Visual stimulation in relationships often enhances emotional connection through nonverbal cues such as eye contact and body language, while verbal stimulation fosters deeper understanding and intimacy through meaningful conversations. Discover how balancing these forms of communication can strengthen your relationship in this article.
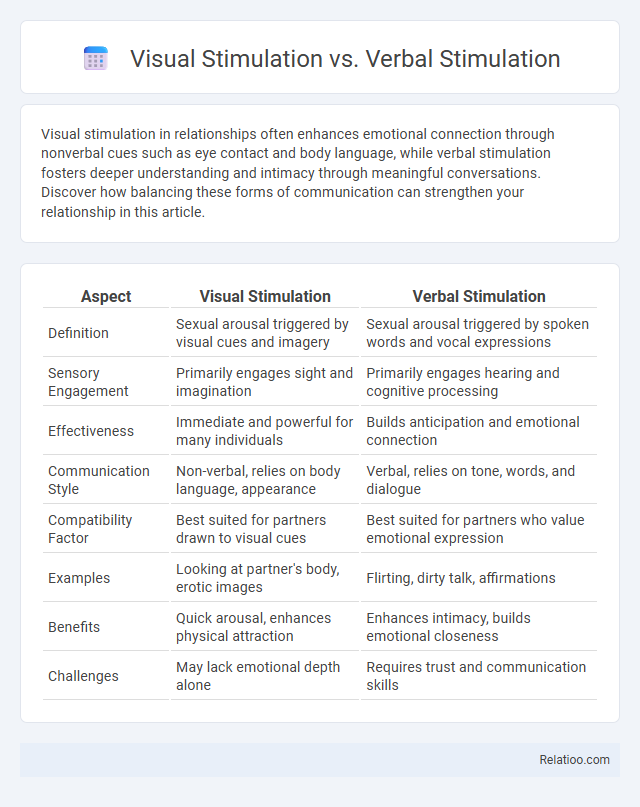
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Visual Stimulation | Verbal Stimulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sexual arousal triggered by visual cues and imagery | Sexual arousal triggered by spoken words and vocal expressions |
| Sensory Engagement | Primarily engages sight and imagination | Primarily engages hearing and cognitive processing |
| Effectiveness | Immediate and powerful for many individuals | Builds anticipation and emotional connection |
| Communication Style | Non-verbal, relies on body language, appearance | Verbal, relies on tone, words, and dialogue |
| Compatibility Factor | Best suited for partners drawn to visual cues | Best suited for partners who value emotional expression |
| Examples | Looking at partner's body, erotic images | Flirting, dirty talk, affirmations |
| Benefits | Quick arousal, enhances physical attraction | Enhances intimacy, builds emotional closeness |
| Challenges | May lack emotional depth alone | Requires trust and communication skills |
Introduction to Visual and Verbal Stimulation
Visual stimulation engages your brain through images, colors, and spatial patterns, enhancing cognitive processing and memory retention by activating the occipital lobe. Verbal stimulation involves language-based inputs such as reading, listening, or speaking, which primarily activate the left hemisphere's language centers, including Broca's and Wernicke's areas. Understanding the distinct pathways these stimulations use helps optimize learning, communication, and emotional responses effectively.
Defining Visual Stimulation: Key Concepts
Visual stimulation involves engaging your brain through imagery, colors, patterns, and movements that activate visual sensory pathways, enhancing cognitive and emotional responses. Key concepts include the processing of light, contrast, and spatial relationships that influence perception and attention. Understanding visual stimulation helps differentiate it from verbal stimulation, which relies on linguistic input, and turn-on, which refers to arousal triggered by sensory or emotional cues.
Understanding Verbal Stimulation
Verbal stimulation involves the use of words, tone, and intonation to evoke emotional and physical responses, making it a powerful tool for connection and arousal. Unlike visual stimulation, which primarily targets the brain's visual cortex through imagery, verbal interaction engages language processing areas, enhancing intimacy and imaginative engagement. Understanding verbal stimulation highlights its role in communication development, emotional bonding, and personalized sensory experiences that unlock deeper psychological triggers.
Cognitive Benefits of Visual Stimulation
Visual stimulation engages multiple areas of the brain, enhancing memory retention, attention span, and problem-solving skills through rich, sensory input. Unlike verbal stimulation, which primarily activates language centers, visual stimuli promote spatial reasoning and creative thinking, offering a more holistic cognitive workout. Your brain benefits from the increased neural connectivity fostered by visual experiences, making it a powerful tool for cognitive development and mental agility.
Cognitive Benefits of Verbal Stimulation
Verbal stimulation enhances cognitive benefits by actively engaging language processing centers in the brain, improving memory retention, critical thinking, and communication skills more effectively than visual stimulation alone. Your brain decodes and constructs meaning from words, fostering deeper understanding and mental flexibility. This mental exercise promotes neural plasticity and supports problem-solving abilities, which are crucial for cognitive development and lifelong learning.
Brain Processing: Visual vs Verbal Stimuli
Visual stimulation activates the brain's occipital lobe, enhancing pattern recognition and spatial awareness, whereas verbal stimulation primarily engages the temporal lobe, boosting language processing and auditory comprehension. Your brain processes visual stimuli faster due to direct sensory input, while verbal stimuli require decoding and semantic integration. Turn-on responses involve the limbic system, linking sensory input with emotional and motivational states for a holistic brain experience.
Learning Styles: Visual Learners vs Verbal Learners
Visual stimulation enhances learning for visual learners by engaging the brain through images, charts, and spatial understanding, improving memory retention and comprehension. Verbal stimulation benefits verbal learners by utilizing spoken or written words, enabling them to process and organize information through language and sound. Understanding the distinct turn-on preferences in sensory input helps tailor educational approaches, maximizing the effectiveness of learning styles for both visual and verbal learners.
Applications in Education and Training
Visual stimulation enhances learning by engaging the brain's visual processing centers, improving memory retention and comprehension through images, videos, and diagrams. Verbal stimulation, involving spoken or written language, supports auditory learners and strengthens language skills, critical for effective communication and knowledge acquisition. Your educational programs can achieve optimal training outcomes by integrating both visual and verbal stimuli, maximizing learner engagement and cognitive retention during turn-on phases of attention.
Impact on Memory Retention and Recall
Visual stimulation enhances memory retention by engaging the brain's spatial and sensory processing centers, making information easier to encode and recall. Verbal stimulation activates linguistic and auditory pathways that support sequential memory and comprehension, improving recall accuracy for spoken or written information. Your memory retention benefits most when visual and verbal stimuli are combined strategically to create richer, multimodal cognitive cues that trigger stronger neural connections.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stimulation Method
Selecting the right stimulation method depends on your individual preferences and cognitive style, with visual stimulation enhancing memory retention and emotional engagement through imagery, while verbal stimulation strengthens analytical thinking and language processing. Turn-on stimulation, which combines sensory and emotional triggers, often results in a more immersive and motivating experience for learning or creativity. Understanding your dominant sensory modality can help tailor strategies that maximize effectiveness and personal satisfaction.
Infographic: Visual Stimulation vs Verbal Stimulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com