Sexual desire refers to the psychological interest or craving for sexual activity, while sexual arousal is the physiological response involving blood flow and genital sensitivity. Explore this article to understand the key differences and how they impact intimate relationships.
Table of Comparison
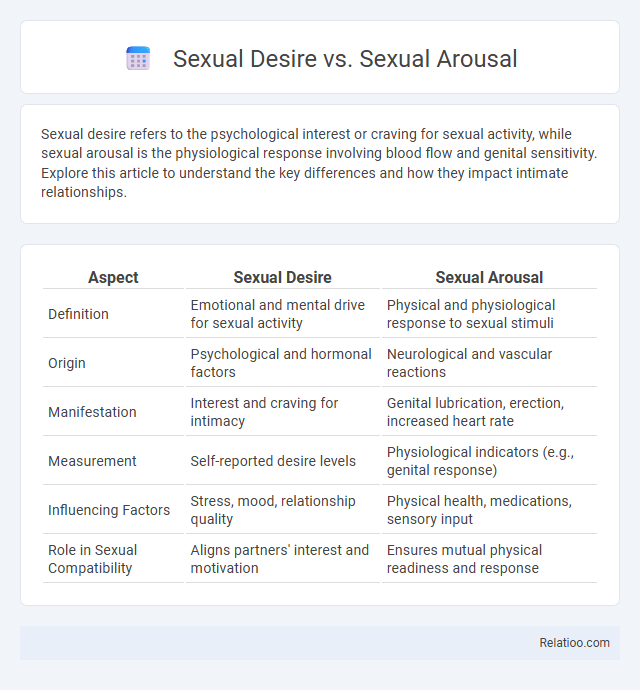
| Aspect | Sexual Desire | Sexual Arousal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional and mental drive for sexual activity | Physical and physiological response to sexual stimuli |
| Origin | Psychological and hormonal factors | Neurological and vascular reactions |
| Manifestation | Interest and craving for intimacy | Genital lubrication, erection, increased heart rate |
| Measurement | Self-reported desire levels | Physiological indicators (e.g., genital response) |
| Influencing Factors | Stress, mood, relationship quality | Physical health, medications, sensory input |
| Role in Sexual Compatibility | Aligns partners' interest and motivation | Ensures mutual physical readiness and response |
Understanding Sexual Desire: Definition and Key Features
Sexual desire refers to the intrinsic motivation or interest in engaging in sexual activity, characterized by psychological and emotional components such as longing, anticipation, and fantasies. It differs from sexual arousal, which involves physiological responses like increased blood flow, lubrication, and genital sensitivity triggered by physical or sensory stimuli. Erotic experience encompasses a broader spectrum that includes sexual desire, arousal, and the psychological context of pleasure, fantasy, and intimacy, defining a complex interplay between mind and body in sexual expression.
What is Sexual Arousal? Exploring the Basics
Sexual arousal refers to the physiological and psychological responses triggered by sexual stimuli, involving increased heart rate, blood flow to genital areas, and heightened sensory awareness. It differs from sexual desire, which is the emotional longing or interest in sexual activity, and from erotic, which relates to content or experiences that induce sexual excitement. Understanding sexual arousal encompasses recognizing its biological mechanisms, including hormonal influences and nervous system activation essential for sexual function and response.
The Science Behind Sexual Desire
Sexual desire refers to the psychological motivation or interest in engaging in sexual activity, rooted in brain regions like the hypothalamus and influenced by hormones such as testosterone and dopamine. Sexual arousal involves physiological responses including increased blood flow, heart rate, and genital sensitivity, often triggered by sensory stimuli and mediated by the autonomic nervous system. Your understanding of the science behind sexual desire helps distinguish it from arousal and eroticism, where desire is the internal drive, arousal is the body's response, and erotic relates to stimuli that evoke sexual feelings.
The Physiology of Sexual Arousal
Sexual arousal involves complex physiological responses including increased blood flow to genital tissues, elevated heart rate, and hormonal changes primarily driven by the autonomic nervous system. Unlike sexual desire, which is a psychological motivation or interest in sexual activity, arousal refers specifically to the body's physical readiness for sexual activity manifested through these measurable bodily changes. Erotic stimuli trigger brain regions such as the hypothalamus and limbic system, which coordinate these autonomic and endocrine responses essential for sexual arousal.
Sexual Desire vs Sexual Arousal: Key Differences
Sexual desire refers to the psychological motivation or interest in engaging in sexual activity, driven by emotional and cognitive factors, whereas sexual arousal is the physiological response involving increased blood flow, heart rate, and genital changes. Desire can exist without physical arousal, highlighting a key distinction where psychological craving precedes or occurs independently of bodily reactions. Erotic stimuli often trigger both desire and arousal but are not synonymous, as erotic refers broadly to content or feelings related to sexual excitement without defining the psychological or physiological state specifically.
Psychological Factors Influencing Desire and Arousal
Sexual desire and sexual arousal are distinct yet interrelated psychological states influenced by cognitive appraisals, emotional well-being, and hormonal fluctuations. Desire involves motivational and anticipatory components driven by neurochemical systems such as dopamine, whereas arousal pertains to physiological and autonomic nervous system responses facilitating genital blood flow and sensitivity. Erotic stimuli activate brain regions like the hypothalamus and limbic system, modulating both desire and arousal through complex interactions of attention, memory, and subjective interpretation.
How Relationships Impact Sexual Desire and Arousal
Sexual desire is the psychological motivation to engage in sexual activity, while sexual arousal refers to the physiological response, such as increased blood flow and genital sensitivity, and erotic elements encompass the sensory and imaginative stimuli that trigger these responses. In relationships, your emotional connection, communication, and intimacy levels significantly influence both sexual desire and arousal, with trust and satisfaction enhancing overall sexual wellbeing. Strengthening relationship bonds can elevate erotic experiences, promoting a healthier and more fulfilling sexual dynamic between partners.
Common Myths About Sexual Desire and Arousal
Sexual desire and sexual arousal are often mistakenly considered identical, but desire refers to the psychological interest in sexual activity, while arousal is the physical response involving increased blood flow and genital sensation. Common myths include the belief that sexual desire always triggers arousal and that arousal guarantees desire, which oversimplifies complex neurobiological and emotional processes. Erotic stimuli can elicit arousal without desire, highlighting the difference between automatic bodily reactions and conscious sexual motivation.
Addressing Issues: Low Sexual Desire vs Arousal Problems
Low sexual desire involves a reduced interest in sexual activity, while arousal problems relate to difficulty achieving or maintaining physical sexual excitement. Addressing your specific issue requires identifying whether the root cause is psychological, hormonal, or physiological, as treatments differ for desire versus arousal concerns. Understanding the distinction between sexual desire, sexual arousal, and erotic stimuli helps tailor effective strategies to improve your sexual wellbeing.
Enhancing Sexual Wellness: Strategies for Balancing Desire and Arousal
Enhancing sexual wellness requires understanding the distinct roles of sexual desire, sexual arousal, and erotic stimuli in overall sexual health. Sexual desire is the psychological interest in sexual activity, while sexual arousal refers to the physiological response, such as increased blood flow and sensitivity, often triggered by erotic cues. Strategies for balancing desire and arousal include mindful communication, stress reduction techniques, and incorporating diverse erotic experiences to improve intimacy and satisfaction.
Infographic: Sexual Desire vs Sexual Arousal
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com