Abandonment wounds stem from early experiences of loss or neglect, causing fear of being left alone, while attachment trauma arises from disrupted or insecure bonds, impacting emotional regulation and trust. Discover the key differences and healing approaches in this article.
Table of Comparison
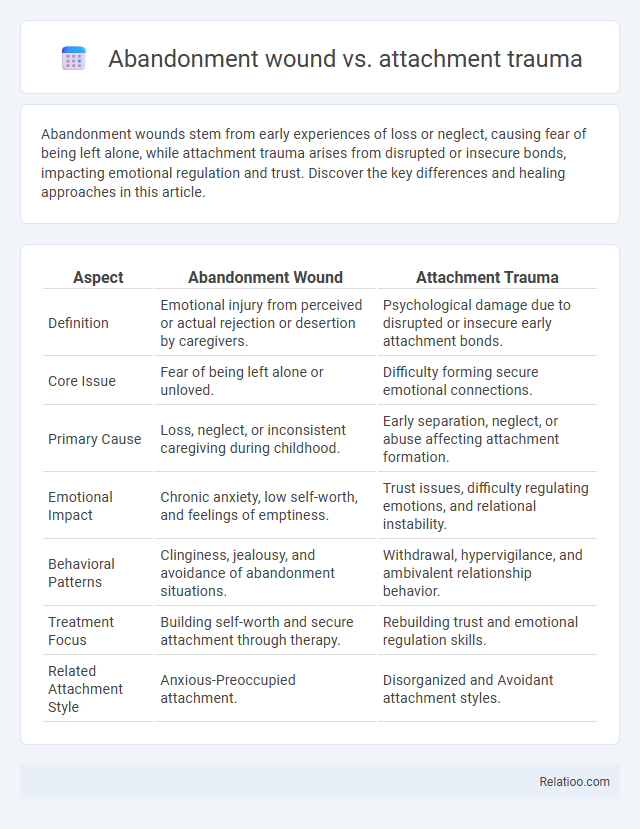
| Aspect | Abandonment Wound | Attachment Trauma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional injury from perceived or actual rejection or desertion by caregivers. | Psychological damage due to disrupted or insecure early attachment bonds. |
| Core Issue | Fear of being left alone or unloved. | Difficulty forming secure emotional connections. |
| Primary Cause | Loss, neglect, or inconsistent caregiving during childhood. | Early separation, neglect, or abuse affecting attachment formation. |
| Emotional Impact | Chronic anxiety, low self-worth, and feelings of emptiness. | Trust issues, difficulty regulating emotions, and relational instability. |
| Behavioral Patterns | Clinginess, jealousy, and avoidance of abandonment situations. | Withdrawal, hypervigilance, and ambivalent relationship behavior. |
| Treatment Focus | Building self-worth and secure attachment through therapy. | Rebuilding trust and emotional regulation skills. |
| Related Attachment Style | Anxious-Preoccupied attachment. | Disorganized and Avoidant attachment styles. |
Understanding Abandonment Wound: Definition and Origins
An abandonment wound refers to deep emotional pain stemming from early experiences of neglect or rejection, often rooted in childhood. It differs from attachment trauma, which involves disruptions in the bond between a child and caregiver, affecting the ability to form secure relationships. Understanding abandonment wounds requires recognizing their origins in unmet needs during critical developmental stages and their impact on emotional regulation and interpersonal trust.
What Is Attachment Trauma? Key Concepts Explained
Attachment trauma occurs when early relationships with primary caregivers fail to provide consistent emotional security, leading to lasting impacts on a person's ability to form healthy connections. Unlike abandonment wounds, which stem specifically from physical or emotional loss, attachment trauma encompasses a broader range of disruptions in bonding, including neglect, inconsistency, or abuse during critical developmental periods. Understanding attachment trauma involves recognizing patterns of mistrust, emotional dysregulation, and difficulty with intimacy that arise from unmet attachment needs in childhood.
Core Differences Between Abandonment Wound and Attachment Trauma
Abandonment wound refers to the deep emotional pain caused by the loss or rejection from a significant person, often leading to feelings of unworthiness and fear of being left alone. Attachment trauma stems from disrupted or insecure bonds during early relationships, impacting trust, emotional regulation, and relational patterns throughout life. Unlike attachment trauma, which centers on foundational relationship insecurities, abandonment wound specifically highlights the trauma of perceived or actual loss and its resulting emotional void.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Abandonment Wound
Common signs and symptoms of abandonment wound include intense feelings of rejection, chronic insecurity, fear of being alone, and difficulty trusting others. Emotional triggers often provoke overwhelming anxiety, sadness, and anger linked to past experiences of neglect or loss. These symptoms may overlap with attachment trauma, which involves disrupted emotional bonds, yet abandonment wounds specifically stem from perceived or actual loss and lack of emotional support during critical developmental periods.
Recognizing Attachment Trauma in Childhood and Adulthood
Recognizing attachment trauma involves identifying patterns of emotional neglect, inconsistent caregiving, and difficulty forming secure relationships that often stem from early childhood experiences. Unlike abandonment wounds that highlight feelings of rejection and loss, attachment trauma deeply impacts your ability to trust and connect with others across both childhood and adulthood. Awareness of these distinctions helps in addressing emotional healing and building healthier relational patterns.
Psychological Impact of Abandonment vs Attachment Disruptions
Abandonment wounds result in deep-seated fears of rejection and chronic feelings of unworthiness, profoundly affecting self-esteem and emotional regulation. Attachment trauma, stemming from inconsistent or neglectful caregiving, disrupts the formation of secure bonds, leading to difficulties in trust, intimacy, and emotional attunement. Both abandonment wounds and attachment disruptions trigger heightened anxiety, difficulty in emotional resilience, and may contribute to mood disorders, but attachment trauma primarily impairs the ability to form and maintain healthy interpersonal relationships.
How Abandonment Wounds Affect Relationships
Abandonment wounds create deep emotional scars that impair trust and intimacy, often causing individuals to fear rejection and excessive dependence in relationships. Attachment trauma, stemming from inconsistent or neglectful caregiving, disrupts secure bonding patterns and leads to anxiety or avoidance in relational dynamics. These wounds collectively foster challenges in forming healthy, stable connections by triggering insecurity, emotional withdrawal, and difficulty managing vulnerability within partnerships.
Attachment Trauma: Long-term Effects on Emotional Health
Attachment trauma profoundly impacts emotional health by disrupting the ability to form secure relationships and regulate emotions. Individuals with attachment trauma often experience chronic anxiety, depression, and difficulty trusting others, stemming from early relational wounds. Unlike abandonment wounds, which relate specifically to loss or rejection, attachment trauma encompasses broader relational dysfunction that affects long-term emotional stability and interpersonal connections.
Healing Strategies for Abandonment and Attachment Trauma
Healing strategies for abandonment wounds and attachment trauma emphasize establishing secure, consistent relationships and practicing self-compassion. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and somatic experiencing help process traumatic memories and regulate emotional responses. Building emotional resilience through mindfulness, boundaries, and support networks is essential for recovery and fostering healthy attachments.
When to Seek Professional Help: Therapy Options and Resources
Recognizing the differences between abandonment wounds, attachment trauma, and their overlapping symptoms is crucial when deciding to seek professional help. Therapy options such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), attachment-based therapy, and trauma-focused approaches can provide targeted support tailored to your specific emotional needs. Accessing resources like licensed therapists, support groups, and online counseling platforms ensures you receive appropriate care to heal and strengthen your emotional well-being.
Infographic: Abandonment wound vs Attachment trauma
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com