Peacekeepers prioritize harmony by avoiding conflict and maintaining stability, while Mediators actively facilitate communication and negotiation between parties to resolve disputes. Discover deeper insights into the roles of Peacekeepers and Mediators in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
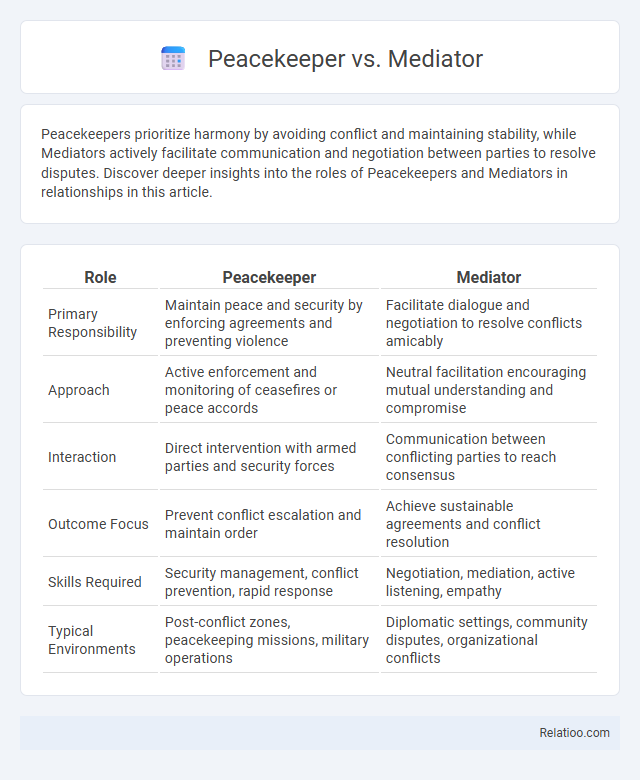
| Role | Peacekeeper | Mediator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Maintain peace and security by enforcing agreements and preventing violence | Facilitate dialogue and negotiation to resolve conflicts amicably |
| Approach | Active enforcement and monitoring of ceasefires or peace accords | Neutral facilitation encouraging mutual understanding and compromise |
| Interaction | Direct intervention with armed parties and security forces | Communication between conflicting parties to reach consensus |
| Outcome Focus | Prevent conflict escalation and maintain order | Achieve sustainable agreements and conflict resolution |
| Skills Required | Security management, conflict prevention, rapid response | Negotiation, mediation, active listening, empathy |
| Typical Environments | Post-conflict zones, peacekeeping missions, military operations | Diplomatic settings, community disputes, organizational conflicts |
Introduction: Defining Peacekeeper and Mediator
A peacekeeper operates by enforcing ceasefires and maintaining order during conflicts, often through military or authoritative presence, to prevent further violence. A mediator facilitates dialogue between conflicting parties, encouraging negotiation and mutual understanding to reach a voluntary agreement without imposing solutions. While peacekeepers maintain physical peace, mediators work to resolve underlying disputes through communication and compromise.
Historical Contexts: Roles in Conflict Resolution
Peacekeepers, mediators, and peacebuilders each play distinct roles in conflict resolution, shaped by their historical contexts. Peacekeepers typically operate under international mandates, such as United Nations missions, to maintain ceasefires and prevent violence between warring parties through a military or police presence. Mediators engage diplomatically to negotiate agreements and foster dialogue between conflicting groups, while peacebuilders focus on long-term social and institutional reconstruction to sustain lasting peace after conflict has ended; your understanding of these roles helps clarify strategies for effective conflict management.
Key Responsibilities: Peacekeeper vs Mediator
Key responsibilities of a Peacekeeper involve maintaining order and preventing conflict escalation through physical presence and enforcement of peace agreements. A Mediator's main role centers on facilitating communication, negotiation, and compromise between conflicting parties to reach mutual understanding and resolution. Your choice between a Peacekeeper and a Mediator depends on whether the situation requires direct intervention or collaborative dialogue for conflict resolution.
Skills and Qualities Required
Peacekeepers excel in conflict resolution by maintaining order and ensuring safety through strong communication, emotional control, and impartiality. Mediators require exceptional negotiation skills, empathy, and active listening to facilitate agreements between disputing parties. Your ability to adapt these distinct skills--assertiveness for peacekeepers, diplomacy for mediators, and patience for arbitrators--determines the effectiveness of conflict management in various scenarios.
Authority and Neutrality Explained
The Peacekeeper maintains authority by enforcing rules and preventing conflict escalation, often taking a clear stance to uphold order. The Mediator exercises neutrality by facilitating dialogue between conflicting parties without imposing decisions, ensuring impartiality to foster mutual understanding. Understanding your role in conflict resolution helps balance authority and neutrality, enabling effective peacebuilding tailored to the situation's demands.
Methods and Approaches in Practice
Peacekeepers employ neutral, often third-party interventions such as monitoring ceasefires and maintaining buffer zones to prevent violence, relying on strict neutrality and enforcement methods. Mediators use facilitative techniques like dialogue promotion, negotiation, and consensus-building, encouraging direct communication between conflicting parties to reach mutually acceptable solutions. Your choice between these approaches depends on the conflict's context, with peacekeeping suited for preventing active hostilities and mediation focused on resolving underlying issues through collaborative problem-solving.
Challenges Faced by Peacekeepers and Mediators
Peacekeepers often encounter challenges such as navigating complex conflict zones with limited resources and mandates, facing hostility from armed groups, and maintaining neutrality. Mediators struggle with building trust between conflicting parties, managing power imbalances, and overcoming deep-rooted historical grievances that impede dialogue. Both roles require adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and resilience in highly volatile environments to achieve sustainable peace agreements.
Impact and Outcomes in Conflict Situations
Peacekeepers maintain stability by enforcing ceasefires and creating secure environments, resulting in reduced violence and protection of civilians. Mediators facilitate dialogue between conflicting parties, fostering mutual understanding and generating sustainable agreements through negotiation and compromise. Peacebuilders work long-term to address root causes of conflict by promoting social cohesion and rebuilding institutions, leading to durable peace and community resilience.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Use Each
Choosing the right approach between Peacekeeper, Mediator, and Negotiator depends on the conflict context and your desired outcome. Use a Peacekeeper to maintain order and prevent escalation in high-tension situations, a Mediator to facilitate open communication and find common ground between disputing parties, and a Negotiator to actively seek mutually beneficial agreements through strategic dialogue. Understanding your role ensures effective conflict resolution tailored to your specific scenario.
Future Trends in Peacekeeping and Mediation
Future trends in peacekeeping and mediation emphasize the integration of advanced technology such as AI-driven data analysis and real-time conflict monitoring to enhance decision-making and responsiveness. Increasingly, hybrid models combining traditional peacekeeping forces with local mediators are employed to foster sustainable conflict resolution and community trust. Emphasis on inclusive approaches involving women, youth, and marginalized groups is shaping the evolution of peace operations toward more holistic and adaptive strategies.
Infographic: Peacekeeper vs Mediator
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com