Honesty involves being transparent and sincere in communication, while truth represents the factual accuracy of information shared. Explore this article to understand how balancing honesty and truth strengthens relationships.
Table of Comparison
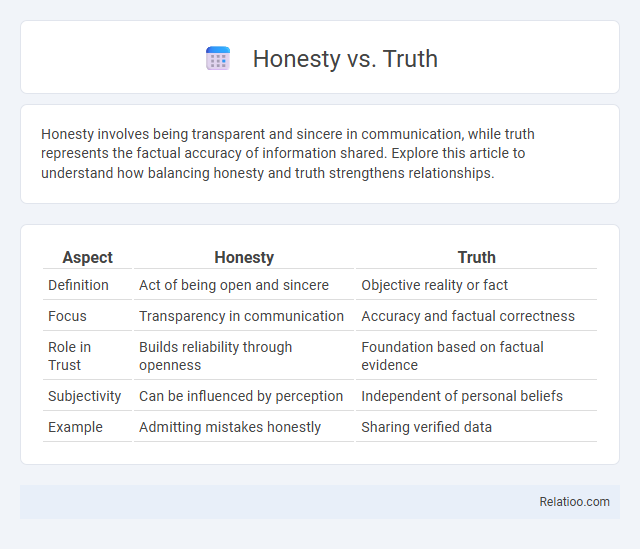
| Aspect | Honesty | Truth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Act of being open and sincere | Objective reality or fact |
| Focus | Transparency in communication | Accuracy and factual correctness |
| Role in Trust | Builds reliability through openness | Foundation based on factual evidence |
| Subjectivity | Can be influenced by perception | Independent of personal beliefs |
| Example | Admitting mistakes honestly | Sharing verified data |
Understanding Honesty and Truth: Key Definitions
Understanding honesty involves recognizing it as the quality of being sincere and free from deceit in your actions and words. Truth refers to facts or realities that remain consistent regardless of perception or belief. While honesty is about your commitment to conveying and embracing truth, truth itself is the objective state that honesty aims to reflect.
The Core Differences Between Honesty and Truth
Honesty involves your commitment to being sincere and transparent in communication, reflecting your intentions and feelings without deception. Truth is an objective reality or fact that exists independently of belief or perception, representing what is accurate and verifiable. The core difference lies in honesty being a personal virtue tied to how you express yourself, while truth is an external standard that your statements or actions may or may not align with.
Why Honesty Doesn’t Always Equal Truth
Honesty involves expressing what one believes to be true, while truth represents an objective reality independent of individual perception. People can be honest yet mistaken, as honesty is tied to personal sincerity rather than absolute facts. Therefore, honesty doesn't always equal truth because truthful accuracy requires evidence and verification beyond subjective conviction.
Real-Life Scenarios: Honesty Versus Truth
In real-life scenarios, honesty involves openly sharing your feelings or intentions, while truth refers to objective facts regardless of perception. You may choose honesty by expressing your genuine thoughts, even if the complete truth is complex or painful. Balancing honesty and truth can enhance relationships by fostering trust without causing unnecessary harm.
The Impact of Cultural Norms on Honesty and Truth
Cultural norms significantly shape perceptions of honesty and truth, influencing how individuals express and interpret these concepts. In collectivist societies, honesty may prioritize social harmony over blunt truth, leading to more context-dependent communication. Variations in cultural expectations affect the balance between transparency and discretion, altering the impact of honesty and truth in interpersonal and societal interactions.
Psychological Perspectives on Honesty and Truth
Psychological perspectives distinguish honesty as a behavior reflecting transparency and authenticity, while truth pertains to factual accuracy and objective reality. Your understanding of honesty involves ethical choices motivated by conscience and social norms, whereas truth requires cognitive processes such as perception and reasoning to align beliefs with reality. Honesty bridges personal integrity and interpersonal trust, highlighting its role in psychological well-being and relational dynamics.
Honesty, Truth, and Ethical Decision-Making
Honesty involves presenting information sincerely and transparently, which is essential for ethical decision-making as it builds trust and accountability. Truth represents the objective reality that honesty aims to convey, ensuring your decisions are based on accurate and reliable facts. Prioritizing honesty in ethical choices promotes integrity and fosters meaningful relationships by aligning your actions with genuine truth.
The Consequences of Prioritizing One Over the Other
Prioritizing honesty without truth can lead to misunderstandings, as honest statements may lack factual accuracy, causing confusion or mistrust. Emphasizing truth over honesty might result in blunt or insensitive communication, potentially harming relationships despite factual correctness. Your ability to balance honesty, truth, and kindness directly influences the quality and trustworthiness of your interactions and the consequences that follow each choice.
Balancing Honesty and Truth in Communication
Balancing honesty and truth in communication requires presenting factual information with sincerity while considering the impact on the listener. Honesty involves openness and transparency about one's feelings or intentions, whereas truth emphasizes accuracy and objectivity in the conveyed message. Effective communication harmonizes these elements to build trust without compromising empathy or clarity.
Building Trust: When to Value Honesty or Truth
Building trust depends on valuing honesty when fostering open communication and emotional connection, as honesty reflects sincerity and personal integrity. Truth becomes essential in situations requiring factual accuracy and objective reality, such as legal matters or scientific discourse, where trust is based on verifiable information. Balancing honesty and truth strengthens relationships by ensuring both genuine expression and reliable facts are respected.
Infographic: Honesty vs Truth
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com