Admiration recognizes exceptional qualities or achievements, while appreciation values the inherent worth and everyday contributions of a person. Discover deeper insights into how admiration and appreciation shape relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
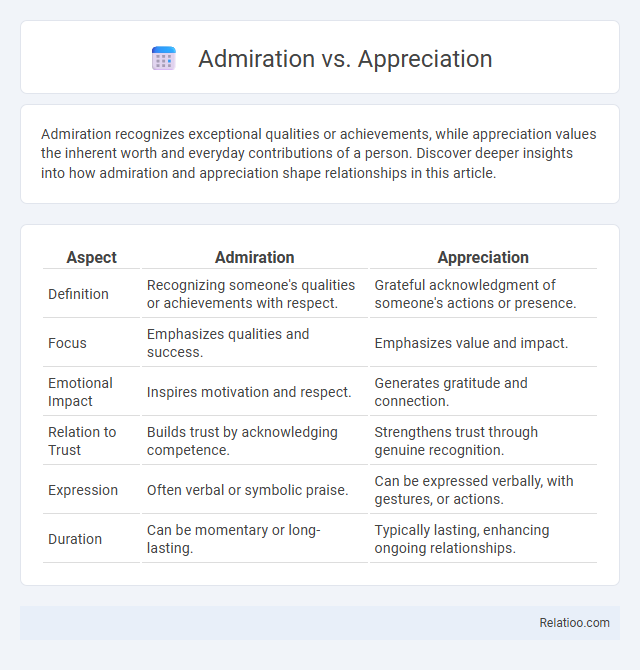
| Aspect | Admiration | Appreciation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognizing someone's qualities or achievements with respect. | Grateful acknowledgment of someone's actions or presence. |
| Focus | Emphasizes qualities and success. | Emphasizes value and impact. |
| Emotional Impact | Inspires motivation and respect. | Generates gratitude and connection. |
| Relation to Trust | Builds trust by acknowledging competence. | Strengthens trust through genuine recognition. |
| Expression | Often verbal or symbolic praise. | Can be expressed verbally, with gestures, or actions. |
| Duration | Can be momentary or long-lasting. | Typically lasting, enhancing ongoing relationships. |
Understanding Admiration: Definition and Key Traits
Admiration is a profound feeling of respect and approval toward someone's skills, qualities, or achievements, characterized by awe and reverence. Key traits of admiration include recognition of excellence, inspiration derived from the admired person, and a positive emotional response that motivates self-improvement. Distinct from appreciation, which emphasizes gratitude and value recognition, admiration centers on deep respect and idealization of specific traits or accomplishments.
What Is Appreciation? A Clear Overview
Appreciation is the recognition and acknowledgment of the value or significance of someone or something, emphasizing gratitude and respect. Your ability to express appreciation strengthens relationships and fosters positive environments by highlighting specific qualities or efforts. Unlike admiration, which often involves idealizing traits, appreciation focuses on sincere acknowledgment without idealization or envy.
Core Differences Between Admiration and Appreciation
Admiration involves recognizing and valuing someone's qualities or achievements, often accompanied by a sense of awe or respect, while appreciation is more about acknowledging the worth or significance of something or someone with gratitude and understanding. Admiration tends to focus on external attributes or accomplishments that inspire, whereas appreciation is a deeper emotional connection emphasizing thankfulness and intrinsic value. The core difference lies in admiration being primarily esteem-based and often aspirational, while appreciation centers on recognition and heartfelt acknowledgment without necessarily involving envy or longing.
Emotional Impact of Admiration vs Appreciation
Admiration evokes a deep emotional response often linked to awe and inspiration, motivating you to aspire toward qualities or achievements you find exceptional. Appreciation, on the other hand, fosters a warm sense of gratitude and recognition for the value or efforts of others, promoting positive relationships and emotional well-being. Unlike admiration's intensity, appreciation creates a continuous emotional connection by acknowledging everyday contributions and kindness.
Social Dynamics: How Admiration and Appreciation Shape Relationships
Admiration often involves recognizing someone's exceptional qualities or achievements, creating a sense of respect and inspiration that strengthens social bonds through positive reinforcement. Appreciation focuses on valuing someone's efforts and presence, fostering emotional closeness and mutual support, which enhances relational depth and trust. Both admiration and appreciation influence social dynamics by promoting positive interactions, but admiration tends to elevate status perception while appreciation cultivates genuine connection.
Psychological Effects of Being Admired vs Being Appreciated
Being admired often boosts self-esteem and fosters a sense of social validation by highlighting perceived worth or achievements. In contrast, being appreciated enhances emotional well-being through feelings of genuine recognition and connection, promoting intrinsic motivation and a supportive environment. While admiration can sometimes create pressure to maintain status, appreciation cultivates deeper relational bonds and sustained psychological resilience.
Real-Life Examples: Admiration and Appreciation in Action
Admiration involves recognizing someone's exceptional qualities or achievements, such as cheering for an athlete's skill during a game, while appreciation expresses gratitude for everyday contributions, like thanking a coworker for their help on a project. Your ability to distinguish between admiration and appreciation enhances relationships by valuing both extraordinary feats and consistent support. Real-life examples include admiring a musician's talent and appreciating a friend's kindness, demonstrating how both emotions play vital roles in social connections.
Cultivating Appreciation Instead of Just Admiring
Cultivating appreciation involves deeply valuing the qualities or efforts behind something rather than merely admiring its surface appeal. Your focus should shift from passive admiration, which often remains fleeting, to active appreciation that fosters gratitude and connection. This approach enhances emotional well-being by recognizing intrinsic worth and encouraging meaningful engagement.
When Admiration Turns Toxic: Potential Pitfalls
Admiration turns toxic when it fosters unrealistic expectations and dependency, leading to distorted perceptions of the admired person. This toxic admiration can result in envy, resentment, or idolization that undermines genuine relationships and self-worth. Recognizing these pitfalls allows individuals to cultivate healthy appreciation, valuing qualities without losing critical perspective or autonomy.
Enhancing Well-being Through Balanced Admiration and Appreciation
Balanced admiration and appreciation enhance well-being by fostering healthy self-esteem and genuine gratitude, reducing envy and dissatisfaction. Admiration focuses on recognizing qualities or achievements in others, while appreciation involves valuing the intrinsic worth and positive impact of people or experiences. Cultivating both admiration and appreciation promotes emotional resilience, social connection, and overall mental health.
Infographic: Admiration vs Appreciation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com