Financiers provide capital through debt or credit arrangements, prioritizing repayment with interest, while investors commit funds in exchange for equity or ownership stakes aiming for long-term growth. Discover detailed distinctions and financial roles in this article.
Table of Comparison
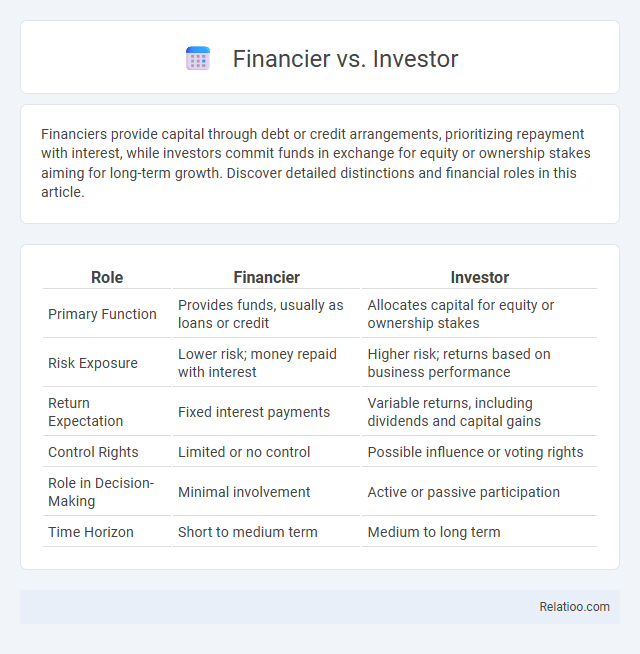
| Role | Financier | Investor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides funds, usually as loans or credit | Allocates capital for equity or ownership stakes |
| Risk Exposure | Lower risk; money repaid with interest | Higher risk; returns based on business performance |
| Return Expectation | Fixed interest payments | Variable returns, including dividends and capital gains |
| Control Rights | Limited or no control | Possible influence or voting rights |
| Role in Decision-Making | Minimal involvement | Active or passive participation |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term | Medium to long term |
Understanding the Concept: Financier vs Investor
Understanding the concept of financier vs investor highlights key differences in roles and objectives within financial markets. A financier primarily provides capital through loans or credit arrangements, focusing on returns from interest, while an investor allocates funds by purchasing equity or assets, seeking profit through dividends or asset appreciation. Your financial strategy benefits from distinguishing these roles to align funding sources and investment goals effectively.
Key Differences Between Financiers and Investors
Financiers primarily provide capital through loans or credit, expecting repayment with interest, whereas investors acquire ownership stakes or equity in companies, aiming for long-term growth and dividends. Your choice between a financier and investor depends on whether you prefer fixed income through debt or potential high returns through equity participation. Understanding these key differences ensures you align funding strategies with business goals and risk tolerance effectively.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Financier
A financier primarily manages the allocation and oversight of capital, ensuring funds are efficiently sourced and deployed to maximize returns while mitigating risks. Unlike investors who focus on acquiring assets to generate profit, financiers structure deals, arrange financing, and facilitate complex financial transactions for businesses or projects. Your understanding of a financier's role highlights their expertise in financial strategy, capital markets, and risk management critical for sustaining business growth and investment success.
Typical Functions of an Investor
An investor typically allocates capital to financial assets, real estate, or businesses expecting a return on investment through dividends, interest, or capital gains. Unlike a financier, who primarily provides funding through loans or credit facilities, an investor assumes ownership risks and actively monitors portfolio performance to optimize returns. Investors conduct market analysis, diversify holdings, and manage risk to achieve long-term financial growth.
Risk Profiles: Financier vs Investor
Financiers typically assume higher risk by providing capital through debt or equity with expectations of substantial returns or control, while investors often seek moderate risk by diversifying portfolios across stocks, bonds, or real estate to balance potential gains and losses. Your risk profile influences whether you prefer the direct involvement and possible large-scale impact of a financier or the more measured, passive approach common to investors. Understanding these distinctions enables tailored financial strategies aligned with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Sources of Capital: Financiers and Investors Compared
Financiers typically provide capital through loans, credit lines, or asset-backed financing, focusing on debt instruments sourced from banks, finance companies, or private lenders. Investors supply capital by purchasing equity, stocks, or stakes, deriving funds mainly from venture capital firms, individual investors, or public markets. Understanding the differences in your sources of capital--debt from financiers versus equity from investors--helps tailor your financial strategy effectively.
Return on Investment: Expectations and Realities
Financiers typically seek structured repayments with fixed returns, emphasizing risk mitigation and capital preservation in their return on investment expectations. Investors pursue higher returns by accepting more uncertainty, aiming for capital gains or dividends aligned with market performance. Understanding the distinct expectations and realities of these roles is essential for aligning financial strategies with risk tolerance and investment horizons.
Strategic Involvement: Passive vs Active Approach
Financiers primarily provide capital with a passive approach, focusing on funding projects or businesses without direct involvement in daily operations or strategic decision-making. Investors may adopt either a passive or active role depending on their investment type, with venture capitalists often engaging actively to influence growth and direction, while stockholders generally remain passive. The distinction hinges on strategic involvement, where financiers typically avoid operational participation, contrasting with active investors who seek to guide business strategy for higher returns.
Impact on Business Growth: Financier vs Investor
Financiers provide the essential capital and funding that enable businesses to scale operations, manage cash flow, and invest in new projects, directly accelerating business growth. Investors contribute by injecting equity or debt with an expectation of future returns, often bringing strategic guidance and long-term resources that can foster sustainable expansion. The combined impact of financiers and investors creates a robust financial foundation that drives innovation, market penetration, and overall competitive advantage.
Choosing the Right Partner: Financier or Investor?
Choosing the right partner involves understanding the roles of a financier and an investor: financiers provide debt-based funding with fixed repayment terms, while investors offer equity capital in exchange for ownership stakes and potential profit sharing. Your decision should consider your business's financial needs, risk tolerance, and long-term goals, as financiers prioritize loan repayment, whereas investors seek growth and value appreciation. Aligning your strategy with the appropriate partner enhances capital efficiency and supports sustainable business growth.
Infographic: Financier vs Investor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com