Authentication verifies a user's identity by confirming credentials like passwords or biometrics, while authorization determines the user's access level to resources or actions within a system. Discover detailed differences and implementation strategies between authentication and authorization in this article.
Table of Comparison
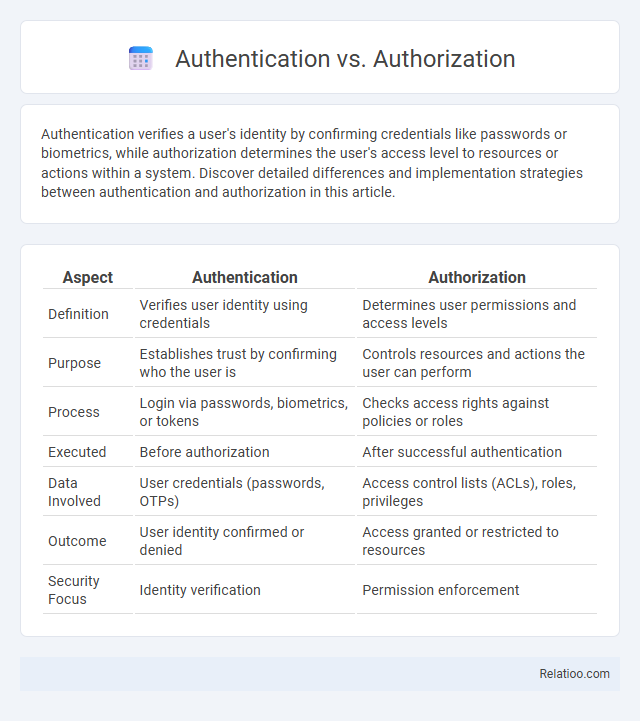
| Aspect | Authentication | Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies user identity using credentials | Determines user permissions and access levels |
| Purpose | Establishes trust by confirming who the user is | Controls resources and actions the user can perform |
| Process | Login via passwords, biometrics, or tokens | Checks access rights against policies or roles |
| Executed | Before authorization | After successful authentication |
| Data Involved | User credentials (passwords, OTPs) | Access control lists (ACLs), roles, privileges |
| Outcome | User identity confirmed or denied | Access granted or restricted to resources |
| Security Focus | Identity verification | Permission enforcement |
Introduction to Authentication and Authorization
Authentication verifies Your identity by requiring credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or tokens to confirm who you are. Authorization determines the access levels and permissions associated with your verified identity, controlling what resources you can use or modify. Security encompasses both authentication and authorization processes to protect systems and data from unauthorized access and potential threats.
Defining Authentication
Authentication verifies a user's identity by requiring credentials such as passwords, biometric data, or security tokens to confirm they are who they claim to be. Authorization determines the permissions and access levels granted to an authenticated user, controlling what resources they can use. Security encompasses both authentication and authorization processes, along with measures like encryption and threat detection, to protect systems and data from unauthorized access and attacks.
What is Authorization?
Authorization is the process of granting or denying specific permissions to a user, application, or system after their identity is authenticated. It determines access levels, controlling what resources or actions are allowed based on predefined roles or policies. Effective authorization mechanisms protect sensitive data and ensure secure interaction within digital environments.
Key Differences Between Authentication and Authorization
Authentication verifies your identity through credentials like passwords or biometric data, ensuring you are who you claim to be. Authorization determines your access level, granting or denying permissions based on your authenticated status and predefined roles. Security encompasses both processes, safeguarding systems by controlling access and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized use.
How Authentication Works
Authentication verifies a user's identity by requiring credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens, which are validated against stored data to grant access. This process often involves multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security by combining something the user knows, has, or is. Authentication serves as the foundational step in security frameworks to ensure only legitimate users proceed to authorization, which determines their access rights.
How Authorization Works
Authorization works by determining user permissions after authentication verifies identity, using access control policies such as role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC) to enforce which resources and operations a user is permitted to access. The system evaluates the user's credentials, roles, and attributes against predefined rules stored in authorization servers or databases to grant or deny access. Effective authorization ensures that even authenticated users can only perform actions aligned with their assigned privileges, maintaining secure resource management.
Common Authentication Methods
Common authentication methods include passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA), each designed to verify Your identity before granting access. Authentication confirms who You are, while authorization determines what resources You can access, together forming core components of overall security. Effective implementation of these methods significantly reduces risks associated with unauthorized access and data breaches.
Popular Authorization Techniques
Popular authorization techniques include Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which assigns permissions based on user roles, and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), which uses policies evaluating user attributes and environmental conditions. OAuth 2.0 is widely adopted for delegated authorization, enabling secure access without sharing credentials, while JSON Web Tokens (JWT) facilitate stateless and scalable authorization across distributed systems. Your security strategy benefits from selecting authorization methods that align with your application's complexity and user access requirements.
Importance of Both in Security
Authentication verifies user identities through credentials like passwords or biometrics, ensuring only legitimate users gain access. Authorization determines the permitted actions and resource access for authenticated users, enforcing security policies and limiting potential damage. Together, authentication and authorization form a robust security framework that protects systems from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Best Practices for Managing Authentication and Authorization
Implementing strong authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and utilizing role-based access control (RBAC) are key best practices for managing authentication and authorization. You should regularly review and update user permissions to ensure least privilege access, minimizing potential security risks. Employing secure protocols like OAuth and maintaining audit logs enhances overall security by providing traceability and reducing unauthorized access.
Infographic: Authentication vs Authorization
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com