Financial managers oversee an organization's financial health by developing strategies, while accountants focus on recording and analyzing financial transactions. Discover the distinct roles and responsibilities of financial managers and accountants in this article.
Table of Comparison
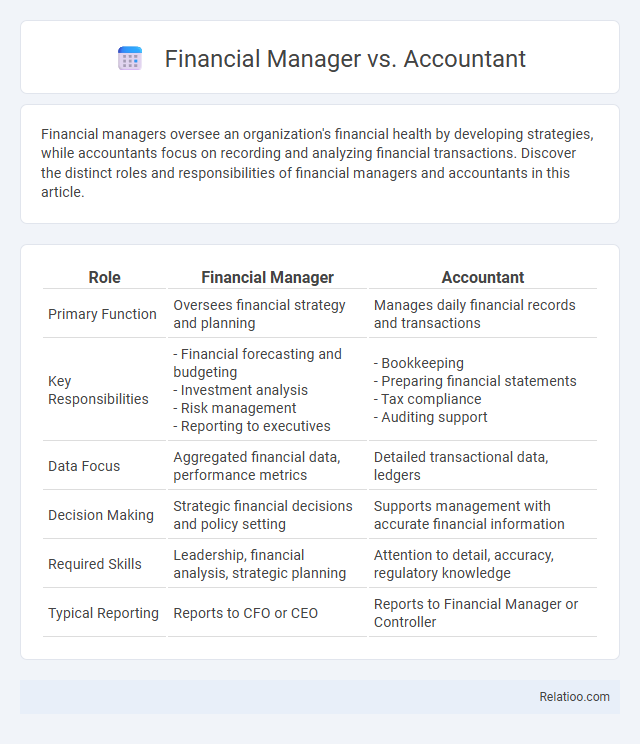
| Role | Financial Manager | Accountant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Oversees financial strategy and planning | Manages daily financial records and transactions |
| Key Responsibilities |
- Financial forecasting and budgeting - Investment analysis - Risk management - Reporting to executives |
- Bookkeeping - Preparing financial statements - Tax compliance - Auditing support |
| Data Focus | Aggregated financial data, performance metrics | Detailed transactional data, ledgers |
| Decision Making | Strategic financial decisions and policy setting | Supports management with accurate financial information |
| Required Skills | Leadership, financial analysis, strategic planning | Attention to detail, accuracy, regulatory knowledge |
| Typical Reporting | Reports to CFO or CEO | Reports to Financial Manager or Controller |
Overview: Financial Manager vs Accountant
Financial managers oversee an organization's financial health by developing strategies, managing budgets, and guiding investment activities, typically requiring skills in financial analysis, planning, and leadership. Accountants focus on preparing, examining, and maintaining accurate financial records including balance sheets, income statements, and tax filings, emphasizing compliance and detailed financial reporting. While financial managers take a strategic role in decision-making, accountants provide the essential data and reports that form the foundation for those decisions.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Financial managers oversee an organization's financial health by developing strategies, managing investments, and preparing reports to guide business decisions. Accountants focus on recording, classifying, and analyzing financial transactions to ensure accurate financial statements and regulatory compliance. Your choice between a financial manager and an accountant should consider whether you need strategic oversight and financial planning or detailed transactional record-keeping and reporting.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Financial managers require advanced skills in strategic planning, risk management, and financial analysis, typically holding a bachelor's degree in finance or business administration, often supplemented by certifications like CFA or CPA. Accountants must possess strong attention to detail, proficiency in accounting software, and knowledge of tax regulations, usually requiring a degree in accounting and CPA certification. Both roles demand expertise in financial reporting and compliance, but financial managers prioritize leadership and decision-making skills, while accountants focus on accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Core Functions: Strategic vs Operational
Financial managers primarily focus on strategic functions such as financial planning, risk management, and investment decisions to drive long-term organizational growth. Accountants handle operational functions like recording transactions, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The blend of strategic oversight by financial managers and operational execution by accountants ensures comprehensive financial management within businesses.
Education and Licensing Requirements
A Financial Manager typically requires a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, economics, or business administration, with many roles favoring candidates who hold a Master of Business Administration (MBA) or professional certifications such as the Certified Financial Manager (CFM) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation. Accountants usually need a bachelor's degree in accounting or a related field and frequently pursue the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license, which mandates passing a rigorous exam and meeting specific state education and experience requirements. While both positions benefit from strong analytical and numerical skills, Financial Managers focus more on strategic financial planning and decision-making, whereas Accountants emphasize accurate financial reporting, compliance, and auditing, influencing the distinct educational paths and licensing credentials required.
Tools and Technologies Used
Financial managers utilize advanced financial software like SAP, Oracle Financials, and predictive analytics tools to oversee budgeting, forecasting, and investment strategies. Accountants rely heavily on accounting-specific tools such as QuickBooks, Xero, and Microsoft Excel for bookkeeping, tax preparation, and compliance reporting. While financial analysts use data visualization software like Tableau and Power BI alongside financial modeling platforms, financial managers focus on integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to align financial operations with overall business strategy.
Salary and Career Prospects
Financial managers typically earn higher salaries than accountants due to their broader responsibilities in overseeing financial strategies and team leadership, with median annual earnings around $131,000 compared to accountants' $77,000. Career prospects for financial managers are robust, driven by business growth and regulatory complexity, whereas accountants have steady demand with advancement often requiring certifications like CPA. Your choice between these roles should consider salary potential and career trajectory, as financial managers tend to transition into executive positions more frequently than accountants.
Influence on Business Decision-Making
Financial managers play a critical role in business decision-making by analyzing financial data, forecasting future financial performance, and developing strategies that align with the company's goals. Accountants provide accurate financial records and ensure compliance with regulations, supplying the essential data that informs these strategic decisions. Your business benefits from the combined expertise of both professionals, as financial managers interpret accounting information to influence investment, budgeting, and growth initiatives.
Reporting Structures and Collaboration
Financial managers oversee reporting structures by consolidating financial data from accountants to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. Accountants prepare detailed financial reports and collaborate closely with financial managers to provide reliable data for strategic decision-making. Your organization benefits when financial managers and accountants maintain clear communication and structured reporting lines, optimizing financial performance and governance.
Choosing the Right Career Path
Choosing the right career path between financial manager, accountant, and financial analyst depends on your skills and interests; financial managers focus on strategic planning and overseeing financial operations, accountants specialize in managing and recording financial transactions, while financial analysts evaluate investment opportunities and market trends. Financial managers typically require strong leadership and decision-making abilities with a focus on corporate finance, accountants need precision and expertise in tax laws and auditing standards, and financial analysts demand analytical skills and proficiency in data modeling. Salaries and job growth projections vary, with financial managers often earning higher median salaries and experiencing faster job growth compared to accountants and financial analysts, influencing career choice decisions.
Infographic: Financial Manager vs Accountant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com