Dismissive and Preoccupied Internal Working Models shape attachment styles, with Dismissive individuals valuing independence and avoiding closeness, while Preoccupied individuals seek constant approval and fear abandonment. Explore the nuances of these contrasting attachment patterns and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
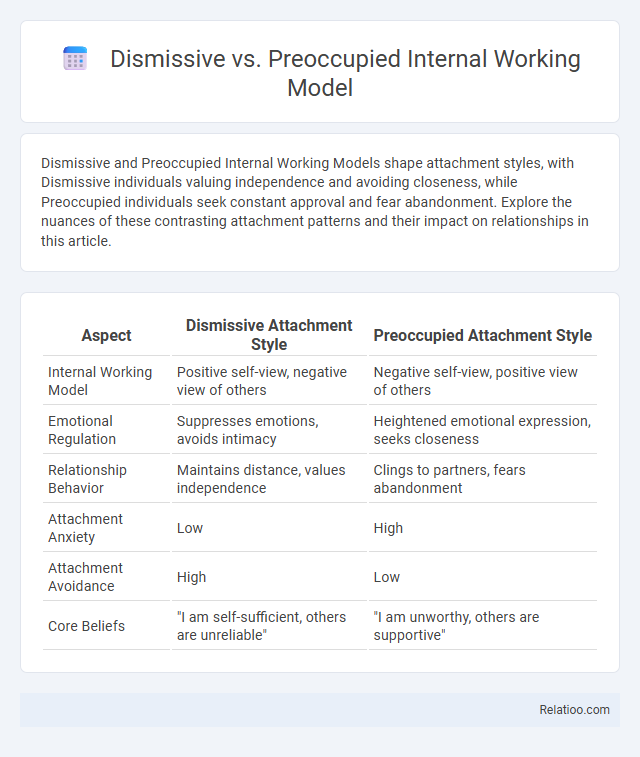
| Aspect | Dismissive Attachment Style | Preoccupied Attachment Style |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Working Model | Positive self-view, negative view of others | Negative self-view, positive view of others |
| Emotional Regulation | Suppresses emotions, avoids intimacy | Heightened emotional expression, seeks closeness |
| Relationship Behavior | Maintains distance, values independence | Clings to partners, fears abandonment |
| Attachment Anxiety | Low | High |
| Attachment Avoidance | High | Low |
| Core Beliefs | "I am self-sufficient, others are unreliable" | "I am unworthy, others are supportive" |
Understanding the Internal Working Model
Understanding the internal working model is essential for recognizing how your attachment style shapes interpersonal relationships and emotional responses. The dismissive internal working model is characterized by a tendency to avoid intimacy and suppress emotions, while the preoccupied internal working model involves heightened anxiety and a strong desire for closeness. Both models influence your expectations and behaviors in relationships, impacting how trust and security are developed over time.
Overview of Attachment Styles
Dismissive and preoccupied attachment styles are key variations within the internal working model, which represents your mental framework for understanding relationships based on early caregiver interactions. The dismissive style is characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance, while the preoccupied style involves anxiety and hypervigilance about relationships. These internal working models influence how you perceive intimacy, trust, and dependence in adult relationships.
What is a Dismissive Internal Working Model?
A Dismissive Internal Working Model reflects a person's tendency to maintain an independent, self-reliant stance while minimizing the importance of close relationships. This model is characterized by suppressing attachment needs and avoiding emotional intimacy, often rooted in early caregiving experiences where caregivers were unavailable or rejecting. Understanding your Dismissive Internal Working Model helps improve awareness of your relational patterns and fosters healthier emotional connections.
Characteristics of Dismissive Individuals
Dismissive individuals in the internal working model exhibit a strong desire for independence and often downplay the importance of close relationships, leading to emotional distance and avoidance of intimacy. Their dismissive attachment style is characterized by self-reliance, reluctance to express vulnerability, and a tendency to suppress feelings to protect themselves from potential rejection. Understanding your own internal working model helps you recognize these traits and foster healthier, more secure emotional connections.
What is a Preoccupied Internal Working Model?
A Preoccupied Internal Working Model is characterized by an anxious attachment style where individuals often doubt their self-worth and seek excessive approval from others, leading to heightened sensitivity in relationships. This model contrasts with the Dismissive Internal Working Model, which involves emotional distancing and a strong sense of self-reliance, often minimizing the importance of close connections. Understanding Your own Preoccupied Internal Working Model can help improve emotional regulation and foster healthier interpersonal dynamics.
Characteristics of Preoccupied Individuals
Preoccupied individuals exhibit an Internal Working Model characterized by anxiety and a strong desire for closeness, often leading to clinginess and fear of abandonment. This contrasts with the dismissive Internal Working Model, where individuals prioritize independence and suppress attachment needs. Understanding Your preoccupied attachment style helps in recognizing patterns of emotional dependency and the need for reassurance in relationships.
Core Differences: Dismissive vs Preoccupied
Dismissive internal working models often involve a deactivation of attachment needs, leading individuals to suppress emotions and maintain emotional distance, whereas preoccupied models are characterized by hyperactivation, resulting in heightened anxiety and a strong desire for closeness. Core differences lie in emotional regulation and attachment behaviors: dismissive individuals emphasize self-reliance and downplay dependency, while preoccupied individuals seek validation and fear abandonment. These contrasting internal frameworks shape distinct patterns in relationships, with dismissive types avoiding intimacy and preoccupied types becoming overly involved or clingy.
Impact on Relationships and Communication
Dismissive and preoccupied internal working models shape your approach to relationships by influencing attachment behaviors and communication patterns. A dismissive model often leads to emotional distance and avoidance of intimacy, while a preoccupied model may cause anxiety and excessive need for reassurance. Understanding these internal working models helps improve your relationship dynamics by fostering healthier communication and emotional regulation.
Psychological Outcomes and Challenges
Dismissive and preoccupied internal working models represent distinct patterns of attachment that influence your emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships. The dismissive model, characterized by avoidance of intimacy and suppression of emotional needs, often leads to challenges in forming close bonds and managing vulnerability. In contrast, the preoccupied model involves heightened anxiety and dependence on others for validation, resulting in difficulties with trust and emotional stability, which can impact overall psychological well-being.
Strategies for Growth and Healing
Dismissive internal working models often involve emotional distancing and self-reliance, requiring strategies that encourage vulnerability and trust-building to foster emotional intimacy. Preoccupied internal working models are characterized by anxiety and fear of abandonment, benefiting from approaches that promote self-soothing, mindfulness, and secure attachment development. Effective growth and healing strategies integrate cognitive-behavioral techniques, emotional regulation skills, and consistent relational experiences to reshape internal working models toward secure attachment patterns.
Infographic: Dismissive vs Preoccupied Internal Working Model
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com