Attachment injury occurs when a trusted partner breaches expectations, causing emotional wounds that challenge the bond, whereas abandonment involves the partner physically or emotionally leaving the relationship, creating deep feelings of loss and insecurity. Explore this article to understand the distinctions between attachment injury and abandonment and their impact on relationship healing.
Table of Comparison
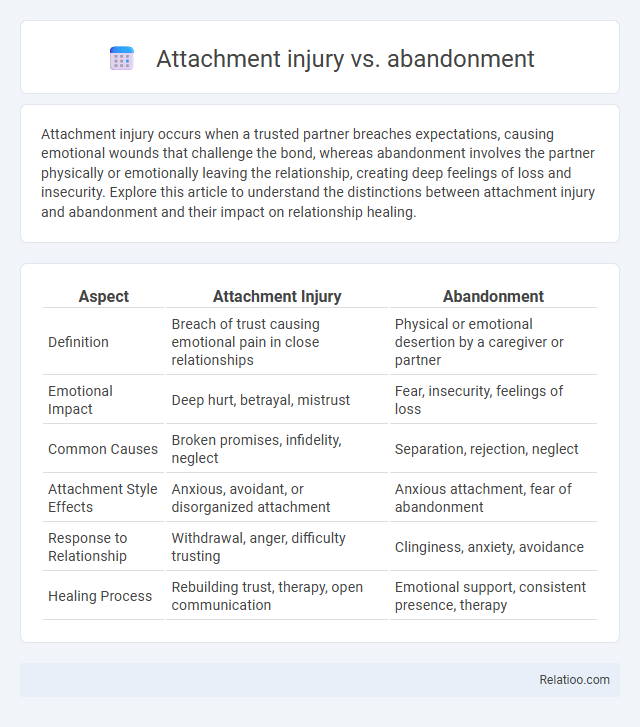
| Aspect | Attachment Injury | Abandonment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breach of trust causing emotional pain in close relationships | Physical or emotional desertion by a caregiver or partner |
| Emotional Impact | Deep hurt, betrayal, mistrust | Fear, insecurity, feelings of loss |
| Common Causes | Broken promises, infidelity, neglect | Separation, rejection, neglect |
| Attachment Style Effects | Anxious, avoidant, or disorganized attachment | Anxious attachment, fear of abandonment |
| Response to Relationship | Withdrawal, anger, difficulty trusting | Clinginess, anxiety, avoidance |
| Healing Process | Rebuilding trust, therapy, open communication | Emotional support, consistent presence, therapy |
Understanding Attachment Injury: Definition and Causes
Attachment injury refers to a deeply distressing event that damages the bond between individuals, commonly occurring in close relationships such as parent-child or romantic partnerships. It differs from abandonment, which involves physical or emotional neglect characterized by leaving someone behind or ignoring their needs, whereas attachment injury specifically pertains to breaches of trust and betrayal within the relationship. Understanding attachment injury involves recognizing its causes, including betrayal, broken promises, or emotional unavailability, which disrupt the sense of safety and security essential for healthy attachment formation.
What is Abandonment in Relationships?
Abandonment in relationships refers to the fear or experience of being left alone or rejected by a significant other, leading to feelings of insecurity and emotional distress. Attachment injury involves a breach of trust or safety within a close relationship, often stemming from perceived neglect or betrayal, which damages the emotional bond. Unlike general abandonment, attachment injury specifically highlights the trauma caused by disrupted attachment patterns, which can result from abandonment but also includes other forms of emotional harm.
Key Differences Between Attachment Injury and Abandonment
Attachment injury involves a breach of trust or betrayal within a close relationship, such as dishonesty or neglect, resulting in emotional pain and relational damage. Abandonment refers specifically to the experience of being left or deserted by a significant attachment figure, often creating feelings of rejection and insecurity. Understanding these key differences helps you identify whether the core issue stems from a broken trust (attachment injury) or the trauma of being left behind (abandonment), guiding more effective healing approaches.
Signs and Symptoms of Attachment Injury
Signs and symptoms of attachment injury often include deep feelings of betrayal, emotional withdrawal, difficulty trusting others, and heightened anxiety or depression stemming from a breach of secure attachment. Unlike abandonment, which primarily triggers catastrophic fear of loss and separation anxiety, attachment injury specifically involves a violation of trust within an established relational bond, leading to chronic relational difficulties and emotional dysregulation. Distinguishing attachment injury from abandonment is crucial as the former is marked by persistent relational pain and impaired emotional connection rather than solely absence or neglect.
Emotional Impact of Abandonment on Individuals
Abandonment triggers deep emotional wounds, often leading to feelings of worthlessness, chronic anxiety, and difficulties in forming secure attachments. Unlike general attachment injury, which encompasses betrayal or neglect within relationships, abandonment specifically involves the intense fear of being left alone or rejected, profoundly affecting emotional stability. This emotional impact can result in long-term struggles with trust, intimacy, and self-esteem, significantly disrupting personal and interpersonal functioning.
Attachment Injury vs Abandonment: Psychological Effects
Attachment injury often results from perceived betrayal or neglect by a primary caregiver, leading to deep emotional wounds that impact trust and relationship security. Abandonment specifically refers to physical or emotional desertion, causing feelings of worthlessness and intense fear of rejection. Your psychological well-being can be significantly affected by attachment injuries, as they disrupt your ability to form secure bonds and may provoke chronic anxiety and difficulty in emotional regulation.
Healing from Attachment Injury: Effective Strategies
Healing from attachment injury involves rebuilding trust and fostering secure emotional bonds through consistent, empathetic communication and professional therapy. Distinguishing attachment injury from abandonment is crucial, as attachment injury arises from specific relational breaches rather than complete loss, requiring targeted interventions like Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) to repair attachment wounds. Strategies such as validating emotions, practicing vulnerability, and engaging in trauma-informed counseling promote recovery and resilience in healing attachment injuries.
Coping with Abandonment: Tools for Recovery
Coping with abandonment requires understanding the distinct impacts of attachment injury versus abandonment trauma, as attachment injuries specifically involve breaches of trust within close relationships that can intensify feelings of rejection. Tools for recovery include cultivating self-compassion, establishing secure boundaries, and engaging in therapeutic techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) to process and heal emotional wounds. Developing a strong support network and practicing mindfulness can further reinforce emotional resilience and foster healthier attachment patterns.
The Role of Childhood in Attachment Injury and Abandonment
Childhood experiences play a crucial role in shaping attachment injuries and abandonment issues, often stemming from inconsistent or unavailable caregiving during critical developmental stages. Attachment injuries occur when a child's emotional needs for safety and connection are unmet, leading to long-term difficulties in trust and relationship stability. In contrast, abandonment focuses more on the experience of loss or perceived rejection, which can trigger profound feelings of insecurity and fear of future separation in adulthood.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapy Options for Healing
Attachment injury involves deep emotional wounds from betrayal or broken trust in relationships, while abandonment trauma stems from physical or emotional loss of a caregiver; both require targeted therapeutic approaches for healing. Therapies such as Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT), Attachment-Based Therapy, and Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT) are effective in addressing attachment injuries and abandonment-related trauma. Seeking professional help from licensed therapists specializing in attachment and trauma can foster emotional regulation, rebuild trust, and promote secure relational bonds.
Infographic: Attachment injury vs abandonment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com