Male orgasm typically involves a shorter, more intense climax, while female orgasm can vary significantly in duration, intensity, and frequency due to complex physiological and psychological factors. Explore the differences, similarities, and ways to enhance intimate experiences between partners in this article.
Table of Comparison
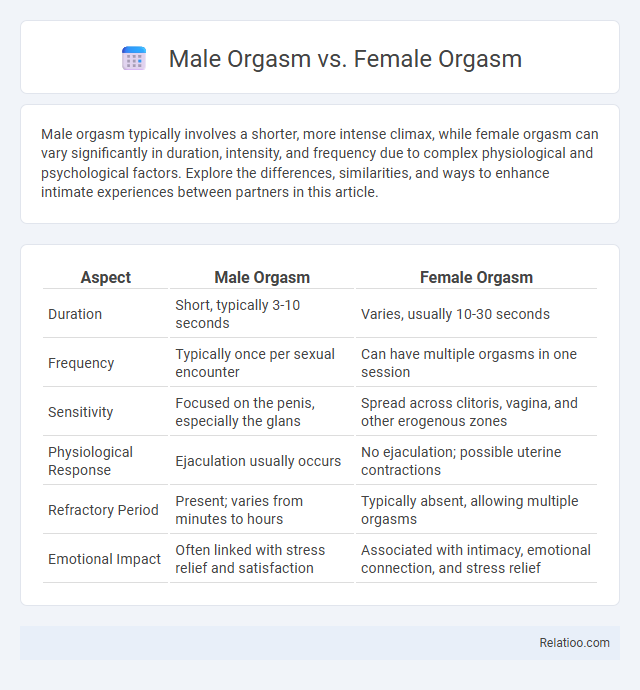
| Aspect | Male Orgasm | Female Orgasm |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short, typically 3-10 seconds | Varies, usually 10-30 seconds |
| Frequency | Typically once per sexual encounter | Can have multiple orgasms in one session |
| Sensitivity | Focused on the penis, especially the glans | Spread across clitoris, vagina, and other erogenous zones |
| Physiological Response | Ejaculation usually occurs | No ejaculation; possible uterine contractions |
| Refractory Period | Present; varies from minutes to hours | Typically absent, allowing multiple orgasms |
| Emotional Impact | Often linked with stress relief and satisfaction | Associated with intimacy, emotional connection, and stress relief |
Understanding the Science of Orgasms
Understanding the science of orgasms reveals distinct physiological and neurological differences between male and female experiences, reflecting variations in hormonal responses, muscle contractions, and brain activity. Research shows that while male orgasms typically involve a more singular, intense climax, female orgasms can exhibit multiple phases and longer durations, influenced by factors like emotional connection and physical stimulation. Enhancing Your knowledge of these complexities can improve communication and intimacy, leading to more satisfying sexual experiences.
Anatomy of Male vs Female Sexual Response
The anatomy of male and female sexual response differs significantly, with males primarily experiencing orgasm through penile stimulation leading to ejaculation, while females often have a more complex response involving clitoral, vaginal, and pelvic muscle contractions. Male orgasm is typically shorter and follows a more predictable sequence of arousal, plateau, orgasm, and resolution, whereas female orgasm can vary widely in duration, intensity, and physical manifestations. Understanding these anatomical differences helps you appreciate the unique physiological processes involved in male orgasm versus female orgasm.
Hormonal Differences in Orgasms
Hormonal differences significantly influence male orgasm, female orgasm, and the orgasm experience overall, with testosterone playing a key role in male sexual arousal and orgasm intensity. Female orgasms involve a complex interplay of hormones such as oxytocin, which enhances bonding and emotional connection, and estrogen, which increases sensitivity and lubrication. Understanding these hormonal variations helps you appreciate how physiological responses differ between sexes, impacting both pleasure and post-orgasmic effects.
Duration and Intensity: A Comparative Analysis
Male orgasms typically last 3 to 10 seconds with intense rhythmic contractions, while female orgasms often extend from 10 to 30 seconds and can include multiple peak phases, enhancing overall intensity. Research indicates that women may experience orgasms with varied patterns and durations, contributing to diverse sensations and potentially higher cumulative intensity. Understanding these differences can help you tailor intimate experiences for greater mutual satisfaction and deeper connection.
Psychological Factors Influencing Orgasm
Psychological factors significantly influence the experience of orgasm, with differences observed between male and female responses. Research indicates that stress, anxiety, and emotional connection strongly impact female orgasmic function, often requiring higher levels of mental relaxation and intimacy. In contrast, male orgasm is typically more directly linked to physiological stimulation but can also be affected by psychological states such as performance anxiety and self-esteem.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Many common myths about male and female orgasms include the belief that male orgasms are always linked to ejaculation and that female orgasms are solely vaginal or clitoral. Scientific research shows that orgasms, regardless of gender, can vary widely in intensity, duration, and sensation, debunking the idea of a "normal" orgasm. Understanding these misconceptions helps you appreciate the complexity and diversity of human sexual response.
The Role of Emotional Connection
Emotional connection significantly enhances the intensity and satisfaction of both male and female orgasms, influencing physiological and psychological responses during sexual climax. Studies show that women typically experience stronger orgasms when there is a deep emotional bond, while men also report increased pleasure and intimacy when emotionally connected to their partner. Overall, the role of emotional connection in orgasm underscores the interplay between mental and physical factors in sexual fulfillment.
Frequency and Triggers of Orgasm
Male orgasm typically occurs more frequently and is often triggered by direct physical stimulation of the genitals, while female orgasm varies widely in frequency and can be triggered by a combination of physical, emotional, and psychological factors. Understanding the diverse triggers, such as clitoral stimulation, mental arousal, and intimate connection, highlights why female orgasms might be less predictable but deeply nuanced. Your awareness of these differences can enhance sexual satisfaction and communication around orgasmic experiences.
Health Benefits of Orgasms for Men and Women
Orgasms provide significant health benefits for both men and women, including stress reduction, enhanced immune function, and improved cardiovascular health through increased heart rate and blood flow. Male orgasms often promote prostate health and help release built-up tension, while female orgasms contribute to pelvic floor muscle strengthening and hormonal balance. Overall, orgasms stimulate the release of endorphins and oxytocin, which enhance mood, promote pain relief, and support emotional bonding across genders.
Enhancing Orgasmic Experiences: Tips for Both Genders
Enhancing orgasmic experiences for both males and females involves understanding physiological differences such as the male refractory period and the female potential for multiple orgasms. Techniques like mindful breathing, pelvic floor exercises, and communication about preferences can intensify pleasure and prolong climax duration. Incorporating sensual touch and varying stimulation methods tailored to individual responses significantly boosts satisfaction for all genders.
Infographic: Male Orgasm vs Female Orgasm
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com