Visual stimulation in relationships enhances immediate attraction and nonverbal communication, while mental stimulation fosters deeper emotional connection and long-term compatibility. Discover how balancing both can strengthen your bond in this article.
Table of Comparison
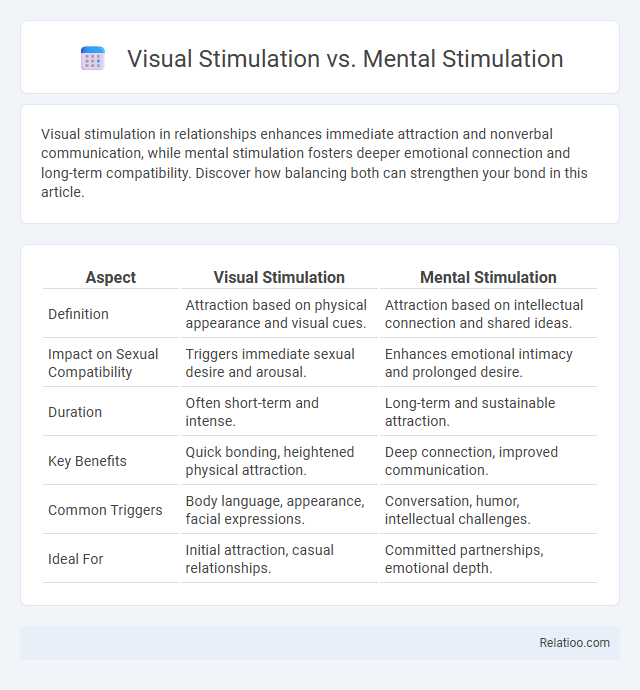
| Aspect | Visual Stimulation | Mental Stimulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attraction based on physical appearance and visual cues. | Attraction based on intellectual connection and shared ideas. |
| Impact on Sexual Compatibility | Triggers immediate sexual desire and arousal. | Enhances emotional intimacy and prolonged desire. |
| Duration | Often short-term and intense. | Long-term and sustainable attraction. |
| Key Benefits | Quick bonding, heightened physical attraction. | Deep connection, improved communication. |
| Common Triggers | Body language, appearance, facial expressions. | Conversation, humor, intellectual challenges. |
| Ideal For | Initial attraction, casual relationships. | Committed partnerships, emotional depth. |
Understanding Visual Stimulation: Definition and Examples
Visual stimulation refers to the process of activating the visual system through exposure to various images, colors, patterns, or movements that engage your eyes and brain. Examples include watching vibrant scenes, observing dynamic shapes, or experiencing changes in light intensity, all of which can enhance cognitive processing and emotional responses. Distinguishing visual stimulation from mental stimulation, which involves deeper cognitive engagement, and arousal, which pertains to physiological alertness, is essential for optimizing your sensory experiences.
What Is Mental Stimulation? Key Concepts Explained
Mental stimulation involves engaging cognitive processes such as thinking, memory, problem-solving, and creativity to enhance brain function and neuroplasticity. Unlike visual stimulation, which primarily activates sensory pathways, mental stimulation activates neural networks related to executive function and learning. Arousal refers to a physiological and psychological state of alertness that can modulate the effectiveness of both visual and mental stimulation by influencing attention and cognitive performance.
Visual vs. Mental Stimulation: Core Differences
Visual stimulation activates the brain through sensory input from sights, colors, and movements, engaging the occipital lobe and enhancing visual perception. Mental stimulation involves cognitive processes such as problem-solving, memory, and reasoning that activate the prefrontal cortex, promoting neuroplasticity and intellectual growth. Your brain reacts differently to these types of stimulation, with visual stimuli primarily triggering sensory pathways, while mental tasks demand deeper cognitive engagement and executive functioning.
Neuroscience Behind Visual and Mental Stimulation
Visual stimulation activates the brain's occipital lobe, enhancing neural pathways related to visual processing and attention, while mental stimulation engages the prefrontal cortex, boosting cognitive functions such as memory, reasoning, and problem-solving. Neuroscientific studies reveal that visual stimuli trigger rapid neural responses through the thalamus, facilitating immediate sensory perception, whereas mental tasks promote neuroplasticity and synaptic strengthening critical for long-term cognitive health. Arousal levels modulate these processes by influencing neurotransmitter release, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine, which enhance alertness and cognitive performance during both visual and mental stimulation.
Benefits of Visual Stimulation for Cognitive Health
Visual stimulation enhances cognitive health by activating neural pathways involved in perception, attention, and memory formation. Exposure to vibrant colors, shapes, and patterns promotes neuroplasticity, improving processing speed and problem-solving abilities. Regular visual engagement supports mental agility and can reduce the risk of cognitive decline associated with aging and neurological disorders.
How Mental Stimulation Boosts Brain Function
Mental stimulation enhances neuroplasticity by promoting the formation of new neural connections, which improves memory, problem-solving skills, and cognitive flexibility. Engaging in complex tasks like puzzles or learning new languages activates multiple brain regions, increasing neurotransmitter production and overall brain efficiency. Compared to visual stimulation or general arousal, mental stimulation provides targeted cognitive challenges that sustain long-term brain health and delay cognitive decline.
Common Activities: Visual Stimulation in Everyday Life
Visual stimulation in everyday life involves engaging activities such as observing natural landscapes, scrolling through vibrant social media feeds, or watching dynamic videos, which activate the brain's visual cortex and enhance cognitive processing. Mental stimulation through puzzles, reading, or problem-solving tasks challenges the brain's executive functions and memory, promoting neural plasticity. Arousal, influenced by stimulating environments or emotional experiences, regulates attention and physiological responses, underpinning how visual and mental stimuli are perceived and processed.
Effective Strategies for Mental Stimulation
Effective mental stimulation involves engaging activities that challenge cognitive functions, such as puzzles, reading, and problem-solving tasks that enhance memory, attention, and critical thinking skills. Visual stimulation, while beneficial for sensory processing and alertness, primarily activates the occipital lobe and is less effective alone in promoting complex cognitive development. Arousal, characterized by physiological and psychological alertness, supports mental stimulation by preparing the brain for optimal information processing, making combined strategies involving cognitive challenges and controlled arousal levels most beneficial for enhancing mental performance.
Integrating Visual and Mental Stimulation for Optimal Wellness
Integrating visual and mental stimulation enhances cognitive function by engaging multiple neural pathways, promoting neuroplasticity and improving memory retention. Visual stimuli activate the occipital lobe and sensory cortices, while mental tasks stimulate the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, creating a synergistic effect that supports optimal brain health. Combining these types of stimulation with appropriate arousal levels optimizes alertness and emotional regulation, fostering overall wellness and cognitive resilience.
Choosing the Right Stimulation: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right stimulation involves understanding the differences between visual stimulation, mental stimulation, and arousal to optimize cognitive and emotional outcomes. Visual stimulation enhances sensory processing and attention through dynamic imagery, while mental stimulation engages higher cognitive functions like problem-solving and memory, promoting neuroplasticity. Arousal levels must be regulated to balance alertness and relaxation, as excessive stimulation can lead to stress, and insufficient stimulation may result in cognitive underperformance.
Infographic: Visual Stimulation vs Mental Stimulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com