Anxious attachment is characterized by a strong desire for closeness coupled with fear of abandonment, while fearful avoidant attachment involves ambivalence, both craving intimacy and fearing it simultaneously. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles affect relationship dynamics and improve emotional connections.
Table of Comparison
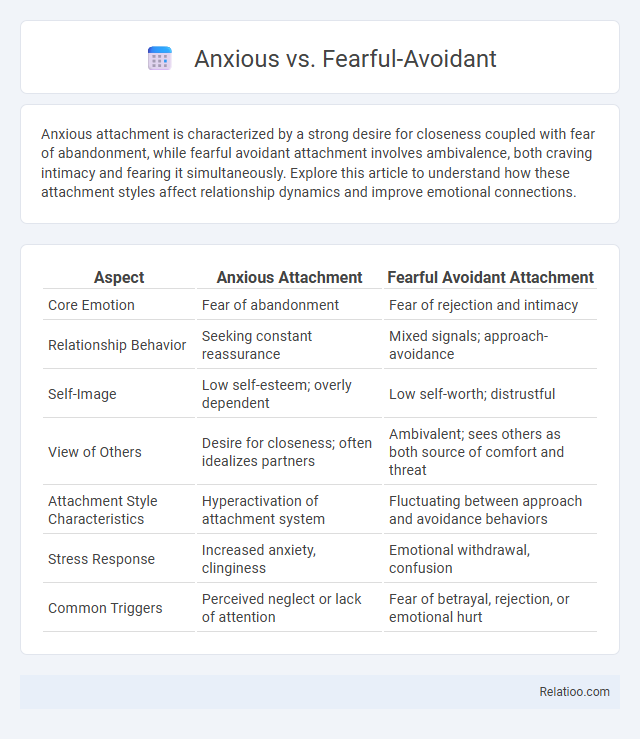
| Aspect | Anxious Attachment | Fearful Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Emotion | Fear of abandonment | Fear of rejection and intimacy |
| Relationship Behavior | Seeking constant reassurance | Mixed signals; approach-avoidance |
| Self-Image | Low self-esteem; overly dependent | Low self-worth; distrustful |
| View of Others | Desire for closeness; often idealizes partners | Ambivalent; sees others as both source of comfort and threat |
| Attachment Style Characteristics | Hyperactivation of attachment system | Fluctuating between approach and avoidance behaviors |
| Stress Response | Increased anxiety, clinginess | Emotional withdrawal, confusion |
| Common Triggers | Perceived neglect or lack of attention | Fear of betrayal, rejection, or emotional hurt |
Understanding Attachment Styles: An Overview
Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep fear of abandonment and a craving for closeness that can lead to clingy or needy behavior. Fearful avoidant attachment merges the desire for intimacy with a significant dread of getting hurt, causing mixed signals and emotional confusion. Understanding your attachment style helps identify patterns in relationships and promotes healthier emotional connections.
Defining Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep-seated fear of abandonment and a constant need for reassurance, often leading to clingy or overly dependent behaviors in relationships. Unlike fearful avoidant attachment, which combines a desire for closeness with a fear of intimacy, anxious attachment primarily focuses on the worry of being unloved or unworthy. Understanding your anxious attachment style can help you recognize patterns of insecurity and work towards building healthier, more secure connections.
What is Fearful Avoidant Attachment?
Fearful avoidant attachment is a complex attachment style characterized by conflicting desires for intimacy and fear of rejection, leading to unpredictable relationship behaviors. Unlike anxious attachment that primarily involves worry about abandonment, fearful avoidant individuals struggle with distrust and emotional avoidance, often rooted in past trauma or inconsistent caregiving. Understanding your fearful avoidant tendencies helps in addressing deep-seated fears and building healthier, more secure connections.
Key Differences Between Anxious and Fearful Avoidant
Anxious attachment is characterized by a strong desire for intimacy and fear of abandonment, leading to clinginess and constant reassurance-seeking, while fearful avoidant attachment combines a fear of intimacy with a fear of rejection, causing ambivalence and emotional withdrawal. Anxious individuals tend to openly express their distress and seek closeness, whereas fearful avoidants experience internal conflict and often suppress their emotions to avoid vulnerability. The key difference lies in the coping mechanism: anxious individuals pursue closeness despite fear, whereas fearful avoidants fluctuate between approaching and avoiding intimacy due to deep-seated mistrust.
Childhood Roots of Anxious and Fearful Avoidant Attachment
Anxious and Fearful Avoidant attachment styles often originate from inconsistent caregiving and childhood emotional neglect, leading to deep-seated insecurity and mistrust in relationships. Children with Anxious attachment typically experience unpredictability in caregiver availability, fostering hypervigilance and a strong desire for reassurance. In contrast, Fearful Avoidant attachment emerges from childhood trauma or abuse, causing conflicting desires for intimacy and fear of abandonment, resulting in emotional withdrawal and confusion in adult relationships.
Manifestations in Adult Relationships
Anxious attachment in adult relationships often manifests as a heightened need for reassurance, intense fear of abandonment, and difficulty trusting partners, leading to clinginess and emotional volatility. Fearful avoidant individuals display a paradoxical desire for intimacy paired with a fear of closeness, resulting in unpredictable push-pull behaviors and emotional withdrawal. You may experience fluctuating emotions and challenges in forming secure bonds when navigating these differing attachment styles.
Emotional Triggers and Responses
Anxious attachment triggers heightened sensitivity to rejection, causing you to seek constant reassurance and intensify emotional responses. Fearful avoidant attachment combines fear of intimacy with mistrust, leading to ambivalence where emotional triggers elicit both desire for closeness and defensive withdrawal. Understanding these emotional triggers and responses helps navigate relationship dynamics by recognizing patterns of anxiety-driven pursuit versus avoidance-driven distancing.
Impact on Communication and Intimacy
Anxious attachment often leads to heightened emotional expressiveness and a craving for reassurance, which can create patterns of clinginess and miscommunication in relationships. Fearful avoidant individuals struggle with trust and vulnerability, frequently oscillating between desire for intimacy and fear of rejection, resulting in mixed signals and emotional withdrawal. These contrasting dynamics significantly impact communication styles and hinder the development of deep, consistent intimacy in romantic partnerships.
Healing and Growth Strategies for Each Style
Anxious attachment involves intense worry about relationships and requires self-soothing techniques and clear communication to foster security. Fearful avoidant individuals benefit from gradual trust-building exercises and therapy focused on trauma resolution to address deep-rooted fears of intimacy. Your healing journey thrives when personalized strategies like mindfulness, emotional regulation, and consistent boundary-setting align with your specific attachment style for optimal growth.
Seeking Help: Therapy and Self-Improvement Paths
Anxious attachment often leads individuals to seek therapy for validation and reassurance, focusing on building self-esteem and emotional regulation. Fearful avoidant attachment requires integrated approaches combining trauma-informed therapy and self-reflection to address underlying fears of abandonment and intimacy. Both attachment styles benefit from cognitive-behavioral strategies and mindfulness practices to improve relational patterns and foster secure connections.
Infographic: Anxious vs Fearful Avoidant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com