Single-tasking enhances relationship quality by promoting active listening and deeper emotional connection, while multitasking often leads to distracted interactions and misunderstandings. Discover insights on how focusing on one task at a time can improve your personal relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
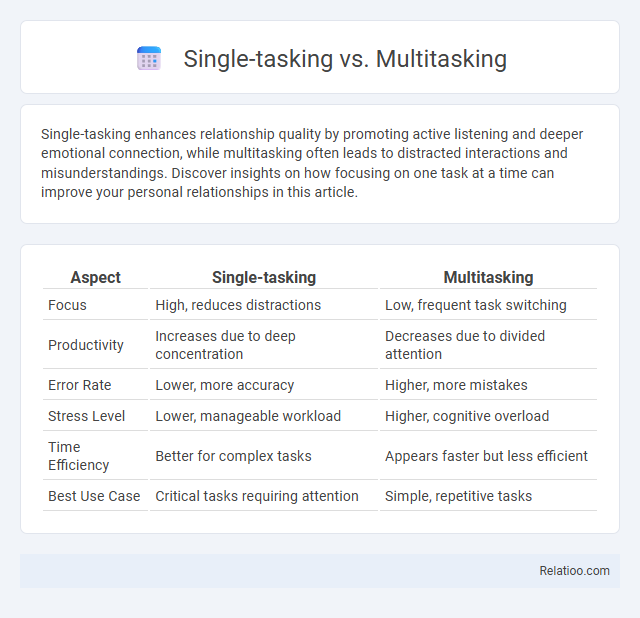
| Aspect | Single-tasking | Multitasking |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | High, reduces distractions | Low, frequent task switching |
| Productivity | Increases due to deep concentration | Decreases due to divided attention |
| Error Rate | Lower, more accuracy | Higher, more mistakes |
| Stress Level | Lower, manageable workload | Higher, cognitive overload |
| Time Efficiency | Better for complex tasks | Appears faster but less efficient |
| Best Use Case | Critical tasks requiring attention | Simple, repetitive tasks |
Introduction to Single-tasking and Multitasking
Single-tasking involves dedicated focus on one task at a time, which can improve concentration and quality of work by minimizing cognitive overload. Multitasking attempts to handle multiple activities simultaneously but often leads to reduced efficiency due to frequent task-switching and divided attention. Understanding these approaches highlights the balance between depth of engagement in single-tasking and the perceived productivity of multitasking.
Defining Single-tasking: Focus on One Task
Single-tasking emphasizes dedicated focus on a single task, enhancing concentration and reducing cognitive load for improved efficiency. This approach minimizes task-switching costs, leading to higher quality work and faster completion times compared to multitasking. Continuity in single-tasking supports sustained attention, enabling deeper understanding and better memory retention.
Understanding Multitasking: Juggling Multiple Tasks
Understanding multitasking involves recognizing the cognitive challenge of managing multiple tasks simultaneously, which often leads to decreased efficiency and increased errors due to divided attention. Single-tasking enables deeper focus and higher quality work by dedicating full cognitive resources to one task at a time. Continuity in task management emphasizes maintaining workflow momentum by minimizing context switching, thereby enhancing productivity and reducing mental fatigue.
Cognitive Impact: How the Brain Handles Tasks
Single-tasking enhances cognitive focus by allowing your brain to allocate full attention to one task, improving memory retention and reducing mental fatigue. Multitasking divides cognitive resources, often leading to decreased efficiency and increased errors due to frequent task-switching. Continuity supports sustained mental engagement by minimizing interruptions, allowing deeper processing and better cognitive performance over time.
Productivity Comparison: Which Yields Better Results?
Single-tasking enhances productivity by allowing focused attention on one task, reducing cognitive load and minimizing errors. Multitasking often leads to decreased efficiency due to frequent task-switching, which interrupts concentration and increases completion time. Continuity, emphasizing sustained work on related tasks, combines the benefits of deep focus with task progression, yielding superior results in overall productivity compared to fragmented multitasking approaches.
Stress and Mental Health Implications
Single-tasking reduces cognitive overload by allowing You to focus intensely on one task, which significantly lowers stress levels and supports better mental health. Multitasking divides attention and increases mental fatigue, often leading to heightened anxiety and decreased productivity. Continuity in tasks promotes a stable workflow and organization, minimizing stress by fostering a sense of control and reducing distractions.
Common Myths About Multitasking
Multitasking is often praised for boosting productivity, but numerous studies reveal that it can reduce efficiency by up to 40% due to frequent cognitive switching. Single-tasking allows your brain to focus deeply on one task, improving accuracy and retention, while continuity emphasizes maintaining attention on a task to achieve flow and consistent output. Understanding these dynamics helps you avoid common myths that multitasking saves time, uncovering that dedicated, continuous effort enhances overall performance and reduces mental fatigue.
Real-world Examples and Case Studies
Single-tasking enhances focus by allowing you to dedicate your full attention to one project, as demonstrated by studies showing increased productivity in creative fields like writing or design. Multitasking, common in customer service roles, can reduce efficiency due to cognitive switching costs, where performance drops by up to 40% according to research from Stanford University. Continuity, exemplified by software development teams using Agile methodologies, fosters seamless workflow and knowledge retention, improving project completion rates and reducing errors significantly.
Practical Tips for Effective Single-tasking
Effective single-tasking enhances productivity by minimizing distractions and improving focus on one task at a time, contrasting with the cognitive overload often caused by multitasking. Continuity in single-tasking can be maintained by setting specific time blocks for tasks, using techniques like the Pomodoro method, and eliminating potential interruptions such as notifications or unrelated apps. Prioritizing tasks and organizing the work environment contribute to sustained attention and higher quality output during focused work sessions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Personal Success
Choosing the right approach for personal success depends on understanding single-tasking, multitasking, and continuity. Single-tasking enhances focus and productivity by dedicating full attention to one task, reducing errors and cognitive load. Multitasking can handle multiple activities but often decreases efficiency and accuracy, while continuity emphasizes sustained effort and seamless transitions, fostering long-term goal achievement and consistent progress.
Infographic: Single-tasking vs Multitasking
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com