Avoidant attachment leads individuals to suppress emotional needs and maintain emotional distance, while defensive distancing involves creating space to protect oneself from perceived threats or discomfort. Explore the nuances of these behaviors and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
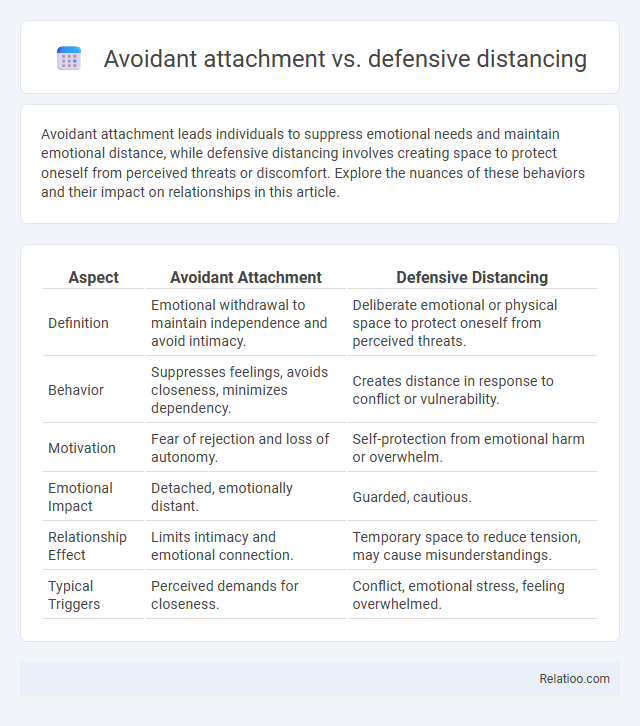
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Defensive Distancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional withdrawal to maintain independence and avoid intimacy. | Deliberate emotional or physical space to protect oneself from perceived threats. |
| Behavior | Suppresses feelings, avoids closeness, minimizes dependency. | Creates distance in response to conflict or vulnerability. |
| Motivation | Fear of rejection and loss of autonomy. | Self-protection from emotional harm or overwhelm. |
| Emotional Impact | Detached, emotionally distant. | Guarded, cautious. |
| Relationship Effect | Limits intimacy and emotional connection. | Temporary space to reduce tension, may cause misunderstandings. |
| Typical Triggers | Perceived demands for closeness. | Conflict, emotional stress, feeling overwhelmed. |
Understanding Avoidant Attachment: Core Characteristics
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a deep-seated fear of intimacy and a tendency to suppress emotional needs, leading to emotional withdrawal. Defensive distancing occurs when individuals consciously or unconsciously create physical or emotional space to protect themselves from perceived threats in relationships. Understanding your avoidant attachment involves recognizing patterns of detachment and defensiveness that hinder genuine emotional connection and addressing these to foster healthier bonds.
Defining Defensive Distancing in Relationships
Defensive distancing in relationships refers to the behavior where individuals create emotional or physical space to protect themselves from perceived threats or vulnerability. Unlike avoidant attachment, which stems from deep-seated fears of intimacy and abandonment, defensive distancing is often a conscious strategy to manage conflict or stress within the relationship. Understanding your patterns of defensive distancing can help identify the underlying causes and promote healthier emotional connection and communication.
Key Differences Between Avoidant Attachment and Defensive Distancing
Avoidant attachment is a long-term relational style characterized by discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to suppress emotional needs, often rooted in early caregiving experiences. Defensive distancing is a behavioral response to perceived threats in relationships, where individuals create emotional or physical space to protect themselves from vulnerability. Key differences lie in avoidant attachment being a stable attachment pattern influencing overall relational expectations, while defensive distancing is a situational coping mechanism triggered by specific stressors or conflicts.
Origins and Developmental Roots of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment originates from early relational experiences where caregivers are consistently unresponsive or emotionally unavailable, causing children to suppress attachment needs to avoid rejection. Defensive distancing develops as a protective strategy in response to perceived emotional threats or inconsistent caregiving, leading individuals to maintain emotional distance to regulate vulnerability. The developmental roots of avoidant attachment are entrenched in childhood interactions that discourage emotional expression, fostering a self-reliant, emotionally detached coping style to manage relational stress.
Psychological Triggers Behind Defensive Distancing
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional withdrawal and discomfort with closeness, often rooted in early caregiving experiences that discouraged dependency. Defensive distancing operates as a coping mechanism triggered by perceived threats to autonomy or fear of vulnerability, leading individuals to create emotional or physical space. Psychological triggers behind defensive distancing include anxiety over rejection, fear of engulfment, and unresolved trauma, which activate protective behaviors to maintain self-preservation.
Impact on Intimacy and Emotional Connection
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a deep-seated fear of intimacy and vulnerability, leading individuals to emotionally withdraw and maintain distance to protect themselves from potential rejection. Defensive distancing involves conscious or unconscious behaviors aimed at creating emotional space to avoid discomfort, which significantly disrupts trust and intimacy in relationships. Both patterns erode emotional connection by limiting open communication and fostering separation, making it challenging to establish authentic closeness and mutual understanding.
Signs to Identify Avoidant Attachment Patterns
Avoidant attachment patterns often manifest through emotional withdrawal, reluctance to share feelings, and discomfort with closeness, distinguishing them from general defensive distancing behaviors that may stem from situational stress. Signs include consistently suppressing emotional needs, minimizing the importance of relationships, and maintaining psychological distance to protect against perceived rejection or vulnerability. Recognizing these signs helps You address avoidant attachment and foster healthier, more connected relationships.
Recognizing Defensive Distancing Behaviors
Recognizing defensive distancing behaviors requires understanding subtle signs like emotional withdrawal, reluctance to engage in deep conversations, or creating physical space during interactions. Unlike avoidant attachment, which stems from deep-seated fears of intimacy, defensive distancing is a conscious strategy to protect oneself from perceived threats or emotional pain. Your awareness of these behaviors helps in addressing relationship challenges by fostering open communication and emotional safety.
Therapeutic Approaches for Healing Emotional Distance
Avoidant attachment often manifests as emotional withdrawal to protect against vulnerability, requiring therapeutic approaches that foster safe connection and emotional regulation skills. Defensive distancing, whether a symptom or behavior pattern, benefits from strategies emphasizing mindfulness, cognitive restructuring, and building trust within the therapeutic relationship. Your healing journey may involve integrating attachment-based therapy and Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) to effectively reduce emotional distance and promote relational intimacy.
Building Healthy Connections: Strategies for Change
Avoidant attachment often manifests as emotional withdrawal to protect against vulnerability, while defensive distancing involves conscious or unconscious efforts to maintain space in relationships to reduce perceived threats. Building healthy connections requires recognizing these patterns and implementing strategies like consistent communication, emotional regulation, and fostering trust through empathy and validation. Establishing secure attachment promotes intimacy and resilience by encouraging openness and reducing fears of rejection or abandonment.
Infographic: Avoidant attachment vs defensive distancing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com