Surveillance technologies increasingly challenge individual privacy rights by collecting vast amounts of personal data, raising ethical and legal concerns. Explore this complex relationship and its implications in more detail in this article.
Table of Comparison
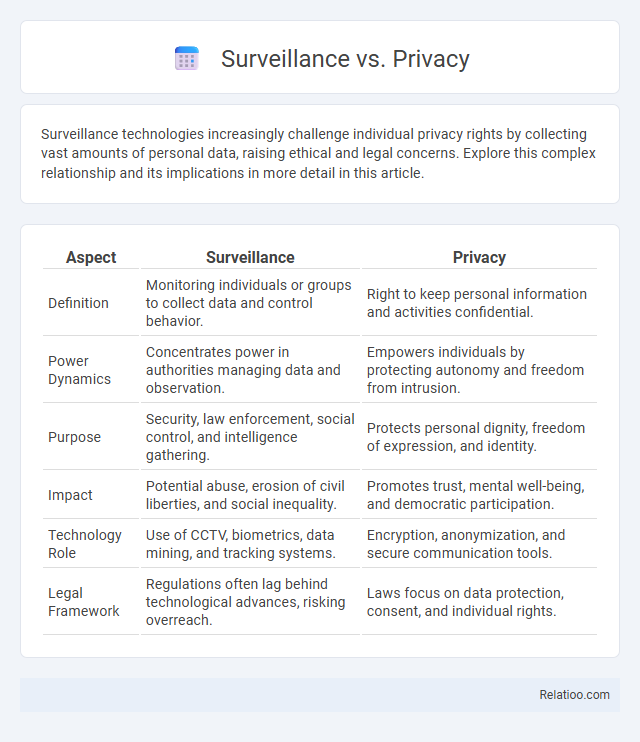
| Aspect | Surveillance | Privacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitoring individuals or groups to collect data and control behavior. | Right to keep personal information and activities confidential. |
| Power Dynamics | Concentrates power in authorities managing data and observation. | Empowers individuals by protecting autonomy and freedom from intrusion. |
| Purpose | Security, law enforcement, social control, and intelligence gathering. | Protects personal dignity, freedom of expression, and identity. |
| Impact | Potential abuse, erosion of civil liberties, and social inequality. | Promotes trust, mental well-being, and democratic participation. |
| Technology Role | Use of CCTV, biometrics, data mining, and tracking systems. | Encryption, anonymization, and secure communication tools. |
| Legal Framework | Regulations often lag behind technological advances, risking overreach. | Laws focus on data protection, consent, and individual rights. |
Introduction: The Evolving Debate Between Surveillance and Privacy
The evolving debate between surveillance and privacy centers on balancing national security and individual freedoms in a digital world. Advances in technology enable comprehensive data collection, challenging your ability to maintain personal privacy while authorities seek to monitor threats. Understanding this tension is critical as governments and corporations expand surveillance capabilities, reshaping societal norms around privacy rights and data protection.
Historical Context: Origins of Surveillance and Privacy Concerns
Surveillance practices date back to ancient civilizations where rulers monitored citizens to maintain control, sparking early privacy concerns rooted in power dynamics and personal autonomy. The invention of technologies like the printing press, telegraph, and later digital devices exponentially increased surveillance capabilities, intensifying debates over individual privacy rights. Your awareness of this historical evolution highlights the ongoing tension between state security interests and personal freedoms.
Types of Surveillance: Digital, Physical, and Hybrid Approaches
Digital surveillance involves monitoring online activities, communications, and data through tools like internet tracking, social media analytics, and cybersecurity systems, while physical surveillance includes direct observation methods such as CCTV cameras, drones, and on-site personnel. Hybrid approaches combine digital and physical tactics to create comprehensive monitoring systems that can track both virtual and real-world behaviors. Your awareness of these surveillance types is crucial to understanding the balance between maintaining security and protecting privacy rights.
Legal Frameworks: Privacy Laws and Surveillance Regulations
Legal frameworks governing privacy laws and surveillance regulations vary significantly across jurisdictions, balancing national security interests with individual rights. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union enforces strict data privacy protections, limiting surveillance scope and emphasizing consent and transparency. In contrast, the USA's Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) authorizes broader government surveillance activities but incorporates judicial oversight to prevent abuse.
Technology’s Role: How Modern Tools Enhance Surveillance
Modern surveillance technology significantly enhances the ability to monitor activities through devices like AI-powered cameras, facial recognition systems, and data analytics platforms. These advanced tools collect and process vast amounts of information in real-time, enabling more precise and efficient surveillance operations. Understanding how Your privacy can be impacted by these technologies is crucial for balancing security needs with personal rights.
Balancing National Security and Individual Privacy Rights
Balancing national security and individual privacy rights requires implementing robust surveillance measures that protect citizens without infringing on personal freedoms. You must ensure that surveillance technologies are transparent, regulated, and subject to oversight to prevent abuse. Effective policies prioritize data protection and establish clear boundaries between lawful security operations and the right to privacy.
Impacts on Society: Psychological, Social, and Cultural Effects
Surveillance profoundly impacts society by altering psychological states, often increasing anxiety and eroding trust among individuals. Widespread monitoring fosters social behaviors driven by conformity and self-censorship, diminishing open expression and cultural diversity. You face a complex balance between security benefits and preserving personal freedoms essential for healthy societal development.
Case Studies: High-Profile Incidents and Legal Battles
High-profile incidents such as the Edward Snowden revelations and the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal highlight the ongoing tension between surveillance practices and individual privacy rights. Legal battles like Carpenter v. United States address warrant requirements for digital data, setting precedents for privacy in the surveillance era. These case studies underscore the need for robust legal frameworks balancing national security interests with privacy protections.
Future Trends: The Path Forward for Surveillance and Privacy
Emerging future trends in surveillance emphasize advanced AI-driven analytics and pervasive sensor networks, which enhance monitoring capabilities across public and private sectors. Privacy protection increasingly relies on robust encryption methods, decentralized data storage, and stricter regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA to balance surveillance benefits with individual rights. The path forward involves integrating ethical AI practices and transparent data governance models to foster trust while addressing security, privacy, and accountability challenges.
Conclusion: Striking an Equitable Balance
Striking an equitable balance between surveillance and privacy requires implementing robust legal frameworks that protect individual rights while enabling effective security measures. Your privacy must be safeguarded through transparent policies, data minimization, and regular oversight of surveillance technologies. Achieving this balance ensures public safety without compromising personal freedoms or trust in governmental institutions.
Infographic: Surveillance vs Privacy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com