Multitasking allows simultaneous handling of multiple relationship tasks but can reduce focus and deepen misunderstandings, while batch processing dedicates focused time to specific issues, enhancing communication and problem-solving. Discover how adopting batch processing strategies can improve your relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
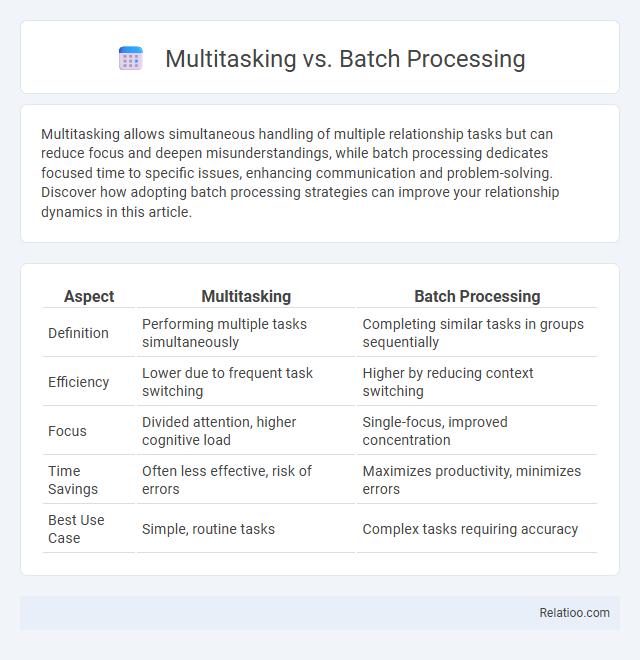
| Aspect | Multitasking | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Performing multiple tasks simultaneously | Completing similar tasks in groups sequentially |
| Efficiency | Lower due to frequent task switching | Higher by reducing context switching |
| Focus | Divided attention, higher cognitive load | Single-focus, improved concentration |
| Time Savings | Often less effective, risk of errors | Maximizes productivity, minimizes errors |
| Best Use Case | Simple, routine tasks | Complex tasks requiring accuracy |
Introduction to Multitasking and Batch Processing
Multitasking allows a computer system to execute multiple processes simultaneously by rapidly switching between tasks, enhancing responsiveness and resource utilization. Batch processing involves executing a series of jobs without user interaction, typically used for large-scale data operations where efficiency and throughput are prioritized. Comparing both, multitasking favors real-time task management while batch processing optimizes processing of grouped tasks in a sequential manner.
Defining Multitasking: Pros and Cons
Multitasking allows your computer to perform multiple tasks simultaneously by rapidly switching between processes, enhancing productivity and responsiveness for real-time applications. Pros include improved system utilization and faster user interaction, while cons involve potential performance degradation due to context switching and increased complexity in resource management. Understanding these trade-offs helps you optimize system performance based on workload characteristics compared to batch processing, which executes jobs sequentially without interruption.
Understanding Batch Processing: Key Features
Batch processing involves executing a series of non-interactive tasks, or jobs, in a scheduled sequence without user intervention, optimizing resource use and system efficiency. Key features include the ability to handle large volumes of data, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance throughput by processing jobs in groups during off-peak hours. This method contrasts with multitasking, where multiple processes run concurrently, and multiprocessing, where multiple CPUs handle tasks simultaneously, emphasizing batch processing's strength in handling bulk operations efficiently.
Efficiency Comparison: Multitasking vs Batch Processing
Multitasking maximizes efficiency by allowing simultaneous processing of multiple tasks, reducing idle CPU time and enhancing responsiveness in real-time applications. Batch processing optimizes resource use by executing large volumes of similar tasks sequentially without user intervention, ideal for data-heavy operations requiring minimal interaction. Compared to batch processing, multitasking is more efficient for environments demanding quick context switching and dynamic task management, while batch processing excels in throughput for large-scale, repetitive jobs.
Impact on Productivity: Which Method Wins?
Batch processing maximizes productivity by handling large volumes of tasks simultaneously without frequent interruptions, leading to efficient resource use and minimal context switching. Multitasking, while appearing efficient, often reduces overall productivity due to cognitive overload and task-switching costs that slow down task completion. Combining multitasking for minor tasks with batch processing for complex, repetitive processes often yields the best productivity balance in diverse workflows.
Use Cases: When to Choose Multitasking
Multitasking excels in environments requiring simultaneous execution of multiple interactive applications, such as real-time communication, gaming, and multitoken productivity tasks. It enables quick switching between processes, making it ideal for user-driven scenarios where responsiveness and immediate feedback are critical. Batch processing fits large-scale data or automated job queues with minimal user interaction, while multiprocessing distributes tasks across multiple CPUs for intensive computational loads, but multitasking remains best for dynamic, user-centric workloads demanding concurrency.
Use Cases: When to Prefer Batch Processing
Batch processing is ideal for handling large volumes of data that do not require immediate user interaction, such as payroll systems, data backups, and end-of-day report generation. Your system benefits from batch processing when tasks can be scheduled to run sequentially without disrupting real-time operations, ensuring optimized resource utilization and reduced system load. Unlike multitasking, which manages multiple tasks simultaneously for responsiveness, batch processing prioritizes efficiency and throughput in scenarios demanding high-volume, repetitive data handling.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in Both Approaches
Common mistakes in multitasking include overloading the CPU, leading to context-switching overhead and reduced performance, while batch processing pitfalls often involve improper job scheduling causing resource underutilization or bottlenecks. Confusing multitasking with multitheading results in inefficient parallelism, as multitasking handles multiple tasks by time-slicing rather than true concurrent execution. Both approaches suffer from a lack of prioritization, where failing to allocate adequate processing time or resources to critical tasks can degrade system responsiveness and throughput.
Tips for Optimizing Your Workflow
To optimize your workflow, prioritize batch processing for repetitive tasks to reduce context switching and increase efficiency. Use multitasking strategically by grouping similar activities to maintain focus and prevent cognitive overload. Your productivity improves when you balance multitasking with focused batch processing, leveraging each method's strengths to fit task complexity and urgency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Goals
Selecting the appropriate processing method depends on the specific goals and system requirements: multitasking excels in interactive environments by allowing simultaneous task execution, batch processing is ideal for large-scale, non-interactive jobs requiring efficient throughput, and multiprogramming maximizes CPU utilization by managing multiple programs in memory concurrently. Evaluating factors such as response time, resource availability, and workload type ensures optimal performance and resource management. Tailoring the choice to these criteria enhances system efficiency and user experience.
Infographic: Multitasking vs Batch Processing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com