Neglect involves failing to provide necessary care, while abuse encompasses intentional harm or mistreatment in relationships. Explore this article to understand the critical differences and impacts of neglect and abuse.
Table of Comparison
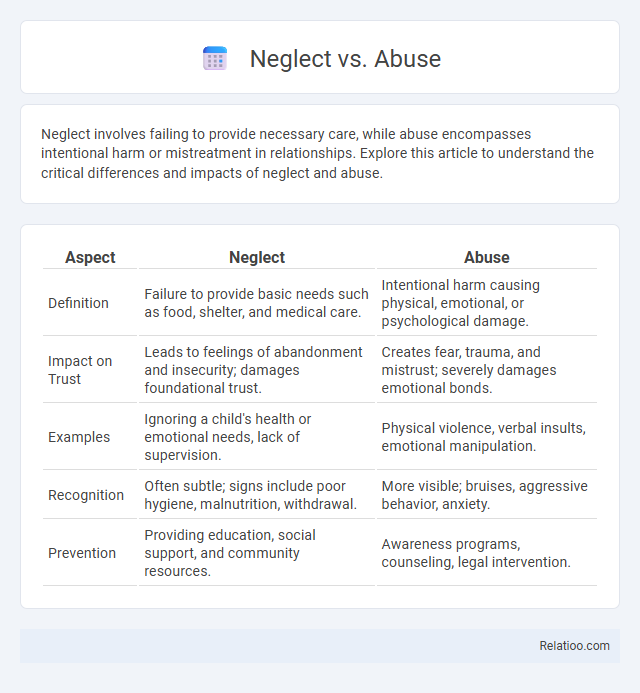
| Aspect | Neglect | Abuse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure to provide basic needs such as food, shelter, and medical care. | Intentional harm causing physical, emotional, or psychological damage. |
| Impact on Trust | Leads to feelings of abandonment and insecurity; damages foundational trust. | Creates fear, trauma, and mistrust; severely damages emotional bonds. |
| Examples | Ignoring a child's health or emotional needs, lack of supervision. | Physical violence, verbal insults, emotional manipulation. |
| Recognition | Often subtle; signs include poor hygiene, malnutrition, withdrawal. | More visible; bruises, aggressive behavior, anxiety. |
| Prevention | Providing education, social support, and community resources. | Awareness programs, counseling, legal intervention. |
Understanding Neglect and Abuse: Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between neglect and abuse is crucial for identifying and addressing harm effectively. Neglect involves the failure to provide essential care, such as food, shelter, medical attention, or supervision, resulting in harm or risk to a person's well-being. Abuse, on the other hand, refers to intentional actions that cause physical, emotional, or psychological harm, including physical violence, emotional manipulation, or sexual exploitation, which you must recognize to protect vulnerable individuals properly.
Defining Neglect: What Constitutes Neglect?
Neglect constitutes the failure to provide necessary care, supervision, or basic needs such as food, shelter, medical attention, and emotional support, resulting in harm or risk of harm to a child's health and well-being. Unlike abuse, which involves intentional harm, neglect is characterized by omission or inaction, often stemming from caregiver incapacity or disregard. Legal and child welfare frameworks define neglect through specific criteria including persistent or severe deprivation that impairs a child's development.
Defining Abuse: Forms and Types
Abuse encompasses various forms including physical, emotional, sexual, and psychological harm inflicted intentionally on an individual. Physical abuse involves deliberate infliction of bodily injury, while emotional abuse targets mental well-being through threats, humiliation, or manipulation. Sexual abuse includes any non-consensual sexual contact, and psychological abuse disrupts a person's sense of safety and self-worth through intimidation or isolation.
Signs and Symptoms of Neglect
Signs and symptoms of neglect include consistent hunger, poor hygiene, untreated medical conditions, and frequent absences from school or activities. Children experiencing neglect may exhibit developmental delays, withdrawal, and low self-esteem. Physical indicators such as malnutrition, inappropriate clothing, and unsafe living conditions also point to neglect.
Signs and Symptoms of Abuse
Signs and symptoms of abuse include unexplained bruises, burns, fractures, and frequent injuries, often in various stages of healing. Behavioral changes such as withdrawal, anxiety, aggression, or fearfulness can also indicate abuse in children or vulnerable adults. Recognizing these symptoms early can protect Your loved ones from ongoing harm and ensure timely intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors of Neglect
Neglect often stems from factors such as parental substance abuse, mental health disorders, poverty, and lack of social support, which can impede a caregiver's ability to meet a child's basic needs. Unlike abuse, which involves intentional harm, neglect is characterized by the consistent failure to provide adequate food, shelter, medical care, or supervision. Risk factors for neglect include caregiver stress, domestic violence, and inadequate knowledge of child development, all contributing to the child's physical and emotional deprivation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Abuse
Child abuse arises from complex causes such as parental substance abuse, mental health disorders, and chronic stress, which impair caregivers' ability to provide safe environments. Risk factors include socioeconomic disadvantages, domestic violence exposure, and lack of social support networks, increasing the likelihood of physical, emotional, or sexual harm to children. Understanding these underlying contributors aids in targeted prevention and intervention strategies to protect vulnerable children.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
Neglect often results in developmental delays, poor physical health, and emotional difficulties, with long-term effects including chronic mental health disorders and impaired social functioning. Abuse causes immediate physical injuries, trauma, and fear, leading to lasting consequences such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), aggressive behavior, and difficulty forming healthy relationships. Repeated exposure to neglect and abuse amplifies risks for substance abuse, cognitive impairments, and increased vulnerability to future victimization throughout adulthood.
Prevention Strategies: Addressing Neglect and Abuse
Effective prevention strategies for neglect and abuse center on early identification through training professionals to recognize warning signs and implementing community awareness programs. Strengthening family support services, such as parenting classes and access to mental health resources, reduces risk factors associated with child maltreatment. Collaboration between social services, healthcare providers, and schools enhances monitoring and intervention, ensuring vulnerable children receive timely protection.
Legal and Support Resources for Victims
Legal frameworks for neglect, abuse, and exploitation vary but consistently prioritize victim protection and accountability through child protective services and specialized law enforcement units. Support resources include crisis hotlines, counseling services, and advocacy groups that assist victims in navigating legal procedures and accessing safety plans. Victims of all three forms benefit from multidisciplinary teams that coordinate medical, psychological, and legal aid tailored to each case's severity and context.
Infographic: Neglect vs Abuse
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com