Guarantee involves a third party promising to fulfill an obligation if the main party defaults, while security refers to collateral or assets pledged to secure a loan or obligation. Explore the distinctions and implications of Guarantee vs Security in this article.
Table of Comparison
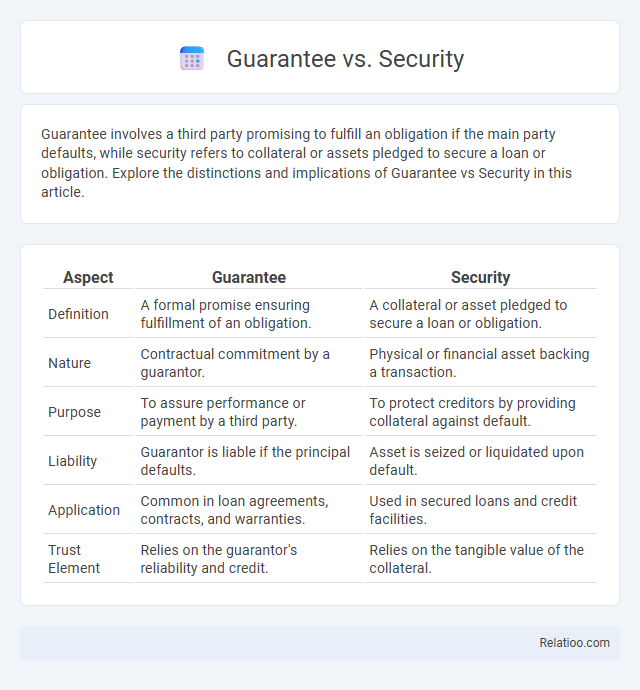
| Aspect | Guarantee | Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal promise ensuring fulfillment of an obligation. | A collateral or asset pledged to secure a loan or obligation. |
| Nature | Contractual commitment by a guarantor. | Physical or financial asset backing a transaction. |
| Purpose | To assure performance or payment by a third party. | To protect creditors by providing collateral against default. |
| Liability | Guarantor is liable if the principal defaults. | Asset is seized or liquidated upon default. |
| Application | Common in loan agreements, contracts, and warranties. | Used in secured loans and credit facilities. |
| Trust Element | Relies on the guarantor's reliability and credit. | Relies on the tangible value of the collateral. |
Understanding the Concepts: Guarantee vs Security
A guarantee is a contractual promise ensuring fulfillment of an obligation, often involving a third party who agrees to pay or perform if the primary party defaults. Security refers to an asset or collateral pledged to secure a debt or obligation, providing a lender with a direct claim in case of non-payment. Understanding the distinction between guarantee and security is crucial: guarantees involve personal commitments, while securities involve tangible or financial assets backing the obligation.
Key Differences Between Guarantee and Security
Guarantee involves a third party promising to fulfill your obligation if you default, while security refers to an asset pledged to secure repayment, providing the lender a claim on it in case of non-payment. The key difference is that a guarantee is a personal commitment enforceable without transferring property rights, whereas security creates a legal interest in specific property. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the appropriate risk mitigation instrument for lending or borrowing situations.
Legal Definitions: Guarantee and Security Explained
Guarantee legally refers to a promise by a third party to fulfill an obligation if the original debtor defaults, ensuring your creditor's risk is minimized. Security involves an asset or collateral pledged to secure the repayment of a debt, providing creditors with a direct claim over that property in case of non-payment. Understanding the distinction between guarantee and security is crucial for managing legal liabilities and protecting your financial interests.
Types of Guarantees in Business and Finance
Types of guarantees in business and finance include performance guarantees, payment guarantees, and financial guarantees, each serving distinct purposes to mitigate risk and ensure fulfillment of obligations. Performance guarantees assure completion of contractual duties, payment guarantees secure debt or credit repayments, and financial guarantees protect against default on loans or bonds. Understanding these guarantees helps your business manage exposure and build trust with partners and creditors.
Types of Securities in Financial Practices
Types of securities in financial practices include collateral securities, personal guarantees, and lien-based securities, each serving different purposes for risk mitigation. Collateral securities involve tangible assets pledged to secure a loan, while personal guarantees bind an individual's personal assets to fulfill obligations. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate security type to protect your financial interests effectively.
Roles and Responsibilities of Parties Involved
Guarantee involves a third party, typically a guarantor, who commits to fulfilling the debtor's obligation if the debtor defaults, requiring clear understanding of the guarantor's liability scope. Security refers to an asset or collateral provided by the debtor to the creditor to secure a loan, giving the creditor rights to seize the asset upon default, thus defining the responsibilities related to asset management and enforcement. Your role as the principal party is to ensure all terms, including liability limits, collateral valuation, and enforcement procedures, are clearly agreed upon by all parties to avoid disputes.
Legal Implications of Guarantees vs Securities
Guarantees impose a direct legal obligation on a guarantor to fulfill a debtor's responsibility if the primary obligor defaults, while securities represent collateral rights enabling a creditor to satisfy a claim from specific assets. Your legal exposure differs as guarantees often require the guarantor's personal assets, whereas securities limit recovery to the secured property without involving personal liability. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for assessing risk, enforcement procedures, and the remedies available under law.
Risk Assessment: Guarantee Compared to Security
Guarantee and security serve distinct roles in risk assessment, where a guarantee involves a third party's commitment to fulfill an obligation if the primary debtor defaults, enhancing creditor confidence by reducing credit risk. Security typically refers to collateral assets pledged by the borrower, which creditors can claim to recover losses, directly mitigating financial risk through asset-backed assurance. Guarantee shifts risk from the creditor to the guarantor, while security transfers risk by providing tangible compensation options in case of default.
Practical Applications in Contracts and Agreements
Guarantee in contracts involves a third party promising to fulfill an obligation if the primary party defaults, ensuring creditor protection. Security refers to collateral assets pledged to secure debt repayment, enabling lenders to recover losses through asset liquidation upon default. Guarantees are commonly used in loan agreements for added assurance, while security interests are prevalent in mortgages and secured loans to provide tangible risk mitigation.
Choosing Between Guarantee and Security: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a guarantee and security depends on your risk tolerance, financial capacity, and the transaction's nature. Guarantees offer a promise from a third party to fulfill obligations if the primary party defaults, while security involves collateral that can be seized upon default. Your decision should weigh factors like enforceability, cost implications, and the potential impact on creditworthiness.
Infographic: Guarantee vs Security
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com