Object constancy refers to the ability to maintain an emotional bond with a person despite physical absence or conflict, while emotional permanence is the sustained sense of emotional connection regardless of changing feelings or situations. Discover how mastering these concepts can strengthen your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
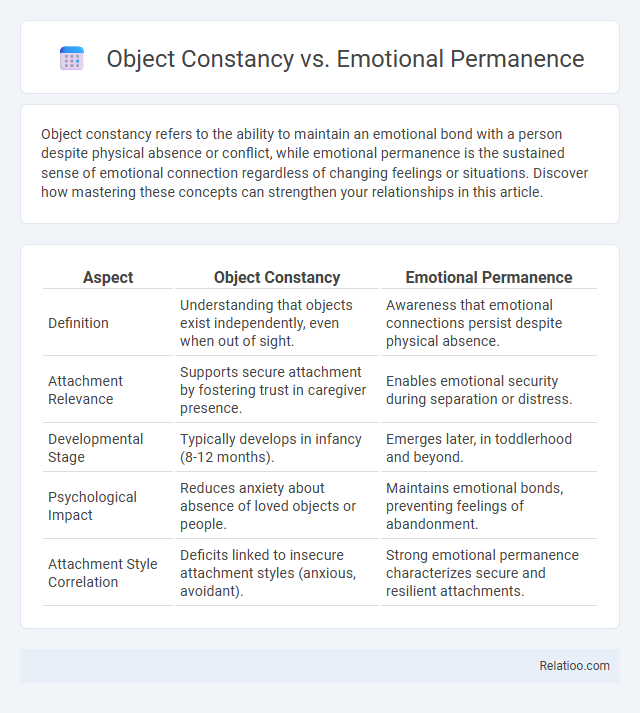
| Aspect | Object Constancy | Emotional Permanence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding that objects exist independently, even when out of sight. | Awareness that emotional connections persist despite physical absence. |
| Attachment Relevance | Supports secure attachment by fostering trust in caregiver presence. | Enables emotional security during separation or distress. |
| Developmental Stage | Typically develops in infancy (8-12 months). | Emerges later, in toddlerhood and beyond. |
| Psychological Impact | Reduces anxiety about absence of loved objects or people. | Maintains emotional bonds, preventing feelings of abandonment. |
| Attachment Style Correlation | Deficits linked to insecure attachment styles (anxious, avoidant). | Strong emotional permanence characterizes secure and resilient attachments. |
Introduction to Object Constancy and Emotional Permanence
Object constancy refers to the developmental ability to maintain an emotional connection and mental representation of a person or object even when they are not physically present. Emotional permanence is closely related, describing the capacity to understand that relationships and feelings persist despite temporary separations or changes in circumstances. Both concepts are crucial for healthy emotional development and secure attachment, enabling individuals to manage separation anxiety and maintain trust in relationships.
Defining Object Constancy: Origins and Psychology
Object constancy, originating from psychoanalytic theory, refers to the cognitive ability to recognize that objects and people remain the same despite changes in perception or emotional state. It develops during early childhood and is crucial for emotional regulation and secure attachment, allowing individuals to maintain a stable internal representation of caregivers or significant others even when not physically present. Object constancy supports emotional permanence, the understanding that feelings and relationships persist over time, reinforcing psychological resilience and interpersonal stability.
What Is Emotional Permanence? Key Concepts Explained
Emotional permanence refers to the understanding that your feelings about someone or something remain constant even when they are not physically present, differing from object constancy which focuses on the continued existence of objects or people outside of immediate perception. This concept is vital in emotional development, allowing you to maintain a stable emotional connection despite absence or change in circumstances. Emotional permanence supports healthy relationships by ensuring that emotional bonds persist beyond momentary interactions or physical presence.
Developmental Stages: How Children Acquire Object Constancy
Children acquire object constancy through developmental stages beginning in infancy when sensory-motor experiences help them understand objects continue to exist even when out of sight. Emotional permanence develops concurrently, allowing you to recognize that others' feelings persist despite their absence or changes in expression. Mastery of object constancy supports secure attachments and emotional regulation by reinforcing your confidence in stable relationships.
Emotional Permanence in Relationships: Why It Matters
Emotional permanence in relationships refers to the ability to understand that emotional connections and feelings remain stable despite physical absence or changes in interaction. This concept is crucial for building trust and security, fostering resilience in the face of conflicts or separations. It differs from object constancy, which emphasizes recognizing that objects exist independently, by specifically focusing on the enduring nature of emotional bonds.
Differences Between Object Constancy and Emotional Permanence
Object constancy refers to the understanding that an object or person continues to exist even when out of sight, while emotional permanence specifically relates to recognizing that your emotional connection to someone remains stable despite physical absence or conflict. The key difference lies in object constancy being about the physical presence or existence of objects or people, whereas emotional permanence focuses on the continuity of feelings and relationships. Mastering emotional permanence supports healthier interpersonal dynamics, as it helps you maintain trust and emotional security regardless of temporary separations.
Object Constancy and Emotional Permanence in Personality Disorders
Object constancy and emotional permanence are crucial psychological constructs influencing personality disorders, especially borderline personality disorder (BPD). Object constancy refers to the ability to maintain an emotional bond with others despite their physical absence or negative interactions, while emotional permanence is the capacity to sustain stable positive feelings toward others over time, even during conflict or separation. Your understanding of these concepts can enhance therapeutic approaches, as deficits in object constancy and emotional permanence often lead to intense fear of abandonment and unstable interpersonal relationships characteristic of many personality disorders.
Impact on Attachment Styles and Emotional Regulation
Object constancy, emotional permanence, and object constancy contribute distinctly to attachment styles and emotional regulation by anchoring your ability to maintain stable relationships despite physical absence or fluctuating emotions. Object constancy involves recognizing that objects or people continue to exist even when out of sight, influencing secure attachments by fostering trust and emotional resilience. Emotional permanence builds on this by sustaining consistent emotional connections, crucial for managing emotional regulation and mitigating anxiety in attachment dynamics.
Practical Strategies to Strengthen Object Constancy and Emotional Permanence
Strengthening object constancy and emotional permanence involves practicing consistent, reliable interactions that reinforce trust and security in relationships. Techniques such as mindfulness exercises, journaling emotional experiences, and openly communicating feelings help individuals maintain a stable internal image of loved ones despite physical absence or emotional fluctuations. Regularly engaging in therapeutic activities like cognitive-behavioral therapy or attachment-based interventions enhances emotional regulation and deepens the understanding of continuous emotional bonds.
Conclusion: Integrating Object Constancy and Emotional Permanence for Emotional Well-being
Integrating object constancy and emotional permanence is essential for emotional well-being, as object constancy refers to the ability to maintain an emotional bond despite physical absence, while emotional permanence involves recognizing consistent emotional states over time. Strengthening both concepts supports resilience in relationships and self-regulation during stress or separation. Therapeutic approaches that enhance these cognitive-emotional skills contribute to improved mental health and interpersonal stability.
Infographic: Object Constancy vs Emotional Permanence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com