Medical assistants perform administrative and basic clinical tasks under physician supervision, while nurses provide comprehensive patient care and manage health plans independently. Discover detailed differences and career insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
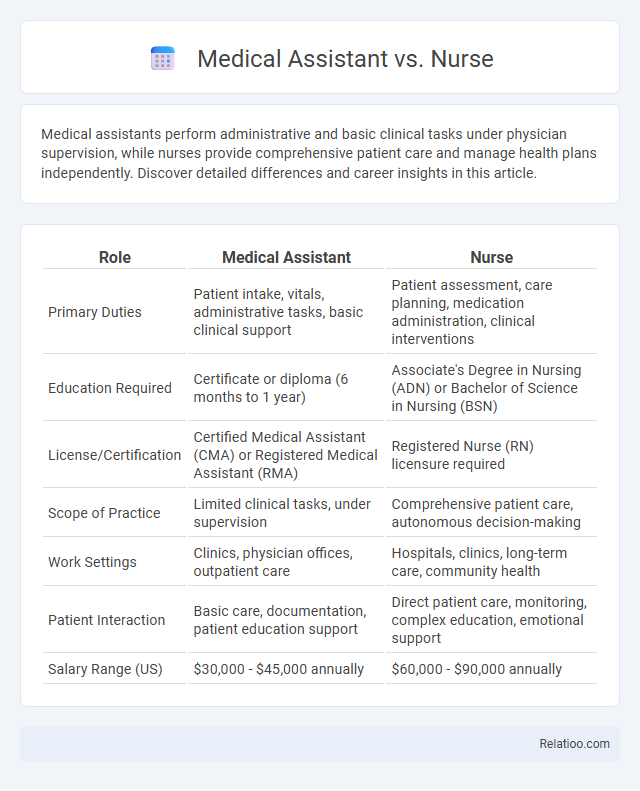
| Role | Medical Assistant | Nurse |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Duties | Patient intake, vitals, administrative tasks, basic clinical support | Patient assessment, care planning, medication administration, clinical interventions |
| Education Required | Certificate or diploma (6 months to 1 year) | Associate's Degree in Nursing (ADN) or Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) |
| License/Certification | Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) or Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) | Registered Nurse (RN) licensure required |
| Scope of Practice | Limited clinical tasks, under supervision | Comprehensive patient care, autonomous decision-making |
| Work Settings | Clinics, physician offices, outpatient care | Hospitals, clinics, long-term care, community health |
| Patient Interaction | Basic care, documentation, patient education support | Direct patient care, monitoring, complex education, emotional support |
| Salary Range (US) | $30,000 - $45,000 annually | $60,000 - $90,000 annually |
Overview: Medical Assistant vs Nurse
Medical assistants perform administrative and clinical tasks to support healthcare providers, including taking vital signs, preparing patients for exams, and managing medical records. Nurses have broader responsibilities, such as administering medications, creating care plans, and providing direct patient care and education. While medical assistants work under supervision with limited scope, nurses hold licensure and possess advanced training to deliver complex patient care across various settings.
Roles and Responsibilities
Medical Assistants perform administrative and clinical tasks such as scheduling appointments, taking vital signs, and preparing patients for examinations, ensuring efficient clinic operations. Nurses provide direct patient care, administer medications, monitor health status, and educate patients on treatment plans, playing a critical role in patient recovery and health maintenance. Patients actively participate in their healthcare by communicating symptoms, following treatment regimens, and collaborating with Medical Assistants and Nurses to ensure effective care delivery.
Education and Training Requirements
Medical Assistants typically complete a one-year certificate or diploma program focusing on administrative and clinical tasks, while Nurses require a more extensive education, usually a two to four-year degree such as an Associate's or Bachelor's in Nursing, along with passing the NCLEX-RN exam to obtain licensure. Patients rely on these trained professionals for quality healthcare, with Nurses providing comprehensive care and Medical Assistants supporting clinical operations under supervision. Understanding the distinct education and training pathways helps you appreciate the specialized skills each role brings to patient care.
Certifications and Licensure
Medical assistants typically hold a Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) or Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) credential, requiring completion of accredited programs and passing certification exams. Nurses must obtain licensure through the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN for registered nurses or NCLEX-PN for practical nurses) after graduating from an accredited nursing program to legally practice. Your choice between these roles should consider the distinct certification and licensure requirements that define their scopes of practice and professional responsibilities.
Work Environments
Medical assistants often work in outpatient clinics, physician offices, and ambulatory care centers, supporting administrative and clinical tasks. Nurses are employed across diverse settings including hospitals, long-term care facilities, and emergency departments, providing direct patient care and managing complex health conditions. Patients navigate these environments depending on their healthcare needs, ranging from routine check-ups in clinics to acute treatment in hospitals.
Key Skills and Competencies
Medical assistants demonstrate proficiency in clinical tasks such as phlebotomy, EKG administration, and patient record management, combined with administrative abilities like scheduling and billing. Nurses possess advanced competencies in patient care, including medication administration, wound care, and critical thinking for treatment planning, alongside strong communication and emotional support skills. Patients benefit from understanding their health conditions and effective communication with healthcare providers to ensure accurate reporting of symptoms and adherence to treatment plans.
Salary and Job Outlook
Medical assistants earn a median salary of approximately $38,000 annually with a projected job growth rate of 19% from 2022 to 2032, reflecting strong demand in outpatient care. Registered nurses command higher average salaries around $77,000 per year and face a similarly robust employment growth of 6-9%, driven by an aging population and expanded healthcare services. Patients benefit indirectly from these workforce trends as increased staffing levels improve access to care and overall healthcare quality.
Advancement Opportunities
Medical assistants often have limited advancement opportunities, typically progressing to specialized certifications or management roles within clinical settings. Nurses enjoy a broader range of career growth, including advanced practice roles such as Nurse Practitioner, clinical nurse specialist, or nurse educator, supported by higher education and licensing. Your choice between these professions impacts long-term career development, with nursing generally offering more extensive advancement potential compared to medical assisting, while patients benefit from the evolving expertise and roles of both healthcare providers.
Pros and Cons of Each Career
Medical Assistants offer versatility in clinical and administrative tasks with shorter training periods, making them accessible entry points into healthcare but often face limited scope of practice and lower salaries. Nurses provide critical patient care with advanced clinical skills and higher earning potential, yet they endure long hours and emotional stress due to direct patient responsibilities. Patients benefit from the combined efforts of both roles, receiving comprehensive care; understanding your care team's strengths can improve health outcomes and satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Path for You
Choosing the right path between a medical assistant, nurse, and patient care role depends on your career goals, required education, and desired responsibilities. Medical assistants typically handle administrative tasks and basic clinical duties with shorter training periods, while nurses provide advanced patient care requiring licensure and specialized knowledge. Understanding the scope of practice, work environment, and long-term career prospects helps in making an informed decision tailored to your skills and interests.
Infographic: Medical Assistant vs Nurse
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com