Admiration in relationships fosters growth and mutual respect, while envy breeds resentment and distance. Explore how distinguishing between these emotions can strengthen your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
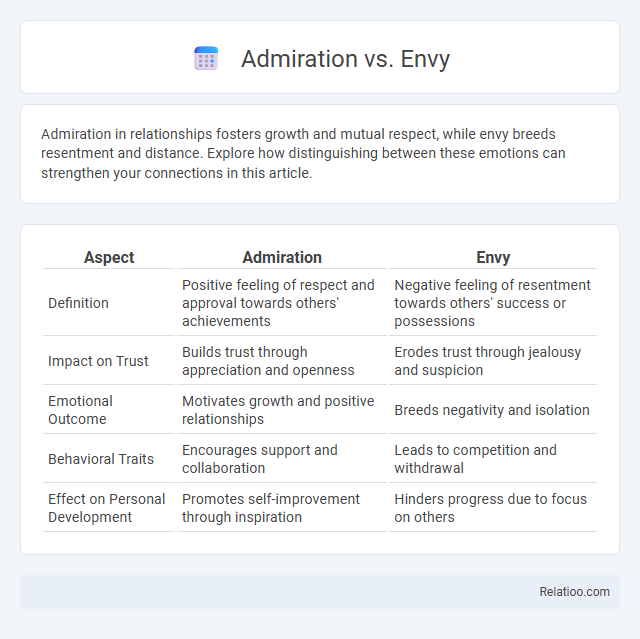
| Aspect | Admiration | Envy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Positive feeling of respect and approval towards others' achievements | Negative feeling of resentment towards others' success or possessions |
| Impact on Trust | Builds trust through appreciation and openness | Erodes trust through jealousy and suspicion |
| Emotional Outcome | Motivates growth and positive relationships | Breeds negativity and isolation |
| Behavioral Traits | Encourages support and collaboration | Leads to competition and withdrawal |
| Effect on Personal Development | Promotes self-improvement through inspiration | Hinders progress due to focus on others |
Understanding Admiration and Envy
Understanding admiration involves recognizing genuine appreciation for someone else's qualities or achievements, which can inspire personal growth and motivation. Envy, in contrast, arises from a feeling of lack or desire for what others possess, often leading to resentment or dissatisfaction. Your ability to distinguish admiration from envy helps foster positive relationships and encourages a healthier mindset focused on self-improvement rather than comparison.
Psychological Roots of Admiration
Admiration originates from recognizing exceptional qualities or achievements in others, stimulating positive emotions and motivation for self-improvement. Unlike envy, which stems from feelings of inferiority or desire for what others possess, admiration is rooted in appreciation and respect without negative self-comparison. Psychological studies link admiration to increased self-efficacy and prosocial behavior, highlighting its role in fostering inspiration and personal growth.
The Origins of Envy
Envy originates from a deep-seated sense of insecurity and lack, often triggered by perceiving others' success or qualities as superior. Neuroscientific studies reveal that envy activates brain regions linked to social pain and comparison, highlighting its evolutionary role in social hierarchy awareness. Unlike admiration, which fosters respect and motivation, envy is rooted in feelings of threat and resentment, impacting emotional well-being and interpersonal relationships.
Key Differences Between Admiration and Envy
Admiration involves recognizing and appreciating someone's qualities or achievements, often inspiring motivation and positivity in your personal growth. Envy, by contrast, stems from a feeling of discontent or resentment due to someone else's success or possessions, driving negative emotions and comparison. Understanding these key differences can help you foster healthier relationships and develop a more constructive outlook on others' accomplishments.
Effects of Admiration on Personal Growth
Admiration fosters personal growth by inspiring individuals to emulate positive traits and achievements, enhancing motivation and self-improvement. Unlike envy, which often triggers negative emotions and comparative dissatisfaction, admiration encourages a constructive mindset that promotes learning and goal-setting. Scientific studies reveal that admiring others activates neural pathways linked to reward and social bonding, thereby reinforcing personal development and well-being.
How Envy Impacts Mental Health
Envy, unlike admiration, often triggers negative emotions such as resentment and insecurity, which can contribute to increased stress and anxiety levels. This toxic comparison undermines your self-esteem and may lead to feelings of inadequacy or depression, impairing overall mental well-being. Recognizing the difference between envy and admiration helps foster healthier emotional responses and promotes positive mental health.
Turning Envy into Constructive Motivation
Envy often arises from comparing Your achievements to others, causing frustration and dissatisfaction, but recognizing this emotion can transform it into a powerful motivational tool. By shifting focus from envy to admiration, You channel negative feelings into constructive energy, inspiring personal growth and goal-setting. Embracing admiration allows You to learn from others' successes, fueling ambition and turning envy into a catalyst for self-improvement.
Cultivating Admiration in Relationships
Cultivating admiration in relationships fosters trust, respect, and deeper emotional connections by recognizing and appreciating others' strengths and achievements. Unlike envy, which breeds resentment and competition, admiration encourages positive reinforcement and mutual growth. Prioritizing admiration helps build a supportive environment where individuals feel valued and motivated to thrive together.
Social Influences on Admiration vs Envy
Social influences significantly shape your tendencies toward admiration or envy by providing role models and social norms that guide emotional responses to others' success. Environments emphasizing collaboration and positive reinforcement foster admiration, while competitive or comparison-driven settings often trigger envy. Understanding these social dynamics helps you navigate emotions constructively, promoting personal growth and healthier relationships.
Strategies to Overcome Envy and Foster Admiration
To overcome envy and foster admiration, focus on shifting your mindset toward gratitude and personal growth, recognizing the unique qualities and achievements of others without comparison. Practicing self-awareness and mindfulness helps you identify envy triggers, allowing you to replace negative emotions with appreciation and motivation. Cultivating supportive relationships and celebrating others' successes can transform envy into genuine admiration, enhancing your emotional well-being and social connections.
Infographic: Admiration vs Envy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com