Healthy relationships balance dependence and independence, fostering mutual support while respecting individual autonomy. Explore this article to understand how finding the right equilibrium strengthens emotional bonds.
Table of Comparison
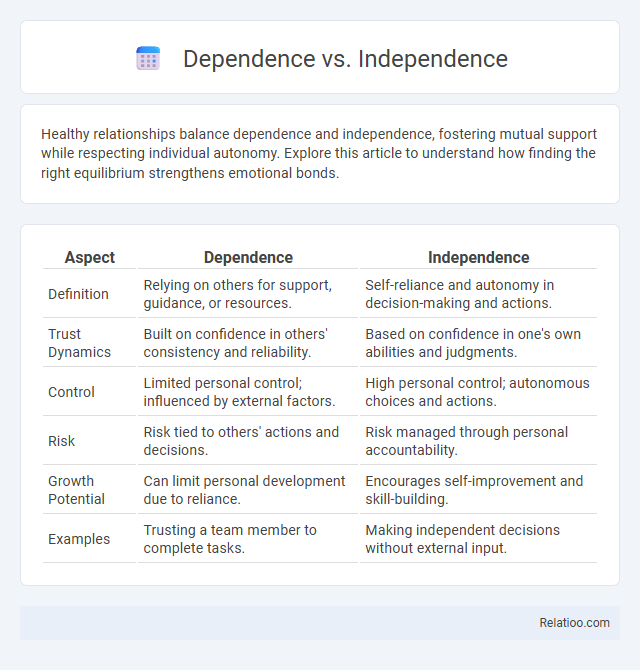
| Aspect | Dependence | Independence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relying on others for support, guidance, or resources. | Self-reliance and autonomy in decision-making and actions. |
| Trust Dynamics | Built on confidence in others' consistency and reliability. | Based on confidence in one's own abilities and judgments. |
| Control | Limited personal control; influenced by external factors. | High personal control; autonomous choices and actions. |
| Risk | Risk tied to others' actions and decisions. | Risk managed through personal accountability. |
| Growth Potential | Can limit personal development due to reliance. | Encourages self-improvement and skill-building. |
| Examples | Trusting a team member to complete tasks. | Making independent decisions without external input. |
Defining Dependence and Independence
Dependence refers to relying on others for support, resources, or decision-making, often limiting personal autonomy. Independence is characterized by self-reliance and the ability to make choices or meet needs without external assistance. Your understanding of these concepts is essential for recognizing the balance between seeking help and fostering personal growth.
Historical Perspectives on Autonomy
Historical perspectives on autonomy reveal shifting interpretations of dependence and independence, where ancient societies often valued communal interdependence as essential for social cohesion, contrasting with Enlightenment ideals that emphasized individual independence as a cornerstone of personal liberty. Philosophers like John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau pioneered concepts of independence rooted in self-governance and natural rights, influencing modern democratic principles. However, contemporary debates highlight a nuanced understanding of autonomy, recognizing the interdependence embedded in social, economic, and political contexts while preserving individual agency.
Psychological Roots of Dependence
Psychological dependence originates from deep-rooted emotional needs shaped by early experiences, attachment styles, and self-esteem levels, often leading individuals to seek constant validation or support. Your sense of security and identity may become intertwined with reliance on others, hindering autonomous decision-making and personal growth. Understanding these psychological roots is essential for fostering independence and balanced interdependence in relationships.
The Benefits of Independence
Independence fosters self-reliance, enabling individuals to make decisions confidently and pursue personal goals without external constraints. It enhances problem-solving skills and resilience by encouraging accountability and initiative in everyday challenges. The benefits of independence extend to improved mental well-being and a stronger sense of identity, promoting overall growth and fulfillment.
Social and Cultural Influences
Social and cultural influences significantly shape your stance between dependence, independence, and interdependence by embedding values and expectations that define acceptable behaviors within communities. Dependence often reflects cultural norms emphasizing family cohesion and collective responsibility, while independence aligns with societies promoting individualism and self-sufficiency. Interdependence represents a balanced approach favored in cultures that value mutual support and cooperation as essential for social harmony and personal growth.
Balancing Support and Self-Reliance
Balancing support and self-reliance involves recognizing when to seek help and when to trust Your own abilities, fostering both dependence and independence in a healthy manner. Dependence provides necessary support during challenges, while independence encourages personal growth and confidence. Finding the right equilibrium empowers You to navigate life effectively, blending collaboration with autonomy.
Dependence in Relationships
Dependence in relationships involves relying on your partner for emotional support, decision-making, or daily needs, which can strengthen closeness but also risk losing personal autonomy. Healthy dependence balances mutual support with individual independence, fostering trust and security without creating unhealthy attachment or codependency. Understanding the dynamics of dependence helps you navigate boundaries to maintain a fulfilling, respectful partnership.
Building and Fostering Independence
Building and fostering independence involves cultivating skills that allow you to make decisions and take responsibility without relying heavily on others. Encouraging problem-solving, self-confidence, and resilience strengthens your ability to navigate challenges autonomously. Balancing dependence and independence promotes healthier relationships by enabling mutual support while maintaining personal growth and self-sufficiency.
Challenges of Excessive Independence
Excessive independence can lead to social isolation, reduced collaboration, and difficulty seeking help, which impedes personal and professional growth. Individuals overly reliant on themselves may struggle to build strong support networks, leading to increased stress and burnout. Balancing independence with interdependence fosters resilience, adaptability, and healthier relationships crucial for long-term success.
Finding the Right Balance for Growth
Finding the right balance between dependence and independence is essential for personal and professional growth, as it enables individuals to leverage support systems while fostering self-reliance. Excessive dependence can hinder decision-making skills and innovation, whereas extreme independence may lead to isolation and missed collaborative opportunities. Cultivating interdependence promotes resilience, adaptability, and the ability to navigate complex challenges effectively.
Infographic: Dependence vs Independence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com