Cisgender individuals identify with the gender assigned at birth, while transgender individuals have a gender identity differing from their birth sex, impacting relationship dynamics and communication. Explore how understanding these differences can enhance empathy and strengthen partnerships in this article.
Table of Comparison
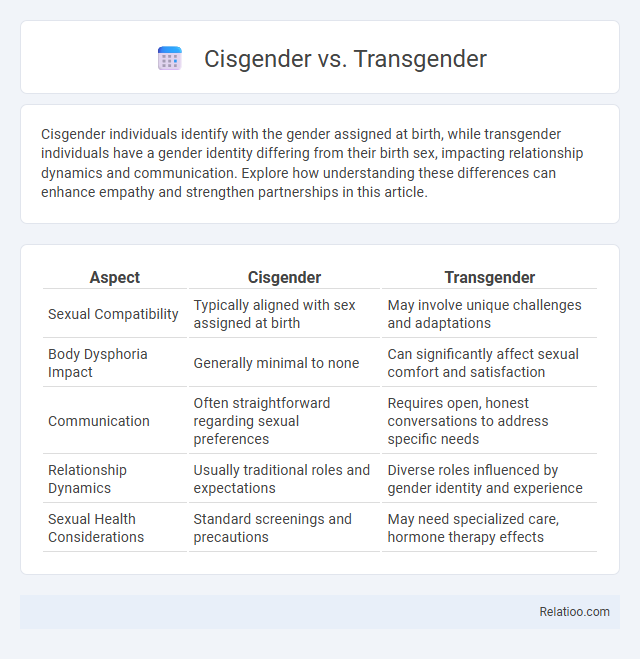
| Aspect | Cisgender | Transgender |
|---|---|---|
| Sexual Compatibility | Typically aligned with sex assigned at birth | May involve unique challenges and adaptations |
| Body Dysphoria Impact | Generally minimal to none | Can significantly affect sexual comfort and satisfaction |
| Communication | Often straightforward regarding sexual preferences | Requires open, honest conversations to address specific needs |
| Relationship Dynamics | Usually traditional roles and expectations | Diverse roles influenced by gender identity and experience |
| Sexual Health Considerations | Standard screenings and precautions | May need specialized care, hormone therapy effects |
Understanding Gender Identity
Gender identity refers to a person's deeply felt internal experience of gender, which may or may not correspond with the sex assigned at birth. Cisgender individuals have a gender identity that aligns with their assigned sex, while transgender individuals have a gender identity that differs from their assigned sex. Understanding gender identity involves recognizing the diverse ways people experience and express their gender beyond binary categories, emphasizing personal authenticity and self-recognition.
What Does Cisgender Mean?
Cisgender refers to individuals whose gender identity aligns with the sex assigned to them at birth, reflecting a congruence between biological sex and personal identity. This term contrasts with transgender, where a person's gender identity differs from their assigned sex, highlighting the diversity of gender experiences. Understanding cisgender as one aspect of gender identity helps clarify social dynamics and promotes inclusivity in discussions about gender.
Defining Transgender
Transgender individuals have a gender identity that differs from the sex they were assigned at birth, reflecting a deeply personal and intrinsic sense of self. Gender identity encompasses a person's internal experience and understanding of their gender, which may be male, female, a blend of both, or neither. Cisgender refers to those whose gender identity aligns with their birth-assigned sex, while transgender people often pursue social, medical, or legal steps to affirm their gender identity.
Key Differences: Cisgender vs. Transgender
Cisgender individuals have a gender identity that aligns with the sex they were assigned at birth, while transgender people experience a gender identity different from their assigned sex. Your understanding of gender identity encompasses personal, deeply-held feelings about being male, female, both, neither, or somewhere along the gender spectrum. Recognizing these key differences is essential for fostering inclusivity and respecting diverse gender experiences.
Social Perceptions and Misconceptions
Social perceptions of cisgender individuals often assume alignment between gender identity and assigned sex at birth, which influences societal norms and expectations. Misconceptions about transgender people frequently involve misunderstanding gender identity as a choice rather than an intrinsic aspect of self, leading to stigma and discrimination. Your awareness of these distinctions promotes inclusivity and challenges harmful stereotypes within communities.
Challenges Faced by Transgender Individuals
Transgender individuals often face significant challenges including social stigma, discrimination in employment and healthcare, and legal barriers to changing gender markers. Compared to cisgender people, who identify with their sex assigned at birth, transgender individuals experience higher rates of mental health issues due to societal rejection and lack of support. Access to gender-affirming care and inclusive policies remains crucial to improving the wellbeing of transgender communities.
The Importance of Pronouns and Language
Understanding the distinctions between cisgender, transgender, and gender identity is crucial for respecting individual experiences and promoting inclusivity. Using correct pronouns affirms a person's identity, fosters dignity, and reduces misgendering, which can impact mental health and social acceptance. Your awareness and intentional use of appropriate language contribute significantly to creating supportive environments for all gender identities.
Legal Rights and Protections
Cisgender individuals often benefit from implicit legal recognition due to their gender identity matching their sex assigned at birth, resulting in fewer legal challenges related to identification and discrimination. Transgender people face varying levels of legal rights and protections depending on jurisdiction, with some regions offering comprehensive laws against discrimination and access to gender-affirming healthcare, while others lack explicit protections or recognition of gender identity. Legal recognition of gender identity is crucial for accessing rights such as accurate identity documents, protection against workplace discrimination, and the ability to legally change one's gender marker, impacting the lived experiences and legal status of transgender individuals.
Supporting Gender Diversity
Supporting gender diversity involves recognizing and respecting the distinctions between cisgender individuals, whose gender identity aligns with their sex assigned at birth, and transgender individuals, whose gender identity differs from that assignment. Embracing gender diversity promotes inclusivity by affirming each person's self-identified gender identity, which encompasses a broad spectrum beyond the binary framework. Educational initiatives and inclusive policies enhance understanding and acceptance, fostering environments where all gender identities are validated and supported.
Fostering Inclusivity and Respect
Cisgender individuals identify with the gender assigned to them at birth, while transgender people experience a gender identity differing from their assigned sex, highlighting the importance of recognizing diverse gender experiences to foster inclusivity. Promoting respect involves using correct pronouns, supporting gender-affirming policies, and creating safe spaces where all gender identities are validated. Emphasizing education about gender identity variations empowers communities to challenge discrimination and build greater acceptance across social, educational, and workplace environments.
Infographic: Cisgender vs Transgender
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com