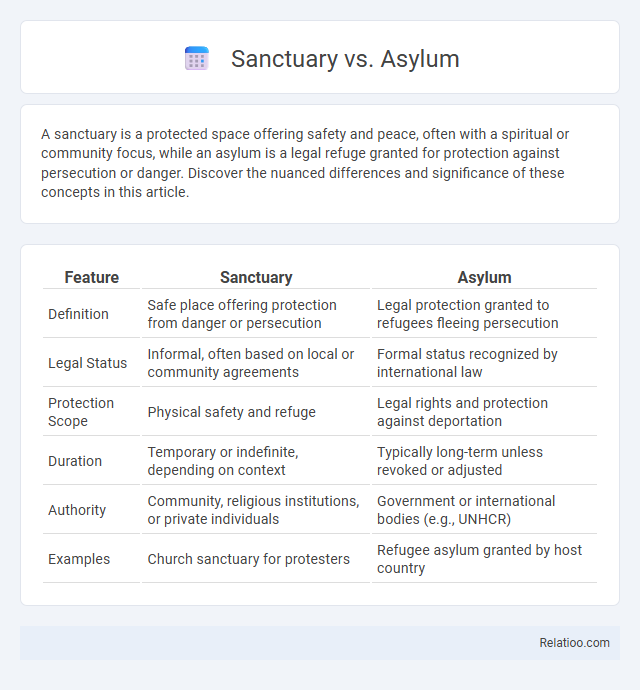
A sanctuary is a protected space offering safety and peace, often with a spiritual or community focus, while an asylum is a legal refuge granted for protection against persecution or danger. Discover the nuanced differences and significance of these concepts in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sanctuary | Asylum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Safe place offering protection from danger or persecution | Legal protection granted to refugees fleeing persecution |
| Legal Status | Informal, often based on local or community agreements | Formal status recognized by international law |
| Protection Scope | Physical safety and refuge | Legal rights and protection against deportation |
| Duration | Temporary or indefinite, depending on context | Typically long-term unless revoked or adjusted |
| Authority | Community, religious institutions, or private individuals | Government or international bodies (e.g., UNHCR) |
| Examples | Church sanctuary for protesters | Refugee asylum granted by host country |
Introduction: Defining Sanctuary and Asylum
Sanctuary refers to a place of refuge offering safety and protection, often within religious or community settings, whereas asylum is a formal legal protection granted by a country to individuals fleeing persecution or danger. Understanding the distinctions helps clarify your rights and the procedures involved in seeking safety. Both concepts prioritize safeguarding individuals, but asylum involves official governmental recognition and processes.
Historical Origins of Sanctuary
Sanctuary, asylum, and refuge all stem from ancient practices offering protection but differ in historical context and legal implications. Sanctuary originated in religious settings, notably within medieval churches, where fugitives sought safety based on spiritual authority. Your understanding of these terms is enriched by recognizing that asylum is a formal, legal protection granted by states, while sanctuary has roots in customary and ecclesiastical law.
Evolution of Asylum in International Law
The evolution of asylum in international law reflects a complex interplay between state sovereignty and human rights protections, developing from ancient customs to codified rights under instruments like the 1951 Refugee Convention. Asylum traditionally provides protection within a state's territory, while sanctuary historically referred to sacred spaces offering refuge, now largely symbolic. International law increasingly emphasizes asylum as a legal right to protect individuals fleeing persecution, balancing obligations under customary law and treaty frameworks.
Key Legal Distinctions: Sanctuary vs. Asylum
Asylum is a formal legal protection granted to individuals who meet specific criteria for persecution based on race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group, whereas sanctuary refers to the physical space or institution that offers refuge often without formal legal status. Sanctuary does not provide legal rights or immigration status but serves as a safe haven from detention or deportation, contrasting with asylum's official recognition through government agencies. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating immigration law, where asylum seekers must prove a credible fear of persecution, while sanctuary advocates prioritize immediate protection and community support.
Sanctuary in Modern Social Movements
Sanctuary in modern social movements represents a proactive community effort to protect marginalized individuals, especially undocumented immigrants, from legal persecution. Unlike asylum, which is a formal legal protection granted by governments to refugees fleeing persecution, sanctuary often operates through grassroots organizations and faith-based groups providing safe spaces. Your involvement in sanctuary movements helps uphold human rights by challenging restrictive immigration policies and promoting social justice.
Asylum: Legal Process and Requirements
Asylum offers a legal protection for individuals fleeing persecution based on race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group, requiring you to demonstrate a credible fear of harm if returned to your home country. The asylum process involves submitting Form I-589 within one year of arrival in the United States, attending a credible fear interview, and potentially undergoing an asylum hearing before an immigration judge. Unlike sanctuary, which refers to policies or places offering shelter without legal status, and sanctuary cities that limit cooperation with immigration enforcement, asylum provides a formal path to legal residence and protection under U.S. law.
Governmental Roles in Sanctuary and Asylum
Sanctuaries offer protection primarily through local government or community efforts, often limiting cooperation with federal immigration enforcement to shield undocumented immigrants. Asylum, in contrast, is a formal legal status granted by national governments based on international law, requiring applicants to prove persecution risk in their home countries. Governmental roles in asylum include processing applications and providing legal protections, while sanctuary policies involve local authorities intentionally restricting enforcement actions to create safe spaces for vulnerable populations.
Impact on Refugees and Immigrants
Sanctuary offers physical protection and community support to refugees and immigrants, fostering a sense of safety and belonging. Asylum is a legal status granted by governments that provides refugees with the right to reside and work safely, impacting their long-term security and access to services. Your experience as a refugee or immigrant depends heavily on the availability and recognition of these protections, which influence your legal rights, social integration, and overall well-being.
Controversies and Challenges
Sanctuary, asylum, and refuge represent critical legal and moral concepts for protecting individuals fleeing persecution, yet each faces distinct controversies and challenges regarding enforcement, eligibility, and international cooperation. You encounter legal debates when determining the validity of claims under asylum law, while sanctuary policies often spark political disputes over municipal authority versus federal immigration enforcement. These challenges are compounded by fluctuating international standards and resource constraints that complicate the protection of vulnerable populations seeking safety.
Future Trends in Sanctuary and Asylum Policies
Future trends in sanctuary and asylum policies emphasize increasing digital integration and data-driven decision-making to streamline application processes and enhance security. Governments are adopting AI-powered tools to predict migration flows and assess risks, optimizing resource allocation and accelerating case evaluations. Your understanding of these advancements can prepare you for more efficient and responsive humanitarian protections worldwide.
Infographic: Sanctuary vs Asylum
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com