Physical chemistry involves the study of molecular interactions and energy changes in chemical reactions, while sexual attraction encompasses biological and psychological factors driving human desire. Discover the detailed differences and insights on how these concepts influence relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
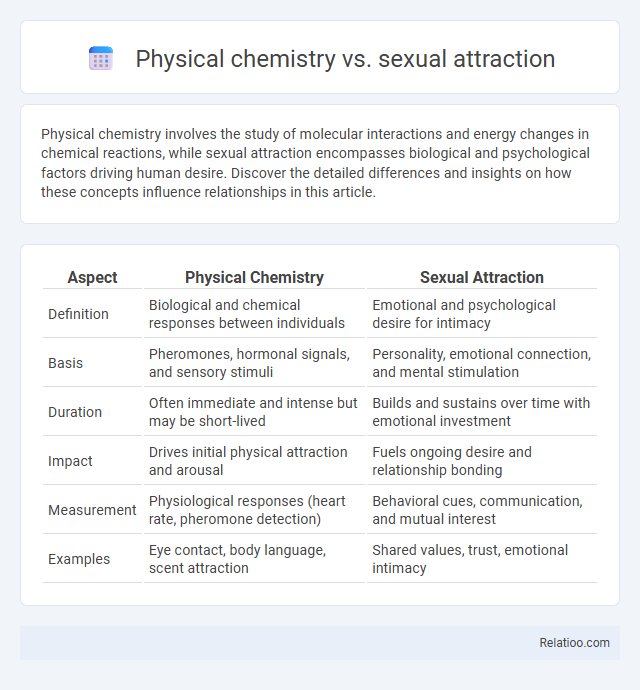
| Aspect | Physical Chemistry | Sexual Attraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological and chemical responses between individuals | Emotional and psychological desire for intimacy |
| Basis | Pheromones, hormonal signals, and sensory stimuli | Personality, emotional connection, and mental stimulation |
| Duration | Often immediate and intense but may be short-lived | Builds and sustains over time with emotional investment |
| Impact | Drives initial physical attraction and arousal | Fuels ongoing desire and relationship bonding |
| Measurement | Physiological responses (heart rate, pheromone detection) | Behavioral cues, communication, and mutual interest |
| Examples | Eye contact, body language, scent attraction | Shared values, trust, emotional intimacy |
Defining Physical Chemistry in Scientific Terms
Physical chemistry scientifically examines the principles and mechanisms governing molecular interactions, energy changes, and reaction dynamics, providing a fundamental understanding of how atoms and molecules behave. Sexual attraction involves psychological and biological factors triggering desire and partner selection, while physical attraction focuses on visual and sensory cues influencing initial physical appeal. To enhance Your comprehension, distinguish physical chemistry as a rigorous scientific discipline explaining chemical behavior, distinct from the emotional and sensory experiences of attraction.
What is Sexual Attraction?
Sexual attraction is an emotional and biological response that draws individuals toward potential mates based on physical, psychological, and pheromonal cues. Unlike physical chemistry, which refers to the scientific interactions between molecules, and physical attraction, which focuses solely on aesthetic appeal, sexual attraction encompasses complex hormonal, neurological, and interpersonal factors driving desire. Understanding your sexual attraction involves recognizing these multi-dimensional influences beyond mere physical appearance.
Key Differences Between Physical Chemistry and Sexual Attraction
Physical chemistry involves the study of physical properties and behaviors of molecules, emphasizing chemical reactions and thermodynamics, whereas sexual attraction relates to the biological and psychological stimuli that trigger desire between individuals. Physical attraction, distinct from sexual attraction, centers on the visual or aesthetic appeal one person has for another, often based on appearance or body language without necessarily involving deeper emotional or chemical connections. Key differences lie in the scope--physical chemistry is a scientific discipline analyzing molecular interactions, while sexual and physical attraction concern human interpersonal dynamics driven by emotion, biology, and perception.
The Role of Molecules in Physical Chemistry vs. Human Chemistry
Physical chemistry explores the interactions of molecules through bonds and reactions, explaining phenomena such as energy transfer and molecular stability. In human chemistry, physical attraction and sexual attraction are influenced by biochemical molecules like pheromones, hormones (e.g., dopamine, oxytocin), and neurotransmitters, which affect emotional and physical responses. The molecular basis in physical chemistry provides a foundation for understanding the chemical signals and receptor interactions driving human attraction and bonding mechanisms.
Psychological Factors Influencing Sexual Attraction
Psychological factors influencing sexual attraction include personality traits, emotional connection, and individual preferences shaped by past experiences and cultural background. Your perception of physical attraction is often intertwined with these mental and emotional elements, which can amplify or diminish initial physical chemistry. Understanding the psychological underpinnings helps differentiate between mere physical attraction and deeper sexual attraction driven by both mind and body.
Biological and Chemical Basis of Attraction
Physical chemistry explores molecular interactions and chemical reactions, laying the foundation for understanding the biological basis of attraction through neurotransmitters like dopamine and oxytocin. Sexual attraction involves hormonal influences such as testosterone and estrogen, which trigger physiological responses impacting mate selection and reproductive behaviors. Your experience of physical attraction is driven by a complex interplay of biochemical signals and sensory stimuli that activate brain regions responsible for reward and bonding.
How Environment Shapes Physical and Sexual Interactions
Environmental factors like temperature, lighting, and social settings influence both physical chemistry and attraction by affecting hormone levels and sensory perception. Physical attraction is often shaped by cues responsive to environmental contexts, such as body scent or visual signals heightened in specific surroundings. Sexual attraction, intertwined with physical and psychological stimuli, is modulated by social and ecological environments that impact emotional bonding and mate selection behaviors.
Physical Chemistry in Everyday Phenomena
Physical chemistry explores the interactions and energy changes at molecular and atomic levels, providing insights into everyday phenomena such as cooking, cleaning, and bodily functions. Physical attraction involves immediate sensory and biological responses to someone's appearance, while sexual attraction combines emotional, psychological, and physical stimuli driving desire and mating behavior. Understanding physical chemistry enhances comprehension of natural processes underlying both physical and sexual attraction in human experiences.
Social and Cultural Influences on Sexual Attraction
Social and cultural influences significantly shape sexual attraction by defining which physical traits are deemed desirable within different communities and historical periods. Media representations, cultural norms, and societal values contribute to the perception of physical attraction, often dictating standards of beauty and influencing interpersonal relationships. Understanding these factors reveals how sexual attraction is not purely a biological response but is deeply embedded in social and cultural contexts.
Integrating Physical Chemistry Concepts in Understanding Human Relationships
Physical chemistry principles such as molecular interactions, energy exchange, and reaction kinetics provide a scientific framework for analyzing the biochemical basis of sexual and physical attraction in human relationships. You can better understand how neurotransmitters, pheromones, and hormonal changes influence emotional bonding and physical desire by integrating concepts like thermodynamics and chemical equilibrium. This approach reveals the dynamic and quantifiable nature of attraction, bridging the gap between physical chemistry and the complex chemistry of human connection.
Infographic: Physical Chemistry vs Sexual Attraction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com