Safe sex practices significantly reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies, promoting healthier relationships. Understanding the differences and benefits of safe sex versus unprotected sex can enhance your knowledge and decision-making; learn more in this article.
Table of Comparison
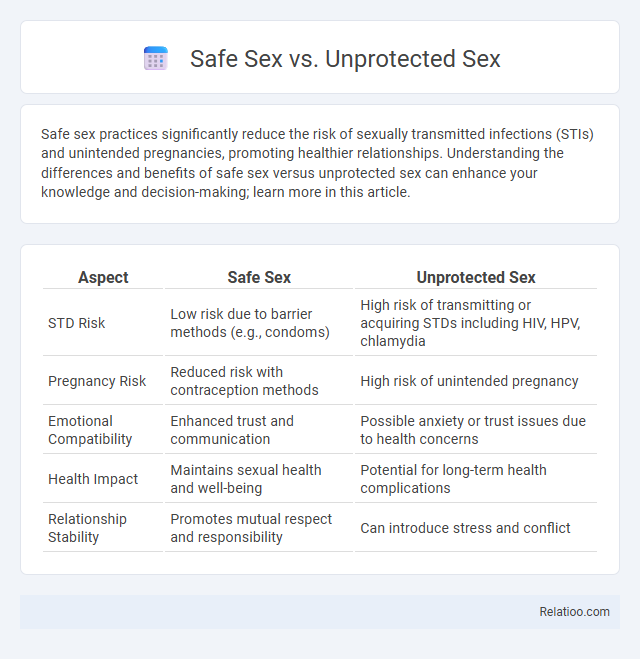
| Aspect | Safe Sex | Unprotected Sex |
|---|---|---|
| STD Risk | Low risk due to barrier methods (e.g., condoms) | High risk of transmitting or acquiring STDs including HIV, HPV, chlamydia |
| Pregnancy Risk | Reduced risk with contraception methods | High risk of unintended pregnancy |
| Emotional Compatibility | Enhanced trust and communication | Possible anxiety or trust issues due to health concerns |
| Health Impact | Maintains sexual health and well-being | Potential for long-term health complications |
| Relationship Stability | Promotes mutual respect and responsibility | Can introduce stress and conflict |
Understanding Safe Sex Practices
Understanding safe sex practices involves using barrier methods like condoms and dental dams to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unwanted pregnancies. Regular testing for STIs and open communication with partners are crucial components of maintaining sexual health. Practicing safe sex promotes physical well-being and emotional security, distinguishing it from unprotected sex, which increases vulnerability to infections and health complications.
Defining Unprotected Sex
Unprotected sex refers to sexual intercourse without the use of barrier methods such as condoms, increasing the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. Safe sex practices prioritize the use of protection, regular STI testing, and open communication between partners to reduce health risks. Maintaining sexual health involves a comprehensive approach that includes protection, consent, and access to healthcare resources.
Risks Associated with Unprotected Sex
Unprotected sex significantly increases the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as HIV, chlamydia, and gonorrhea, as well as unintended pregnancies. Practicing safe sex through consistent use of condoms and regular STI testing helps safeguard your sexual health by reducing exposure to these risks. Understanding the dangers associated with unprotected sex empowers you to make informed decisions that protect your overall well-being.
Benefits of Practicing Safe Sex
Practicing safe sex significantly reduces the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unwanted pregnancies, protecting your long-term reproductive health. Consistent use of condoms and regular sexual health screenings contribute to safer intimacy and peace of mind. Prioritizing safe sex ensures your overall well-being, fostering healthy relationships and enhancing sexual satisfaction.
Methods of Protection During Sexual Activity
Methods of protection during sexual activity include the consistent use of condoms, dental dams, and hormonal contraceptives that significantly reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. Safe sex practices involve not only barrier methods like male and female condoms but also regular STI testing and open communication between partners about sexual health status. Unprotected sex, lacking these protective measures, greatly increases vulnerability to infections such as HIV, chlamydia, and gonorrhea, as well as the possibility of unplanned pregnancy.
STI Prevention: Safe Sex vs Unprotected Sex
Safe sex practices, including the consistent use of condoms and regular STI testing, significantly reduce the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Unprotected sex, involving the absence of barrier methods, increases the risk of contracting and spreading STIs such as HIV, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. Prioritizing sexual health through education and preventive measures enhances overall well-being and decreases STI prevalence.
Unplanned Pregnancy: Comparing the Risks
Unprotected sex significantly increases the risk of unplanned pregnancy compared to safe sex practices, which involve the use of contraception methods such as condoms or birth control pills. Sexual health encompasses awareness and prevention strategies that reduce these risks, promoting informed decisions to protect Your reproductive well-being. Understanding the differences between safe sex and unprotected sex is crucial in minimizing the chances of unintended pregnancy and maintaining overall sexual health.
Emotional and Psychological Impacts
Safe sex practices significantly reduce anxiety and stress linked to the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies, promoting emotional well-being. Unprotected sex often leads to feelings of guilt, fear, and heightened emotional vulnerability due to potential health risks and social consequences. Prioritizing sexual health through education and communication fosters psychological resilience, self-esteem, and healthier intimate relationships.
Communication and Consent in Sexual Health
Effective communication and mutual consent are fundamental components of sexual health, serving as the foundation for safe sex practices that prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. Discussing boundaries, contraception options, and STI status openly strengthens trust and ensures all partners are fully informed and comfortable. Prioritizing consent and transparent dialogue significantly reduces risks associated with unprotected sex and fosters healthier intimate relationships.
Making Informed Decisions for Sexual Well-being
Making informed decisions about your sexual well-being involve understanding the differences between safe sex and unprotected sex. Safe sex practices, such as using condoms and regular STI testing, significantly reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections and unintended pregnancies. Prioritizing sexual health means being proactive, informed, and communicative to ensure a positive and responsible sexual experience.
Infographic: Safe Sex vs Unprotected Sex
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com