Sexual trauma involves past abusive or non-consensual experiences that impact intimacy, while sexual incompatibility arises from differing preferences or desires between partners. Explore how understanding these distinctions can improve relationship dynamics in this article.
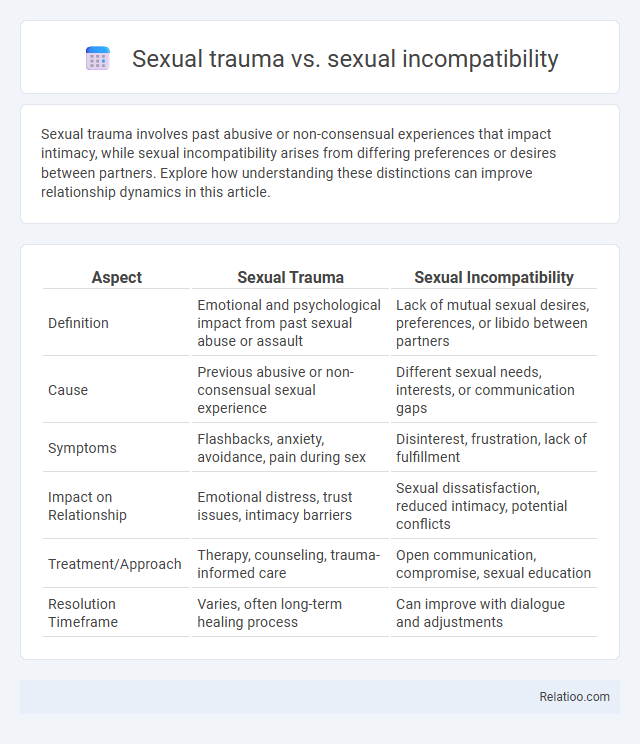
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sexual Trauma | Sexual Incompatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional and psychological impact from past sexual abuse or assault | Lack of mutual sexual desires, preferences, or libido between partners |
| Cause | Previous abusive or non-consensual sexual experience | Different sexual needs, interests, or communication gaps |
| Symptoms | Flashbacks, anxiety, avoidance, pain during sex | Disinterest, frustration, lack of fulfillment |
| Impact on Relationship | Emotional distress, trust issues, intimacy barriers | Sexual dissatisfaction, reduced intimacy, potential conflicts |
| Treatment/Approach | Therapy, counseling, trauma-informed care | Open communication, compromise, sexual education |
| Resolution Timeframe | Varies, often long-term healing process | Can improve with dialogue and adjustments |
Understanding Sexual Trauma: Definitions and Types
Sexual trauma encompasses experiences of sexual abuse, assault, or violence causing lasting psychological and physical effects. It differs from sexual incompatibility, which refers to mismatched desires or preferences between partners without traumatic impact. Understanding sexual trauma involves recognizing various types such as childhood abuse, assault, or coercion, each requiring tailored healing approaches for your recovery.
Defining Sexual Incompatibility in Relationships
Sexual incompatibility in relationships refers to a mismatch in sexual desires, preferences, or needs between partners, often leading to dissatisfaction and conflict. Unlike sexual trauma, which involves a history of abuse causing psychological and emotional distress, sexual incompatibility stems from differences in libido, communication, or intimacy styles. Understanding and addressing sexual incompatibility through open dialogue and counseling can improve relationship satisfaction and intimacy.
Key Differences Between Sexual Trauma and Sexual Incompatibility
Sexual trauma involves a history of abusive or non-consensual sexual experiences that profoundly impact an individual's emotional and physical response to intimacy, often requiring therapeutic intervention for healing. Sexual incompatibility refers to mismatched sexual desires, preferences, or frequencies between partners, which typically affects relationship satisfaction but does not stem from trauma. The key differences lie in the origin--sexual trauma is rooted in distressing events causing psychological harm, whereas sexual incompatibility arises from differing sexual needs without inherent psychological damage.
Common Signs of Sexual Trauma vs Sexual Incompatibility
Common signs of sexual trauma include flashbacks, anxiety during intimacy, and avoidance of sexual activity, reflecting deep emotional distress and potential PTSD symptoms. Sexual incompatibility often manifests through differing libido levels, mismatched sexual preferences, and communication challenges, without the trauma-related psychological responses. Recognizing these differences aids in targeted therapeutic approaches, with trauma requiring trauma-informed care and incompatibility focusing on improved communication and mutual understanding.
Psychological Impact: Trauma vs Incompatibility
Sexual trauma often results in profound psychological effects such as anxiety, depression, PTSD, and diminished self-esteem due to the violation of personal boundaries and trust. Sexual incompatibility, while typically less severe, can cause frustration, emotional distance, and decreased relationship satisfaction stemming from mismatched desires or preferences. Understanding the psychological impact highlights that trauma requires trauma-informed therapy to heal, whereas incompatibility may benefit from communication and counseling strategies to improve intimacy.
Communication Strategies for Addressing Sexual Issues
Effective communication strategies for addressing sexual trauma, sexual incompatibility, and sexual misconduct prioritize empathy, active listening, and establishing a safe environment. Tailoring conversations to acknowledge emotional sensitivity while encouraging honest dialogue helps partners navigate complex feelings and align expectations. Professional guidance, such as couples therapy or trauma-informed counseling, often enhances communication, fostering mutual understanding and healing.
The Role of Therapy: Trauma Recovery and Couples Counseling
Therapy plays a crucial role in addressing the distinct challenges of sexual trauma and sexual incompatibility by offering tailored approaches for trauma recovery and couples counseling. Trauma recovery focuses on healing psychological wounds caused by sexual trauma through modalities such as EMDR and cognitive-behavioral therapy, which help survivors regain safety and trust. Couples counseling targets sexual incompatibility by improving communication, fostering intimacy, and exploring sexual preferences, allowing partners to establish mutual satisfaction and rebuild connection.
Navigating Consent: Building Trust After Trauma or Incompatibility
Navigating consent after sexual trauma or incompatibility involves clear communication and establishing boundaries tailored to Your comfort and safety. Building trust requires patience and respect, acknowledging past experiences while fostering mutual understanding between partners. Prioritizing ongoing dialogue creates a foundation for healing and positive sexual connection.
When to Seek Professional Help: Red Flags to Consider
Recognizing when to seek professional help is crucial for addressing sexual trauma and sexual incompatibility effectively. Red flags include persistent anxiety, avoidance of intimacy, emotional numbness, or unresolved conflict affecting your relationships. Your mental and emotional well-being should guide you to consult a therapist or counselor specializing in sexual health when these symptoms interfere with your daily life or relationship satisfaction.
Healing, Growth, and Moving Forward Together
Sexual trauma requires compassionate healing strategies that prioritize your emotional safety and gradual recovery, while sexual incompatibility involves understanding and communication to find mutual satisfaction. Addressing sexual trauma often includes therapy and support groups that foster resilience, whereas navigating sexual incompatibility benefits from open dialogue and exploring new experiences together. Combining these approaches encourages growth and strengthens your relationship, enabling you and your partner to move forward with trust and intimacy.
Infographic: Sexual trauma vs sexual incompatibility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com