Trust in relationships is built on emotional connection and reliability, while assurance provides confidence through clear communication and consistent actions. Explore this article to understand how balancing trust and assurance strengthens your relationships.
Table of Comparison
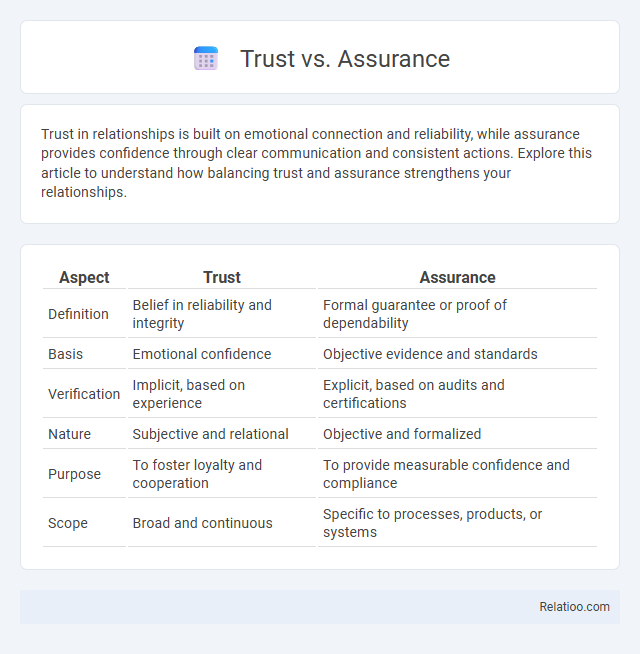
| Aspect | Trust | Assurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in reliability and integrity | Formal guarantee or proof of dependability |
| Basis | Emotional confidence | Objective evidence and standards |
| Verification | Implicit, based on experience | Explicit, based on audits and certifications |
| Nature | Subjective and relational | Objective and formalized |
| Purpose | To foster loyalty and cooperation | To provide measurable confidence and compliance |
| Scope | Broad and continuous | Specific to processes, products, or systems |
Understanding Trust and Assurance
Trust represents the belief in the reliability, truth, or ability of a person or system, often built through consistent interactions and reputation over time. Assurance involves explicit guarantees, such as certifications or warranties, that provide formal confirmation about performance, security, or compliance standards. Understanding trust requires recognizing the emotional and psychological factors influencing confidence, while assurance emphasizes objective validation through documented evidence and risk mitigation strategies.
Key Differences Between Trust and Assurance
Trust is the reliance on the integrity and character of a person or entity, often based on subjective confidence, while assurance involves objective verification through evidence or guarantees, such as audits or certifications, to reduce uncertainty. Trust typically depends on relationships and reputation, whereas assurance relies on formal processes and standards to validate claims or performance. You can strengthen business decisions by understanding that trust is built over time through consistent behavior, while assurance provides measurable confirmation of compliance or quality.
The Role of Trust in Relationships
Trust forms the foundation of strong relationships by fostering confidence and reliability between parties. Assurance serves to validate trust through concrete evidence or guarantees, enhancing security and reducing uncertainty. While assurance provides measurable proof, trust remains essential for emotional connection and ongoing commitment in personal and professional relationships.
Assurance: Definition and Importance
Assurance refers to the formal guarantee or promise provided by a trusted authority that a product, service, or system meets specified standards and requirements. It plays a crucial role in risk management by instilling confidence in stakeholders through independent verification, audits, and certifications. High assurance levels reduce uncertainty, enhance credibility, and support compliance with regulatory frameworks across industries such as finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity.
Building Trust vs Providing Assurance
Building trust involves establishing consistent reliability, transparency, and emotional connection, which fosters long-term confidence and loyalty between parties. Providing assurance centers on delivering verifiable evidence, guarantees, or certifications that reduce uncertainty and demonstrate compliance or quality standards. While trust relies on relationship dynamics and perceived integrity, assurance emphasizes objective validation to support decision-making and risk management.
Trust in Business and Customer Relations
Trust in business and customer relations is the foundational belief that a company will act with integrity, reliability, and honesty, fostering long-term loyalty and repeat engagement. Unlike assurance, which provides formal guarantees or warranties about product quality and performance, trust is built through consistent positive experiences and transparent communication. Establishing trust reduces perceived risk for customers and enhances brand reputation, ultimately driving sustainable business growth.
Assurance in Quality and Compliance
Assurance in quality and compliance ensures your products and processes consistently meet established standards and regulatory requirements, reducing risks of defects and non-conformities. Unlike trust, which is based on belief without proof, and general assurance, quality assurance involves systematic activities such as audits, inspections, and testing to provide verifiable confidence. Implementing robust quality and compliance assurance frameworks strengthens your organization's reputation and operational efficiency.
Trust and Assurance in Digital Environments
Trust in digital environments relies on users' confidence that systems will perform securely and reliably, protecting their data and privacy. Assurance provides measurable evidence through certifications, audits, and compliance standards that reinforce this trust by demonstrating adherence to security protocols. You can enhance your digital security strategy by prioritizing both trust-building practices and robust assurance mechanisms.
Challenges in Balancing Trust and Assurance
Balancing trust and assurance presents challenges such as managing the inherent uncertainty in relying on trust while meeting stringent assurance requirements through verifiable controls and audits. Organizations must address the complexity of aligning subjective trust perceptions with objective assurance measures, ensuring transparency without compromising security or privacy. The dynamic nature of risk and evolving regulatory landscapes further complicate achieving an effective equilibrium between trust and assurance.
Strategies to Foster Both Trust and Assurance
Implementing transparent communication and delivering consistent, reliable performance are key strategies to foster both trust and assurance in customer relationships. Incorporating robust risk management practices alongside clear, measurable service level agreements enhances clients' confidence and demonstrates commitment to accountability. Leveraging regular feedback loops and proactive problem resolution further builds an environment where both trust and assurance are deeply ingrained.
Infographic: Trust vs Assurance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com