Attachment anxiety involves fear of abandonment and excessive need for closeness in relationships, while separation anxiety centers on distress when separated from significant others. Explore this article to understand key differences and strategies for managing both anxieties.
Table of Comparison
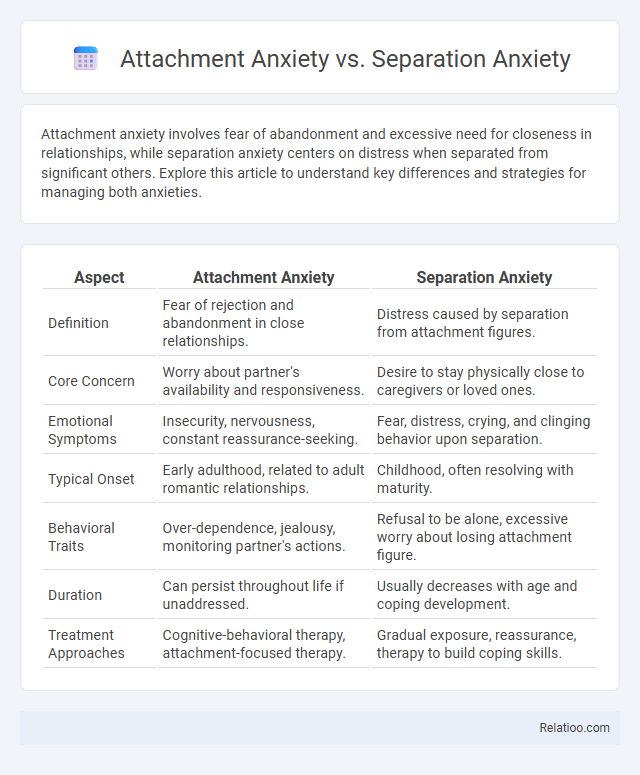
| Aspect | Attachment Anxiety | Separation Anxiety |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fear of rejection and abandonment in close relationships. | Distress caused by separation from attachment figures. |
| Core Concern | Worry about partner's availability and responsiveness. | Desire to stay physically close to caregivers or loved ones. |
| Emotional Symptoms | Insecurity, nervousness, constant reassurance-seeking. | Fear, distress, crying, and clinging behavior upon separation. |
| Typical Onset | Early adulthood, related to adult romantic relationships. | Childhood, often resolving with maturity. |
| Behavioral Traits | Over-dependence, jealousy, monitoring partner's actions. | Refusal to be alone, excessive worry about losing attachment figure. |
| Duration | Can persist throughout life if unaddressed. | Usually decreases with age and coping development. |
| Treatment Approaches | Cognitive-behavioral therapy, attachment-focused therapy. | Gradual exposure, reassurance, therapy to build coping skills. |
Understanding Attachment Anxiety
Attachment anxiety involves intense fear of rejection and abandonment within close relationships, often originating from inconsistent caregiving in early life. Separation anxiety primarily affects children and manifests as excessive distress during physical separation from attachment figures, potentially leading to clinginess and behavioral issues. Understanding attachment anxiety requires recognizing the emotional hypervigilance and need for reassurance that disrupt interpersonal stability and emotional regulation.
What Is Separation Anxiety?
Separation anxiety is a psychological condition characterized by excessive fear or distress when an individual is separated from a primary attachment figure, often a parent or caregiver. Unlike attachment anxiety, which involves constant worry about the availability and responsiveness of attachment figures, separation anxiety specifically triggers intense emotional reactions during actual or anticipated separation. It commonly affects children but can persist into adulthood, impacting daily functioning and emotional well-being.
Key Differences Between Attachment and Separation Anxiety
Attachment anxiety primarily involves intense fear of rejection or abandonment within close relationships, often stemming from inconsistent caregiving during early development. Separation anxiety specifically refers to excessive distress experienced when apart from a primary attachment figure, commonly manifesting in childhood but also in adults. Key differences include attachment anxiety's focus on relationship insecurity and fear of abandonment, while separation anxiety centers on distress triggered solely by physical separation.
Common Causes of Attachment Anxiety
Attachment anxiety commonly stems from inconsistent caregiving during early childhood, such as unpredictable parental responses or emotional unavailability. Your brain develops heightened sensitivity to rejection and abandonment due to these early relational disruptions, differentiating it from separation anxiety which is primarily fear of being apart. Understanding these common causes helps in addressing attachment anxiety distinctively from separation anxiety or general separation anxiety disorder.
Triggers of Separation Anxiety
Separation anxiety is primarily triggered by situations where individuals face the prospect of being physically or emotionally apart from attachment figures, such as caregivers or close family members, causing significant distress. Common triggers include transitions like starting school, moving homes, or the absence of a parent due to work or travel, amplifying feelings of vulnerability and insecurity. Unlike attachment anxiety, which stems from inconsistent caregiving and fear of rejection, separation anxiety specifically revolves around the stress experienced when separation occurs or is anticipated.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Attachment anxiety manifests through excessive worry about being abandoned, clinginess, and difficulty trusting others, often leading to emotional distress in relationships. Separation anxiety is characterized by intense fear or distress when anticipating or experiencing separation from a primary attachment figure, commonly seen in children but also in adults. Key signs to watch for include persistent crying, tantrums, sleep disturbances, physical symptoms like headaches or stomach aches, and difficulty concentrating or engaging in daily activities.
Impact on Daily Life and Relationships
Attachment anxiety triggers intense fear of rejection, leading Your relationships to suffer from clinginess and emotional dependency. Separation anxiety causes distress when away from a specific person or place, disrupting daily routines and limiting social activities. Distinguishing between attachment anxiety and separation anxiety helps target treatment, improving emotional stability and strengthening interpersonal connections.
Effective Coping Strategies
Attachment anxiety involves intense fear of rejection and abandonment in close relationships, while separation anxiety primarily centers on distress during actual or anticipated separation from attachment figures. Effective coping strategies for attachment anxiety include building secure relationships through communication and therapy like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), fostering self-compassion, and practicing mindfulness to regulate emotional responses. Separation anxiety benefits from gradual exposure to separation events, establishing routines for reassurance, and cognitive restructuring techniques to challenge catastrophic thoughts related to separation.
When to Seek Professional Help
Attachment anxiety involves intense fear of abandonment in relationships, while separation anxiety centers on distress when apart from loved ones, often seen in children. Separation anxiety disorder, a more severe form, can disrupt daily functioning and persist beyond typical developmental stages. You should seek professional help if anxiety causes significant impairment, lasts longer than four weeks, or leads to avoidance of essential activities.
Tips for Supporting Loved Ones with Anxiety
Supporting loved ones with attachment anxiety involves offering consistent reassurance and validating their feelings to reduce fears of abandonment. For separation anxiety, establishing predictable routines and gradual exposure to time apart helps build confidence and lessen distress. Encouraging open communication and professional therapy can benefit both conditions by fostering coping skills and emotional resilience.
Infographic: Attachment Anxiety vs Separation Anxiety
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com