Schedulers optimize task execution by dynamically allocating resources and managing execution order for efficiency. Coordinators oversee workflow dependencies and synchronization to ensure smooth process integration; learn more about their distinct roles in this article.
Table of Comparison
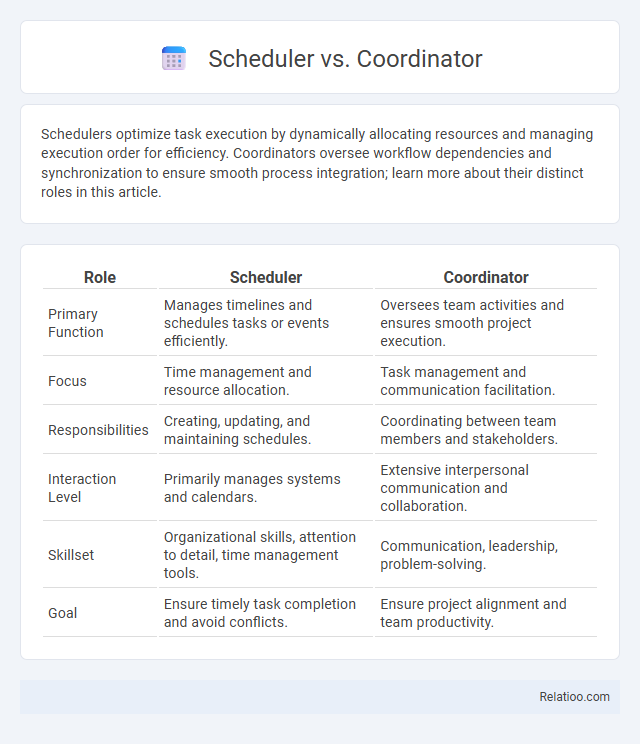
| Role | Scheduler | Coordinator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages timelines and schedules tasks or events efficiently. | Oversees team activities and ensures smooth project execution. |
| Focus | Time management and resource allocation. | Task management and communication facilitation. |
| Responsibilities | Creating, updating, and maintaining schedules. | Coordinating between team members and stakeholders. |
| Interaction Level | Primarily manages systems and calendars. | Extensive interpersonal communication and collaboration. |
| Skillset | Organizational skills, attention to detail, time management tools. | Communication, leadership, problem-solving. |
| Goal | Ensure timely task completion and avoid conflicts. | Ensure project alignment and team productivity. |
Introduction to Scheduler vs Coordinator
Understanding the distinction between Scheduler and Coordinator is crucial for effective task management in distributed systems. The Scheduler allocates resources and determines the execution order of tasks to optimize performance, while the Coordinator manages the overall workflow by monitoring task dependencies and ensuring synchronization. Your choice between Scheduler and Coordinator depends on whether your priority lies in resource optimization or in orchestrating complex task sequences.
Defining Scheduler: Core Functions
The Scheduler in distributed systems orchestrates resource allocation by assigning tasks to available nodes based on priority, workload, and resource constraints, ensuring efficient utilization and system scalability. Its core functions include job queuing, task dispatching, and monitoring execution status to optimize throughput and minimize latency. Unlike Coordinators, which manage workflow dependencies and state transitions, Schedulers primarily focus on task scheduling and resource management to maintain balanced and effective operations.
Defining Coordinator: Core Responsibilities
The Coordinator manages the overall workflow by orchestrating tasks and ensuring dependencies are met within distributed systems. It is responsible for assigning resources, maintaining synchronization, and monitoring task execution to guarantee efficiency and fault tolerance. Unlike a Scheduler, which primarily focuses on timing and resource allocation, the Coordinator provides higher-level control and coordination across multiple nodes or services.
Key Differences Between Scheduler and Coordinator
The Scheduler manages the allocation of resources and job execution timing within a system, optimizing task prioritization and workload distribution. The Coordinator oversees the orchestration and synchronization of distributed tasks, ensuring communication and dependencies among various components are maintained. Your choice between a Scheduler and Coordinator depends on whether your focus is on resource management or distributed task coordination.
Use Cases for Schedulers
Schedulers manage task execution timing and resource allocation, optimizing workflows in computing environments such as cloud platforms, batch processing, and real-time systems. Coordinators oversee task dependencies and data flow across complex pipelines, ensuring proper sequencing and data consistency. By leveraging schedulers, your applications can efficiently handle parallel processing, job prioritization, and load balancing to maximize system performance.
Use Cases for Coordinators
Coordinators are essential in managing complex workflows by orchestrating distributed tasks across multiple systems, ensuring reliability and fault tolerance in data pipelines. Unlike schedulers that simply trigger jobs at specific times, coordinators handle dependencies, retries, and event-based triggers, making them ideal for data integration and ETL processes in enterprise environments. Your use of coordinators optimizes operational efficiency by automating task executions only when all prerequisite conditions are satisfied, reducing manual intervention and errors.
Performance Impact: Scheduler vs Coordinator
The Scheduler manages task execution priorities and resource allocation, directly influencing system throughput and latency, while the Coordinator oversees task dependencies and workflow orchestration to ensure process consistency. Your system's performance hinges on the Scheduler's efficiency in minimizing idle time and balancing load, whereas the Coordinator impacts stability by preventing task conflicts and deadlocks. Optimizing the Scheduler accelerates job completion rates, and refining the Coordinator enhances overall workflow reliability.
Integration and Scalability Comparisons
Scheduler manages task execution timing, ensuring efficient resource allocation, while Coordinator oversees workflow dependencies and task state management, facilitating seamless integration across distributed systems. Compared to Scheduler, the Coordinator offers enhanced scalability by coordinating multiple tasks and handling failure recovery, which supports complex data pipelines and large-scale deployments. Your choice depends on the integration complexity and scalability requirements, with Coordinators favored for dynamic, multi-node environments and Schedulers ideal for simpler, time-based task execution.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Workflow
Choosing the right tool for your workflow involves understanding the distinct roles of Scheduler, Coordinator, and Workflow Scheduler. Schedulers primarily manage task execution timing, Coordinators handle complex dependencies between multiple workflows, and Workflow Schedulers automate entire sequences of processes to optimize efficiency. Your choice should align with the complexity and scale of your tasks to enhance productivity and ensure seamless workflow management.
Future Trends in Scheduling and Coordination Systems
Future trends in scheduling and coordination systems emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize resource allocation and predict potential delays more accurately. Coordinator roles are evolving to support real-time collaborative decision-making through cloud-based platforms, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. You can expect advanced automation and adaptive scheduling algorithms to drive efficiency in complex environments across industries.
Infographic: Scheduler vs Coordinator
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com