Opportunity cost represents the potential benefits lost when choosing one option over another, while explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket expenses incurred. Discover more about how these costs impact decision-making in this article.
Table of Comparison
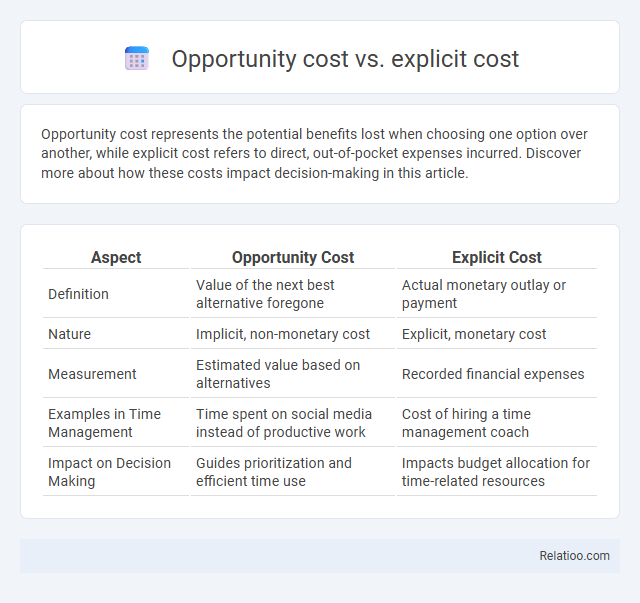
| Aspect | Opportunity Cost | Explicit Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value of the next best alternative foregone | Actual monetary outlay or payment |
| Nature | Implicit, non-monetary cost | Explicit, monetary cost |
| Measurement | Estimated value based on alternatives | Recorded financial expenses |
| Examples in Time Management | Time spent on social media instead of productive work | Cost of hiring a time management coach |
| Impact on Decision Making | Guides prioritization and efficient time use | Impacts budget allocation for time-related resources |
Understanding Opportunity Cost
Understanding opportunity cost involves recognizing the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision, contrasting it with explicit costs, which are direct, out-of-pocket expenses. Opportunity cost captures both tangible and intangible trade-offs, while explicit cost only accounts for measurable monetary payments. Your ability to evaluate opportunity costs effectively informs better financial and resource allocation choices, leading to more strategic decision-making.
Defining Explicit Cost
Explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket payments made by a business for resources such as wages, rent, and materials. Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when a choice is made, encompassing both explicit and implicit costs. Understanding explicit cost helps you differentiate actual monetary expenses from the broader concept of opportunity cost, which includes non-monetary sacrifices.
Key Differences Between Opportunity Cost and Explicit Cost
Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision, while explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket expenses incurred in the production or acquisition of goods and services. You must consider opportunity cost to evaluate the true economic impact of your choices beyond the tangible, monetary payments captured by explicit costs. Understanding the key differences helps optimize resource allocation by balancing recorded expenses with potential benefits lost.
Importance in Economic Decision-Making
Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative forgone when making a decision, while explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket expenses incurred. Recognizing both opportunity and explicit costs allows you to evaluate the true economic impact of choices, ensuring efficient resource allocation and maximizing potential benefits. Balancing these costs is crucial for making informed decisions that enhance overall economic outcomes.
Real-World Examples of Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost represents the foregone benefits when choosing one alternative over another, such as a student opting to work instead of studying, sacrificing potential higher future earnings. Explicit costs include direct monetary payments, like paying rent for office space or purchasing raw materials. Real-world opportunity costs are evident when businesses forgo investments in new technology to allocate funds for marketing, potentially missing out on efficiency gains and long-term profitability.
Practical Applications of Explicit Cost
Explicit cost represents actual monetary payments made by a business for resources like wages, rent, and materials, directly impacting your financial statements and cash flow management. Understanding explicit costs helps you identify the true out-of-pocket expenses involved in production, aiding in budgeting and pricing strategies. These practical applications showcase how explicit costs influence profitability analysis and operational decisions in everyday business practices.
Calculating Opportunity and Explicit Costs
Calculating opportunity cost involves identifying the value of the next best alternative foregone when a decision is made, while explicit cost represents the direct, out-of-pocket expenses incurred in a business transaction. Opportunity cost is measured by comparing the expected returns of the chosen option against the foregone alternative, whereas explicit cost is calculated by summing actual monetary payments such as wages, rent, and materials. Both costs are crucial for comprehensive economic decision-making, ensuring resource allocation aligns with potential benefits and actual expenditures.
Opportunity Cost vs Explicit Cost: Impact on Business Strategy
Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision, while explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket expenses recorded in financial statements. Understanding the distinction between opportunity cost and explicit cost is crucial for business strategy, as it enables firms to evaluate not only actual expenditures but also the potential benefits sacrificed, leading to more informed resource allocation. Incorporating opportunity costs into decision-making helps businesses identify the true economic impact of their choices, optimizing profitability and competitive advantage.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision, whereas explicit cost refers to direct, out-of-pocket expenses paid in the transaction. A common misconception is that opportunity cost and explicit cost are mutually exclusive, but opportunity cost includes both explicit costs and implicit benefits lost. Clarifying this distinction helps in comprehensive decision-making by accounting for all economic trade-offs, not just the immediate financial expenditures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cost Concept
Understanding opportunity cost, explicit cost, and implicit cost is crucial for effective decision-making in business and personal finance. Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone, explicit cost involves direct monetary payments, and implicit cost includes non-monetary sacrifices such as time or resources. Your ability to choose the right cost concept depends on the context, with opportunity cost providing a comprehensive view of trade-offs, explicit cost aiding clear financial accounting, and implicit cost revealing hidden sacrifices that influence long-term strategic decisions.
Infographic: Opportunity cost vs Explicit cost
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com