A confidant provides emotional support and personal trust, while a counselor offers professional guidance and therapeutic strategies. Discover more about how these roles impact relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
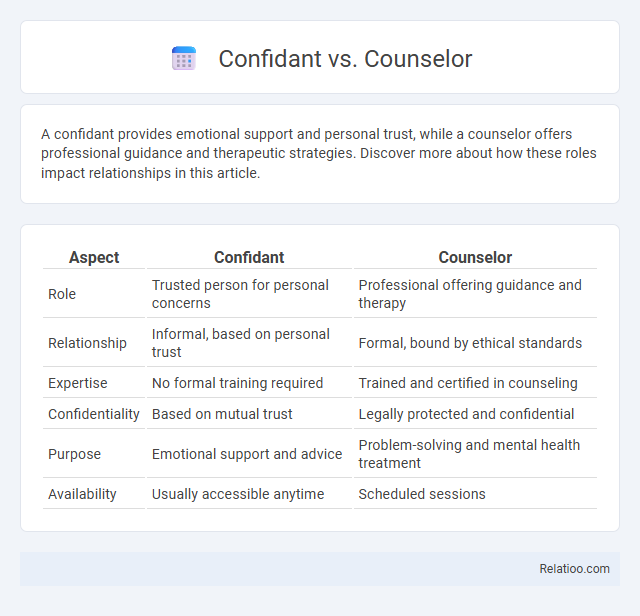
| Aspect | Confidant | Counselor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Trusted person for personal concerns | Professional offering guidance and therapy |
| Relationship | Informal, based on personal trust | Formal, bound by ethical standards |
| Expertise | No formal training required | Trained and certified in counseling |
| Confidentiality | Based on mutual trust | Legally protected and confidential |
| Purpose | Emotional support and advice | Problem-solving and mental health treatment |
| Availability | Usually accessible anytime | Scheduled sessions |
Understanding the Roles: Confidant vs Counselor
A confidant is someone you trust deeply with your personal thoughts and feelings, offering emotional support without formal training, while a counselor is a licensed professional providing structured guidance and therapeutic strategies for mental health and personal development. Your choice depends on the level of expertise and type of support you need; confidants offer empathy and companionship, whereas counselors deliver evidence-based interventions tailored to your specific issues. Understanding these distinctions helps you seek the appropriate help to address emotional challenges effectively.
Defining a Confidant: Trusted Friend or Ally
A confidant is a trusted friend or ally who provides a safe space for sharing personal thoughts and emotions without judgment. Unlike a counselor, who is a trained professional offering structured guidance and therapeutic support, a confidant relies on empathy and mutual trust rather than formal techniques. Your confidant plays a crucial role in emotional well-being by listening attentively and offering genuine understanding during challenging times.
What is a Counselor? Professional Guidance Explained
A counselor is a trained professional who provides expert guidance and support to individuals facing emotional, psychological, or behavioral challenges, using evidence-based techniques to promote mental health and well-being. Unlike a confidant, who offers informal and empathetic listening without professional credentials, a counselor utilizes therapeutic strategies to help clients develop coping skills and achieve specific goals. Your choice between a counselor and a confidant depends on the level of expertise and structured assistance you seek for personal growth or overcoming difficulties.
Key Differences Between Confidant and Counselor
A confidant is a trusted person with whom one shares personal thoughts and feelings, typically in informal or private contexts. A counselor, by contrast, is a trained professional providing guidance and support for emotional, psychological, or behavioral issues through structured sessions. The key difference lies in confidentiality and expertise: counselors adhere to ethical standards with formal training, while confidants rely on personal trust without formal qualifications.
Emotional Support: Who Provides It Better?
Counselors offer professional emotional support through trained therapeutic techniques tailored to your specific mental health needs, ensuring structured guidance and confidentiality. Confidants provide informal emotional support, often based on personal trust and shared experiences, fostering a sense of comfort and understanding. While both roles support emotional well-being, counselors deliver evidence-based interventions, making them better suited for addressing complex emotional challenges.
Boundaries and Ethics in Each Role
Boundaries in a confidant role are generally informal with a strong emphasis on trust and privacy, while counselors operate within strict ethical guidelines and professional boundaries designed to protect both you and the therapeutic process. Counselors adhere to ethical codes mandated by licensing boards, ensuring confidentiality, informed consent, and clear limits on dual relationships, whereas confidants may lack formal training or accountability. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate support systems effectively while maintaining personal and ethical integrity.
Confidentiality: Personal Trust vs Professional Obligation
A confidant typically operates within the realm of personal trust, offering a private space where individuals share intimate thoughts without fear of disclosure, relying on mutual loyalty and discretion. Counselors, bound by professional ethics and legal obligations, maintain strict confidentiality while navigating mandatory reporting laws and therapeutic boundaries to protect client welfare. The key difference lies in the source of confidentiality: informal trust governs a confidant's secrecy, whereas formal codes and regulations define a counselor's confidentiality framework.
When to Seek a Confidant
When you need a trusted individual to share personal feelings or secrets without judgment, a confidant offers empathetic support and emotional safety. Seek a confidant when your goal is emotional relief and honest feedback rather than professional guidance, which is the role of a counselor. Your choice depends on whether you require informal comfort from someone close or structured help from a mental health expert.
When to Consult a Counselor
Consult a counselor when facing persistent mental health challenges, emotional distress, or situations requiring professional guidance beyond informal support. Counselors provide evidence-based strategies for coping with anxiety, depression, trauma, and relationship issues, ensuring confidentiality and structured intervention. Unlike a confidant, who offers emotional support and empathy, counselors have specialized training to assess and treat psychological conditions effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Well-being
Choosing between a confidant and a counselor hinges on the nature and depth of support you need for your well-being; a confidant offers personal, empathetic listening often within trusted relationships, while a counselor provides professional guidance grounded in psychological training. For complex mental health challenges or structured coping strategies, counselors deliver evidence-based interventions tailored to your unique circumstances. Assessing your emotional needs and the level of expertise required ensures that your decision aligns with fostering optimal mental health and personal growth.
Infographic: Confidant vs Counselor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com