A Financial Manager typically oversees daily financial operations and budgeting, while a Finance Director sets strategic financial goals and ensures alignment with overall business objectives. Discover the key differences and how these roles complement each other in this article.
Table of Comparison
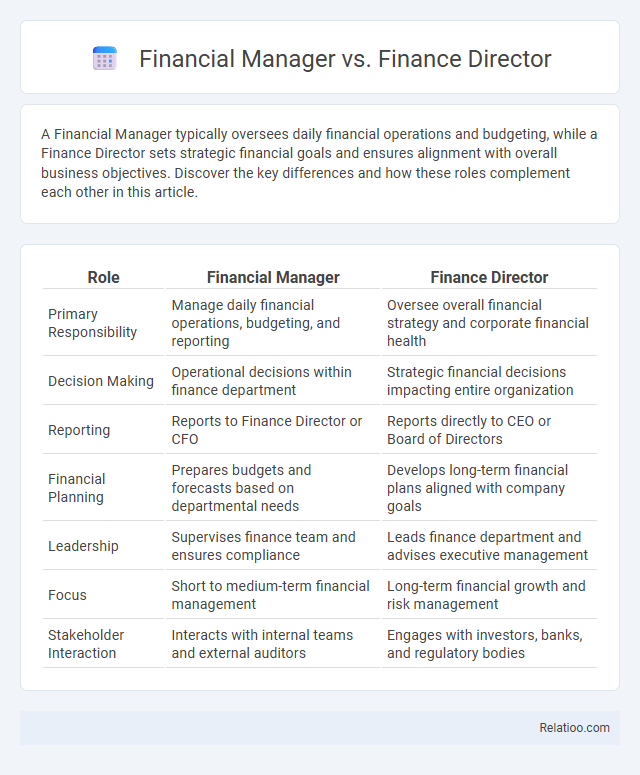
| Role | Financial Manager | Finance Director |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Manage daily financial operations, budgeting, and reporting | Oversee overall financial strategy and corporate financial health |
| Decision Making | Operational decisions within finance department | Strategic financial decisions impacting entire organization |
| Reporting | Reports to Finance Director or CFO | Reports directly to CEO or Board of Directors |
| Financial Planning | Prepares budgets and forecasts based on departmental needs | Develops long-term financial plans aligned with company goals |
| Leadership | Supervises finance team and ensures compliance | Leads finance department and advises executive management |
| Focus | Short to medium-term financial management | Long-term financial growth and risk management |
| Stakeholder Interaction | Interacts with internal teams and external auditors | Engages with investors, banks, and regulatory bodies |
Introduction to Financial Manager vs Finance Director
A Financial Manager oversees daily financial operations, budgeting, and reporting to ensure organizational stability and compliance. A Finance Director holds a strategic leadership role, guiding long-term financial planning, investment decisions, and corporate financial policy formulation. Understanding the distinction between these roles helps you align career goals with the appropriate level of responsibility and influence within a company's financial hierarchy.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A Financial Manager oversees daily financial activities such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting to ensure organizational efficiency. A Finance Director holds a strategic leadership role, responsible for long-term financial planning, risk management, and aligning financial goals with business objectives. Both positions require expertise in financial analysis, regulatory compliance, and team management, but the Finance Director focuses more on corporate governance and high-level decision-making.
Educational and Professional Qualifications
A Financial Manager typically holds a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or business administration, with certifications like CFA or CPA enhancing credibility and career prospects. Finance Directors usually possess advanced degrees, such as an MBA or a master's in finance, combined with extensive industry experience and leadership credentials. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Finance Directors demand deeper strategic expertise and often prioritize professional qualifications that align with executive-level responsibilities.
Core Skills and Competencies
Financial Managers excel in budgeting, financial reporting, and risk management, emphasizing analytical skills and operational decision-making. Finance Directors possess strategic planning expertise, leadership abilities, and comprehensive knowledge of regulatory compliance to guide organizational financial policy. Financial managers combine strong communication, forecasting proficiency, and proficiency in financial software to optimize resource allocation and support executive objectives.
Scope of Authority and Decision-Making
Financial Manager typically oversees day-to-day financial operations and reports to senior leadership, focusing on budgeting, financial analysis, and internal controls within a limited scope of authority. Finance Director holds a broader scope of authority, responsible for strategic financial planning, long-term financial goals, and often decision-making authority that impacts company-wide financial policies. Your choice between these roles depends on the level of influence and decision-making power you seek, with the Finance Director holding a higher position in the corporate hierarchy than a Financial Manager.
Strategic vs Operational Focus
A Financial Manager typically emphasizes operational focus, managing day-to-day financial tasks such as budgeting, reporting, and cash flow management to ensure the company's financial stability. In contrast, a Finance Director assumes a strategic role, overseeing long-term financial planning, investment decisions, and alignment of financial goals with overall business strategy. The Financial Manager's role is more tactical, whereas the Finance Director drives strategic financial initiatives that support organizational growth and sustainability.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchy
A Financial Manager typically reports to the Finance Director or Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and oversees the day-to-day financial operations within specific departments or projects. The Finance Director holds a higher position within the corporate hierarchy, responsible for strategic financial planning, risk management, and coordinating reporting directly to the CFO or executive board. In larger organizations, the Financial Manager operates within mid-level management, whereas the Finance Director serves as a senior executive shaping overall financial policy and governance.
Salary Expectations and Career Progression
Financial Manager salaries typically range from $70,000 to $120,000 annually, reflecting mid-level responsibilities in corporate financial management, while Finance Directors command higher compensation, often between $120,000 and $200,000, due to their strategic oversight and leadership roles. Career progression from Financial Manager to Finance Director involves acquiring advanced financial expertise, leadership skills, and experience in budgeting, forecasting, and regulatory compliance, positioning professionals for executive responsibilities. Financial analysts, often entry-level, earn between $50,000 and $75,000 and may progress to Financial Manager roles as they develop managerial and strategic financial capabilities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Each Role
Financial Managers face challenges in managing day-to-day financial operations while seizing opportunities to optimize cash flow and budgeting processes for Your organization. Finance Directors encounter the complex task of strategic planning and regulatory compliance, leveraging opportunities to influence broader business decisions and drive long-term growth. Financial Controllers, often confused with Financial Managers, focus on maintaining accurate financial reporting and internal controls, presenting challenges in data integrity yet opportunities to enhance organizational transparency and efficiency through precise financial governance.
Choosing Between Financial Manager and Finance Director
Choosing between a Financial Manager and a Finance Director depends on the scope of responsibility and strategic involvement within the organization. A Financial Manager typically oversees day-to-day financial operations, budgeting, and reporting, ensuring effective financial control and compliance. In contrast, a Finance Director plays a more strategic role, focusing on long-term financial planning, investment decisions, and aligning financial goals with overall business objectives.
Infographic: Financial Manager vs Finance Director
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com