy proximity-seeking in secure attachments supports resilience, emotional well-being, and positive mental health outcomes throughout life.
Therapeutic Approaches for Each Attachment Style
Therapeutic approaches for avoidant attachment focus on building trust and emotional expression through gradual relationship-building and experiential therapies like emotion-focused therapy. Disorganized attachment requires trauma-informed interventions integrating attachment-based therapy and somatic experiencing to address unresolved trauma and foster safety in proximity seeking behaviors. Proximity-seeking attachment benefits from consistent, responsive caregiving modeled in therapy, utilizing mentalization-based treatment to enhance self-regulation and secure relational patterns.
Infographic: Avoidant vs Disorganized (Proximity Seeking)
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com