Advocates specialize in representing clients in court and providing legal opinions, while lawyers offer broader legal advice and services beyond litigation. Explore this article to understand the distinct roles and functions of advocates versus lawyers.
Table of Comparison
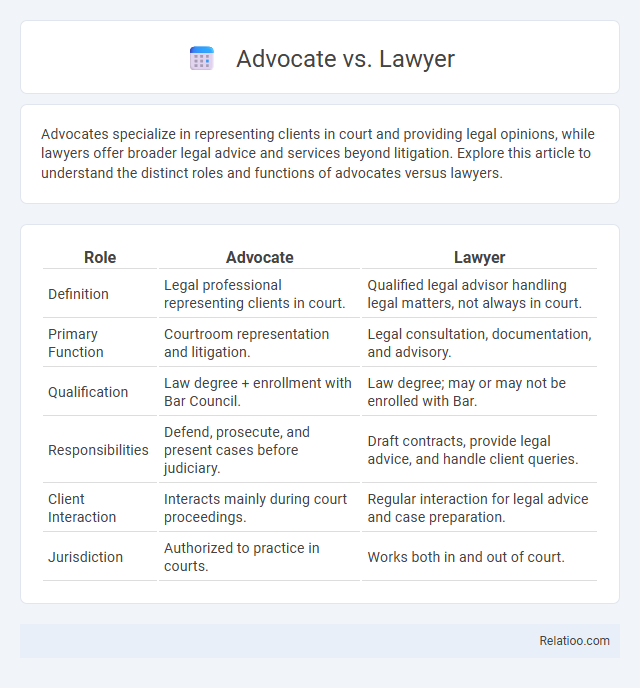
| Role | Advocate | Lawyer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal professional representing clients in court. | Qualified legal advisor handling legal matters, not always in court. |
| Primary Function | Courtroom representation and litigation. | Legal consultation, documentation, and advisory. |
| Qualification | Law degree + enrollment with Bar Council. | Law degree; may or may not be enrolled with Bar. |
| Responsibilities | Defend, prosecute, and present cases before judiciary. | Draft contracts, provide legal advice, and handle client queries. |
| Client Interaction | Interacts mainly during court proceedings. | Regular interaction for legal advice and case preparation. |
| Jurisdiction | Authorized to practice in courts. | Works both in and out of court. |
Definition of Advocate vs Lawyer
An Advocate is a legal professional authorized to represent clients in court, specializing in litigation and legal argumentation, while a Lawyer is a broader term encompassing all individuals qualified to practice law, including those who offer legal advice and draft contracts. Advocacy refers to the act of supporting or pleading a case in legal or public settings, often performed by Advocates during courtroom proceedings. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right legal expert for your specific needs.
Key Differences Between Advocate and Lawyer
Advocates are legal professionals who represent clients in higher courts, specializing in litigation and courtroom advocacy, whereas lawyers provide broader legal services including advisory, documentation, and representation in lower courts. The primary distinction lies in the role; advocates primarily focus on arguing cases before the judiciary, while lawyers handle legal counsel, documentation, and clients' overall legal needs. Advocacy refers to the act of pleading or arguing a case in court, a function that advocates specialize in, differentiating them from lawyers who may not engage in courtroom representation.
Qualifications and Educational Requirements
Advocates typically require a law degree followed by bar certification to represent clients in higher courts, emphasizing specialized courtroom skills. Lawyers possess a law degree and pass the bar exam, enabling them to provide legal advice, draft documents, and represent clients in various legal matters. Advocacy refers to the practice of supporting or recommending a cause or policy, often without the formal educational requirements demanded of advocates or lawyers. Your choice depends on the level of legal representation or support you need.
Roles and Responsibilities
Advocates represent clients in higher courts, specializing in courtroom litigation and legal argumentation, while lawyers provide broader legal services including advising, drafting documents, and negotiating settlements. Advocacy refers to the act of pleading or arguing in favor of a cause or client, often involving persuasive communication and legal strategy. Understanding these distinctions empowers your legal decisions by aligning your needs with the appropriate legal professional's expertise and role.
Rights to Practice in Court
Advocates hold specialized rights to practice in higher courts, often requiring certification or membership in specific bar councils, whereas lawyers encompass a broader category that includes all legal professionals licensed to practice law, including solicitors and attorneys. Advocacy refers to the act of representing and defending clients' interests in court, demanding not only legal knowledge but also the right to plead before particular courts. Your ability to appear and argue cases depends on the legal qualifications and court-specific certifications defining advocates and lawyers within your jurisdiction.
Areas of Specialization
Advocates typically specialize in courtroom litigation, focusing on criminal law, civil disputes, and appellate cases, representing clients during trials and hearings. Lawyers have a broader range of specializations including corporate law, intellectual property, family law, and contract law, offering legal advice, drafting documents, and negotiating settlements outside the courtroom. Advocacy refers to the practice of supporting or recommending a cause or policy, often specialized in fields like human rights, environmental law, and social justice, aiming to influence legal and public policy decisions.
Jurisdictional Variations
Jurisdictional variations significantly impact the roles and definitions of Advocate, Lawyer, and Advocacy, with "Advocate" commonly referring to a legal professional who pleads cases in higher courts in countries like India and South Africa, while "Lawyer" is a broader term used globally to denote any person qualified to practice law. Advocacy practices and qualifications differ widely, with some jurisdictions requiring specific certifications or bar admissions for Advocates but not necessarily for Lawyers. Understanding these differences is crucial for Your legal representation, especially when navigating international legal systems or cross-border disputes.
Professional Ethics and Conduct
Advocate and lawyer both refer to legal professionals who represent clients, but advocates often specialize in court proceedings and oral arguments, while lawyers may provide broader legal services including consultation and documentation. Advocacy emphasizes the ethical responsibility to uphold justice, confidentiality, and integrity, ensuring that Your representation aligns with professional codes of conduct such as those outlined by the American Bar Association or similar regulatory bodies. Maintaining professional ethics involves adherence to impartiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and prioritizing Your client's best interests within lawful boundaries.
Career Opportunities and Scope
Advocate, lawyer, and advocacy each present distinct career opportunities and scopes within the legal field, with advocates primarily focusing on representing clients in court, lawyers offering broader legal services including consultation and documentation, and advocacy emphasizing policy change and social justice initiatives. Your career choice depends on whether you prefer courtroom litigation, legal advisory roles, or working within organizations to influence law and public policy. Each path offers a range of opportunities from private practice and corporate roles to nonprofit and governmental positions, reflecting diverse demands in the global legal market.
Choosing Between an Advocate and a Lawyer
Choosing between an advocate and a lawyer depends on your specific legal needs and jurisdiction. Advocates are typically specialized in courtroom representation and litigation, while lawyers provide broader legal advice and services. Understanding these distinctions helps you make an informed decision for effective legal assistance tailored to your case.
Infographic: Advocate vs Lawyer
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com